A Final Year Project on “Residential Vertical Axis Wind Turbine” submitted by Aravindh. B (from Alagappa Chettiar Government College Of Engineering And Technology karaikudi) to extrudesign.com.

ABSTRACT
Wind energy is a promising scheme in the power generation sector due to pollution-free power production and wind resources’ sufficiency worldwide. Installing wind turbines in all the possible extents can mitigate the rising energy demand. Built-up areas possess high potential for wind energy, including the rooftop of high-rise buildings, railway track, the region between or around multi-story buildings, and city roads.
There are multiple approaches of design for Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT) that have been studied by engineers and leaps have been made in high-performing innovations. By harnessing the energy from these wind turbines, the problem of roadside lights shortage can be solved. This can help to prevent accidents while providing clean energy.
The importance of coastal areas like Australian beaches regarding wind turbines cannot be neglected as a higher number of people like to live near coastal vicinity. Also, most of the freeways in Australia expand across the sea. In this paper, one such design has been analyzed to implement across the highways.
But still, with many advancements in technology, an immense gap is present in the research of implementation of VAWTs. The design discussed in the current study is a VAWT which can be installed on the side of the highway roads to provide clean and cheap energy for illuminating the roads.
1. Introduction To Residential Vertical Axis Wind Turbine
For the past few decades, there has been a rise in the factors that are damaging the earth. Their extent is reached to all the natural phenomenon and ecosystems. With this rate, the upcoming generations will have to suffer the most from it. Energy is one of the main resources that support the lifestyle of the humans in current era but almost 80% of the energy produced today is generated from fossil fuels.
With the ever-increasing industry, the use of natural resources has increased tenfold. This has caused them to deplete at very high rates. It is commonly assumed that the complete depletion of these finite resources will throw the world out of balance.
Currently, the world is in dire need of renewable energy sources due to the adverse effects of conventional ones. Also, many researchers have proven that renewable energy sources are way cheaper than conventional methods in terms of production. Many sources around the globe can generate renewable energy. Many types of research have shown that the earth has a great capability of wind energy, especially along the coastlines.
The concept of generating energy through the wind was first introduced in 1931 which led to the invention of the Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT). Although Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT) had already caught researchers’ attention. The general working of a wind turbine is not very complex. The main parts of the turbine are its returning blades, which are attached to the main rotor part with the help of radial arms.
Recently, the researchers have turned their attention towards VAWT. Even though this turbine is very cost-effective and it is easier to manufacture, however, there is a big research gap left by the researchers on VAWT due to their unfettered work on HAWT. Many researchers have provided a lot of new innovative ideas to use wind energy effectively, but most of them couldn’t be implemented. It is the need of time that this industry elaborates and finds the solutions of the fundamental aspects that question the credibility of (Wind energy efficiency evaluation procedure).
One of the best places to gain the most from wind energy in Australia as most of its population lives along with the coastal areas. Such areas are ideally used to harness wind energy as they have violent winds.
Due to the country’s size, the supply of electricity to all the people is a really big challenge, especially when it comes to highways. The lights on highways are very important as there have been a lot of road accidents due to its absence on the roads under various circumstances.
Another reason for the accidents is the extra fatigue drivers have to face during travel. Drivers get under the influence of fatigue mostly at night time and near the regional areas. It is thereby required that the lights on the roads must be given equal importance like other programs of road safety such as limiting the hours of work, taking time to rest, etc., Road lights are very important and they can be provided energy using renewable sources. A successful implementation in this regard is the lights that use solar energy.
The use of wind turbines goes back to the 7th century in the region of the middle east. They had a very small efficiency and operated on a horizontal axis. Several centuries later the Dutch developed windmills that were used to pump out the water. The US used wind turbines to irrigate the lands in the 19th century. The first wind turbine to generate electricity was developed in the early 90s.
The benefits of VAWT are more than that of HAWT. For most of the VAWT designs, the wind traction mechanism is not required. HAWTs have a lesser efficiency in the areas where the turbulence of the winds is very high. The reason is that a high amount of fatigue is caused by these winds. As compared to that the performance of VAWT is quite higher in all such conditions;
Less amount of fatigue is generated in VAWT due to its assembly consisting of smaller gearboxes. The design of these turbines is very simple and gives accessibility to the gearboxes from the ground. While in HAWT an elevated platform is required to access the gearboxes to maintain them. By carefully designing the VAWT the obtained output can be increased tenfold as compared to HAWT. In certain assemblies of VAWT screws are used and can be transported to other locations, while the long blades of HAWT can’t be broken down and are much more difficult to transport.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
1. Prof. Sunil Shukla, Dr. P. K. Sharma , Suryabhan A. Patil
(Head of Mechanical Engineering Department, NIIST, Professor in Mechanical Engineering Department(NIIST), 0115MR11MT11 PG student Mechanical Engineering Department, NIIST)
This paper is based on a Review Paper on Vertical Axis Wind Turbine for Design and Performance Study to Generate Electricity on Highway and they fulfilled about the wind power generation on all over the countries. And also they researched the ‘Wind Energy Scenario in India’. They did a detailed explanation of wind farms in India.
