Engineering mechanics is a branch of science, that deals with the which deals with the laws and principles of Mechanics, along with their applications to engineering problems. As a matter of fact, knowledge of Engineering Mechanics is very essential for an engineer in planning, designing, and constructing various types of structures and machines. In order to understand the problem and solve the task skillfully manner, every engineer must study Engineering Mechanics in a systematic and scientific manner.
Humans used to content themselves, by holding gods responsible for all the processes. For a long time, humans had been trying to improve their ways of working. The first step, in this direction, was the discovery of a circular wheel, which led to the use of animal-driven carts.
Amazing right.
Let us see a little bit of the history of Engineering mechanics. Believe me, it will be interesting.
History of Engineering Mechanics
As I Have mentioned the first step in understanding engineering was the discovery of a circular wheel, which led to the use of animal-driven carts. The study of the ancient civilization of Babylonians, Egyptians, Greeks, and Roman reveals the use of water wheels and windmills even during the pre-historic days.
- It is believed that the word ‘Mechanics’ was coined by the Greek philosopher Aristotle (384–322 BC).
- Aristotle used this word for the problems of the lever and the concept of center of gravity.
- At that time, it included a few ideas, which were odd, unsystematic and based mostly on observations containing incomplete information.
- The first mathematical concept of this subject was developed by Archimedes (287–212 BC).
Little story time (Discovery of the Hydrostatics)
- The story, for the discovery of First Law of Hydrostatics, is very popular even today in the history of the development of Engineering Mechanics.
- In the normal course, Hieron king of Syracuse got a golden crown made for his use.
- He suspected that the crown has been made with an adultrated gold.
- The king liked the design of the crown so much that he did not want it to be melted,in order to check its purity. It is said that the king announced a huge reward for a person, who can check the purity of the crown gold without melting it.
- The legend goes that Archimedes, a pure mathematician, one day sitting in his bath room tub realised that if a body is immersed in water, its apparent weight is reduced.
- He thought that the apparent loss of weight of the immersed body is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced.
- It is believed that without further thought, Archimedes jumeped out of the bath tub and ran naked down the street shouting ‘Eureka, eureka !’ i.e. I have found it, I have found it !’
The subject did not receive any concrete contribution for nearly 1600 years. In 1325, Jean Buridan of Paris University proposed the idea that a body in motion possessed a certain impetus i.e. motion.
First Study on Motion of body
- In the period 1325–1350, a group of scientists led by the Thomas Bradwardene of Oxford University did a lot of work on the plane motion of bodies.
- Leonardo Da Vinci (1452–1519), a great engineer and painter, gave many ideas in the study of the mechanism, friction, and motion of bodies on inclined planes.
- Galileo (1564–1642) established the theory of projectiles and gave a rudimentary idea of inertia.
- Huyghens (1629–1695) developed the analysis of the motion of a pendulum.
First Conceptof Force and Mass (Laws of Motions)
- As a matter of fact, the scientific history of Engineering Mechanics starts with Sir Issac Newton (1643–1727).
- Sir Issac Newton introduced the concept of force and mass and gave Laws of Motion in 1686.
- James Watt introduced the term horsepower for comparing performance of his engines.
- John Bernoulli (1667–1748) enunciated the priciple of virtual work.
- In eighteenth century, the subject of Mechanics was termed as Newtonian Mechanics.
- A further development of the subject led to a controversy between those scientists who felt that the proper measure of force should be change in kinetic energy produced by it and those who preferred the change in momentum.
- In the nineteenth century, many scientists worked tirelessly and gave number of priciples, which enriched the scientific history of the subject.
Development Of Engineering Mechanics
- In the early twentieth century, a new technique of research was pumped into all activities of science.
- It was based on the fact that progress in one branch of science, enriched most of the bordering branches of the same science or other sciences.
- Similarly, with the passage of time, the concept of Engineering Mechanics aided by Mathematics and other physical sciences, started contributing and the development of this subject gained new momentum in the second half of twentieth century.
- Today, knowledge of Engineering Mechanics, coupled with the knowledge of other specialized subjects for example Calculus, Vector Algebra, Strength of Materials, Theory of Machines etc. has touched its present height.
- This engineering mechanics also reffered as Applied Mechanics.
This Engineering Mechanics is classified as follows.
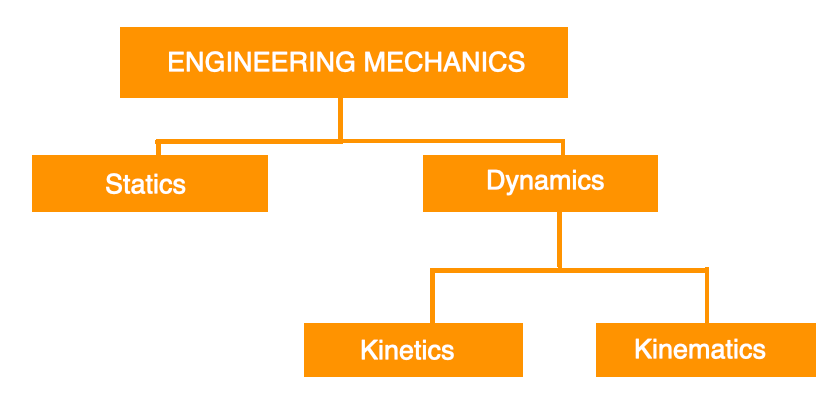
Statics
Statics deals with the forces and their effects on the machine parts at which these machine parts are at rest. The mass and the inertia forces of the parts are assumed to be negligible.
Dynamics
Dynamics deals with the forces and their effects while acting upon the machine parts in motion.
- Kinetics: This study of kinetics deals with the inertia forces which arise from the combined effect of the mass and the motion of the machine parts.
- Kinematics: This study of kinematics deals with the relative motion between the various parts of the machines.
The knowledge of Engineering Mechanics is very essential for every engineer to design, develop and invent all types of structures and machines.
Best Books for Engineering Mechanics
When I am studying my pursuing my graduation, I have studied Engineering Mechanics by R.S kami. which is good, simple, and understandable, and enough example problems for the graduation. But over the years I have referred few of the textbooks for my work purpose which are good. I also collected some of the opinions of the readers from different sources. I hope you like the list.
- Engineering Mechanics by Timoshenko (This was suggested by so many readers, definitely worth it.)
- Engineering Mechanics by S. Ramamrutham (This text book was personally prefered by My professor, this is good)
- Engineering Mechanics by Beer and Johnston (For the ones who wants to prepare for GATE)
- Engineering Mechanics by S S Bhavikatti (for your Reference)
- Applied Mechanics By R.S Kurmi ( For little advances to the Engineering mechanics by the same auther)
Hope this list helps you to pick one. Let me know in the comment section, which one you picked and why?

Leave a Reply