The ratio of the maximum fluctuation of speed to the mean speed is called the coefficient of fluctuation of speed. The difference between the maximum and minimum speeds during a cycle is called the maximum fluctuation of speed. Let us discuss how the flywheel can reduce the fluctuation of speed.

Flywheel
We have already discussed what a flywheel is and its uses in the previous article. A flywheel used in machines serves as a reservoir that stores energy during the period when the supply of energy is more than the requirement and releases it during the period when the requirement of energy is more than the supply. In the case of steam engines, internal combustion engines, reciprocating compressors, and pumps, the energy is developed during one stroke and the engine is to run for the whole cycle on the energy produced during this one stroke.
For example, in I.C. engines, the energy is developed only during power stroke which is much more than the engine load, and no energy is being developed during suction, compression, and exhaust strokes in the case of four-stroke engines and during compression in the case of two-stroke engines. The excess energy developed during a power stroke is absorbed by the flywheel and released it to the crankshaft during other strokes in which no energy is developed, thus rotating the crankshaft at a uniform speed. A little consideration will show that when the flywheel absorbs energy, its speed increases, and when it releases, the speed decreases. Hence a Flywheel does not maintain a constant speed, it simply reduces the fluctuation of speed.

In machines where the operation is intermittent like punching machines, shearing machines, riveting machines, crushers, etc., the flywheel stores energy from the power source during the greater portion of the operating cycle and gives it up during a small period of the cycle. Thus the energy from the power source to the machines is supplied practically at a constant rate throughout the operation.
The function of a governor in the engine is entirely different from that of a flywheel. It regulates the mean speed of an engine when there are variations in the load, e.g. when the load on the engine increases, it becomes necessary to increase the supply of working fluid. On the other hand, when the load decreases, less working fluid is required. The governor automatically controls the supply of working fluid to the engine with the varying load conditions and keeps the mean speed within certain limits.
As discussed above, the flywheel does not maintain a constant speed, it simply reduces the fluctuation of speed. In other words, a flywheel controls the speed variations caused by the fluctuation of the engine turning moment during each cycle of operation. It does not control the speed variations caused by the varying load.
Coefficient of Fluctuation of Speed
The difference between the maximum and minimum speeds during a cycle is called the maximum fluctuation of speed. The ratio of the maximum fluctuation of speed to the mean speed is called the coefficient of fluctuation of speed.
Let us say
N1 = Maximum speed in r.p.m. during the cycle
N2 = Minimum speed in r.p.m. during the cycle
N = Mean speed in r.p.m
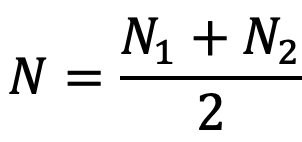
Coefficient of fluctuation of speed,
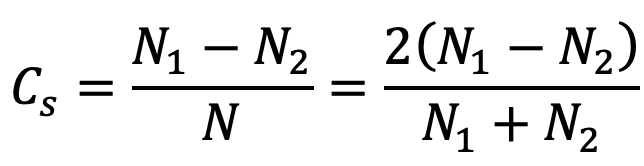
Coefficient of fluctuation of speed, (In terms of angular speeds)
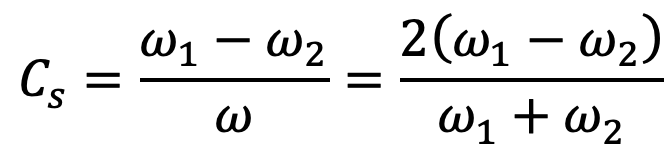
Coefficient of fluctuation of speed, (In terms of linear speeds)
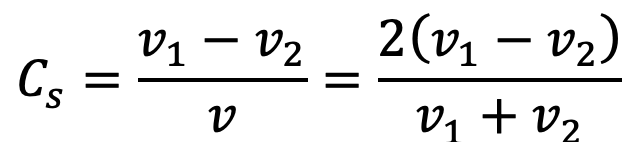
The coefficient of fluctuation of speed is a limiting factor in the design of flywheel. It varies depending upon the nature of service to which the flywheel is employed. The following table shows the permissible values for the coefficient of fluctuation of speed for some machines.
| S.No. | Type of machine or class of service | Coefficient of fluctuation of speed (CS) |
| 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. | Crushing machines Electrical machines Electrical machines (direct drive) Engines with belt transmission Gear wheel transmission Hammering machines Pumping machines Machine tools Papermaking, textile, and weaving machines Punching, shearing, and power presses Spinning machinery Rolling mills and mining machines | 0.200 0.003 0.002 0.030 0.020 0.200 0.03 to 0.05 0.030 0.025 0.10 to 0.15 0.10 to 0.020 0.025 |
The reciprocal of the coefficient of fluctuation of speed is known as the coefficient of steadiness and it is denoted by m.
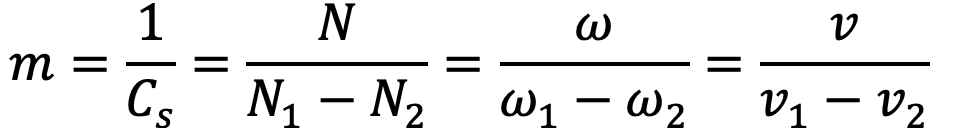
This is all about the Coefficient of Fluctuation of Speed for the steam engines or IC engines. Let us know what you think about this article in the comment section below.

Leave a Reply