2. Palanisamy Mohan Kumar, Krishnamoorthi Sivalingam, Teik-Cheng Lim, Seeram Ramakrishna
(Centre for Nanofibers and Nanotechnology, Department of Mechanical Engineering, National University of Singapore, School of Science and Technology, Singapore University of Social Sciences)
The objective of the current review is to present the development of a large vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) since its Naissance to its current applications. The turbines are critically reviewed in terms of performance, blade configuration, tower design, and mode of failure. The early VAWTs mostly failed due to metal fatigue since the composites were not developed. Revisiting those configurations could yield insight into the future development of VAWT. The challenges faced by horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT), especially in the megawatt capacity, renewed interest in large-scale VAWT.
3. Vinit .V. Bidi1, Devendrappa .M. K, Chandan .S .P, Arun .J. P, Maruthi, (Assistant Professor 5 Department of Mechanical Engineering STJIT, RNR, India)
They did a project on” Highway Power Generation using Low-Cost Vertical Axis Wind Turbine [VAWT]” In this paper, the fabrication of prototype model of Savonius type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT) is made using easily available materials like front wheels of bicycle with ball bearing, half-cut PVC pipes, wooden base, etc. The CADD model of the VAWT is prepared. This VAWT is placed in the medians of the highway. The vehicles from both sides of medians accelerate the wind thus increasing its kinetic energy which forces the turbine blades to rotate in a clockwise direction.
3. BLOCK DIAGRAM
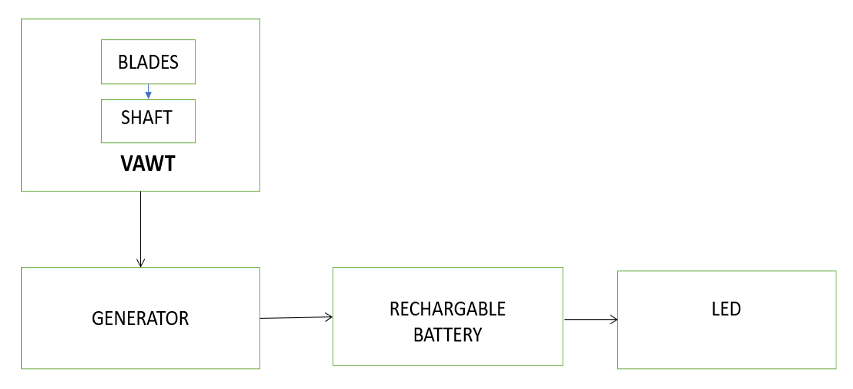
3.1 BLOCK DIAGRAM EXPLANATION
The wind flow due to the vehicle movement causes the movement of blades which is connected to the motor and the motor generates the output power. The blades used here are PVC pipe semi-side which act as wind blades. PMDC Motor is used to generate the induced voltage.
3.2 MAIN OBJECTIVE
The main objective is to utilize the maximum amount of wind energy from the automobiles running on the highways. The unused and considerable amount of wind is used to drive the vertical axis wind turbine, which will use the kinetic energy of the wind to produce electrical energy.
Increased turbulence levels yield greater fluctuations in wind speed and direction.
Unlike traditional horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT), vertical axis wind turbine effectively captures turbulent winds which are typical in urban settings. An effort is made to fabricate a vertical axis windmill of higher output capacity
We aim to design and fabricate the wind turbine using easily available, low-cost raw materials like wheels of the cycle with inbuilt ball bearing, half-cut PVC pipes, etc. This wind turbine is made to capture the maximum of wind energy in any direction by placing it at the optimum place and by considering both the cost and safety of the system.
This system can be used in huge numbers to generate a huge amount of useful electrical energy. This energy can be stored and transferred to the nearest rural places where we can fulfill the electricity demand.
