An Engine is a device which transforms one form of energy into another form of Energy. An internal combustion engine is a heat engine where it undergoes different cycles of operations in a sequent manner to convert the thermal energy into useful work. In this article, we are going to discuss the 2 Stroke Engine working principle with the Spark ignition. so it is also known as the 2 Stroke Spark-Ignition Engines or 2 Stroke Petrol engine.
Working Principle of Engines
IC engines work on either Spark ignition or the Compression Ignition working principle.
Spark Ignition: Usually a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug.
compression ignition: Generally the Diesel Engines, where the combustion of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to the mechanical compression.
2 Stroke Engine | 2 Stroke Petrol Engine
In the previous article, we have discussed the 4 Stroke engines working principles with the Compression ignition and the Spark Ignition. Now we are going to discuss the 2 Stroke engine working principle.
- In 2 stroke engine, the Thermodynamic cycle will be completed within the one revolution of the crankshaft.
- The only difference between the 2 stroke engine and the 4 stroke engine is that the method of taking the charge(Air/fuel mixture) into the cylinder. And exhausting the combustion products from the cylinder.
- In 2 Stroke Engine, the charge will be filled with the help of the blower. But in 4 stroke due to the movement of the piston, the suction of the air-fuel mixture will be automatically drawn into the cylinder.
- In 2 Stroke Engine, we use ports rather than the valves.
- Port: Fluid can be operated inward and outward, Valve: The fluid can be operated in one direction only
- The closing and the opening of the ports will be operated by the movement of the piston itself.
The cycle of operation of a 2 Stroke Engine consists of the following strokes:
- Intake stroke,
- Compression stroke,
- Expansion or power stroke,
- Exhaust stroke.
Intake stroke & Exhaust
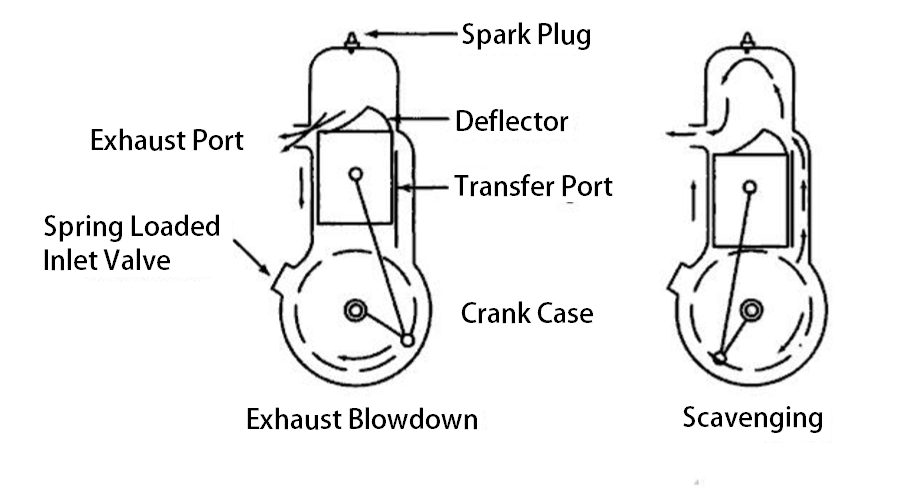
First of all the charge will be inducted into the crankcase thru the spring-loaded valve. As the piston moves downwards the transfer port opens and the charge which is pushed into the cylinder from the crankcase.
This charge automatically pushes the charge into the cylinder thru the transfer port due to the downward movement of the piston. And also the Charge will be drawn thru the Spring loaded valve into the crankcase during the upward movement of the piston.
This intake stroke will be said from when only the transfer port is open. During the Transfer port is open The Exhaust port will also be in open condition.
But this Exhaust port is open little earlier than the Transfer port to exhaust the combustion particle from the previous combustion. When the transfer port is open the charge is pushed into the cylinder, this fresh charge also helps to push the combustion particles out of the cylinder thru the exhaust port.
For this action, there is this deflector design on the piston head, in such a way that it will create the Scavenging action.
These two actions complete in the 180° of crankshaft rotation.
Compression and Expansion Stroke
During this compression stroke and expansion stroke, The two ports will be closed. The compression is while the piston moving upwards, and the expansion stroke will be while the piston moving downwards direction.
At the end of the compression stroke, the spark plug will give the spark to ignite the charge, and this is the starting of the expansion stroke also known as the power stroke.
Compression stroke and the expansion stroke complete in the 180° of crankshaft rotation.
At the end of the expansion stroke, the exhaust stroke starts when the expansion ports are open. and the intake stroke will also start when the Transfer port is open. This is how a complete thermodynamic cycle completes in a 2 Stroke Engine.
So within 360° crankshaft rotation, the complete four actions will be completed.
Conclusion
The working principles of the internal combustion engines are the Spark ignition and the compression ignition. The 2 stroke engine is available in both the Spark ignition and the compression ignition working principles. We have discussed the 2 stroke engine with the spark ignition engine. And the 2 stroke engine with the compression ignition is rarely used. If you have any thoughts leave them in the comment section below.


It’s the best for research