The thought of design directs us to look into the various aspects such as manufacturing, noise, cost which leads us to our additional aim of analyzing the system to overcome the usual technical glitches. The project brief involves the
design of a small-scale wind turbine that can be easily mass-produced and fitted on every highway maiden to aid electricity consumption.
3.3 PROBLEM DEFINITION:
In India, the need for electricity is more than its production. The focus on energy generation from Renewable Energy Resources has increased significantly in recent years in the wake of growing environmental pollution, rising energy demand, and depleting fossil fuel resources.
Different sources of renewable energy include biomass, solar, geothermal, hydroelectric, and wind energy. Among these resources, the wind has proved to be a cheaper alternative energy resource and hence extensive research efforts have been put to improve the technology of electricity generation through wind energy.
The world has enormous potential for wind energy that should be utilized for electricity generation. Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) and the wind industry are working together to accomplish the improvements through various research and development programs.
In areas where favorable sites exist, it has already been preferred over conventional fossil fuels resources for electricity generation. Wind power is now the world’s fastest-growing energy resource utilized.
The fixed wind-powered electricity generation systems in use, till now are dependent on wind direction and the force of the wind. But the wind is not available at all places and all time throughout the year.
Also, the wind forces from moving vehicles are getting useless, therefore, there exists an immense need for a system for generating electricity from wind-induced by moving vehicles, trains, or airplanes, which is available throughout the year at various places and with sufficient force of the wind.
The VAWT is a turbine in which the axis of the rotor is perpendicular to the wind stream and the ground. VAWT commonly function nearer to the ground and has the benefit of enabling placement of heavy equipment, such as the gearbox and generator, close to the ground level and not in the nacelle
Therefore, this invention provides a solution to the problem of generating electricity in this manner. On keeping prime focus on the heavy-duty automobiles on highways/expressways, we found out that there is a large amount of wind pressure generated on these roads due to wind disturbance/ wind turbulence created by these automobiles.
As any automobile passes along the path, it creates a very huge air pressure on the nearby surrounding areas. This high pressure of the wind is still now of no use, especially in India. Till now there is no such technology developed and implemented in India to utilize this high-pressure column of wind so generated. With concern to this, we had tried to develop a vertical axis wind turbine which works on the principle of these highway wind energy.
4. HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION
4.1 HARDWARE INTRODUCTION:
FABRICATION:
Fabrication of vertical axis wind turbine (Darrieus type) consists of different parts which are needed to be fabricated as parts of the main assembly. Following are the parts of VAWT, to be fabricated.
BASE:
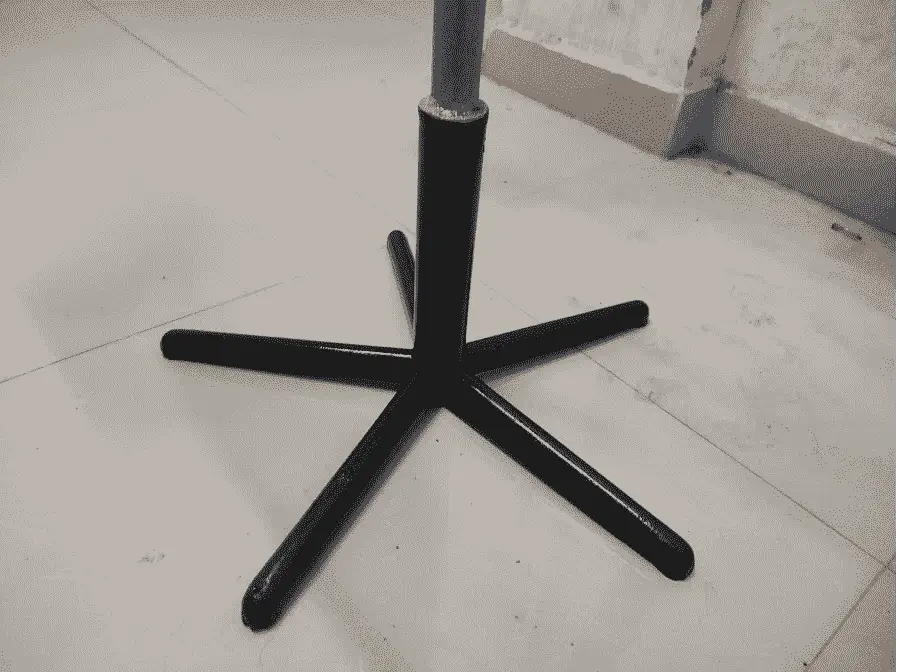

Fabrication of the base aims at providing strong support to the generator against the highspeed wind. It is designed in such a way as to reduce the vibrations of the turbine due to turbulent winds. The base is made up of a broken chair base. The base also holds the power generating unit, it gives rigid support to the upper blades.
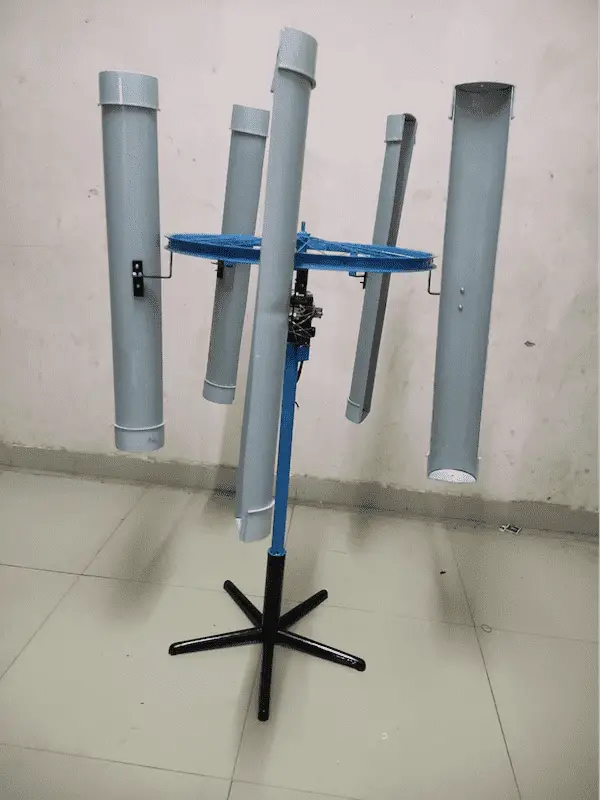
BLADES:
In this project 4inch, half-cut PVC pipes are used as turbine blades. The blades are approximately 3mm thick. Five blades of equal length are being used. The analysis is made using a set of three, four, and five blades. These blades are attached perpendicular to the rotor [cycle wheel] using clamps with nut and bolt arrangement.

GENERATOR:
The generator used here is a PMDC motor, which is capable of producing 24 v output when the speed is achieved by 2200rpm.
Specification:
- RPM-2400rpm
- Voltage -24v

FINAL STRUCTURE:

CALCULATIONS:
1. Sweep area of the turbine
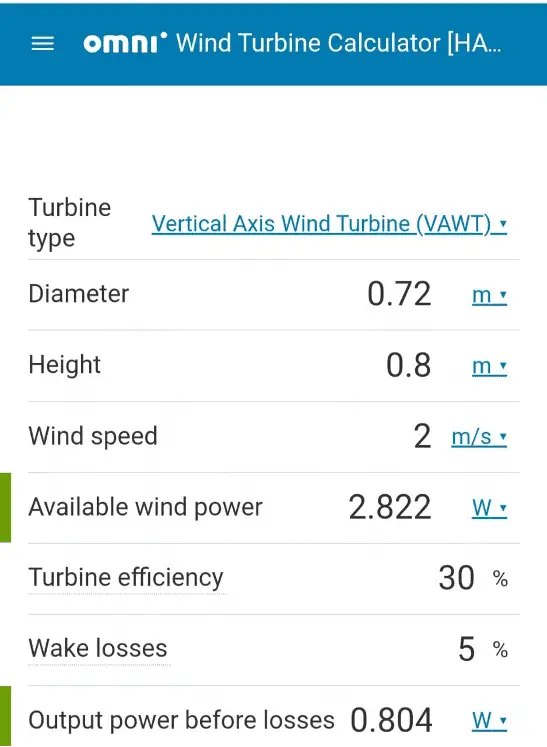
Before finding the wind power, you need to determine the swept area of the turbine according to the following equations:
For VAWT: A = D * H
where:
Lis the blade length – the radius of the horizontal-axis turbineDis the diameterHis the turbine height
2. Calculate the available wind power
Once you know the swept area, you can find the available wind power according to this formula:
Pwind = 0.5 * ρ * v³ * A
where:
Ais the sweep areaρis the air intensity, assumed to be 1.225 kg/m³ by default (you can change it in advanced mode)vis the wind speed – the typical usable range is approximately 2-5m/sPwindis the available wind power
3. Finding the efficiency of the turbine
You can find the total efficiency of the turbine as follows:
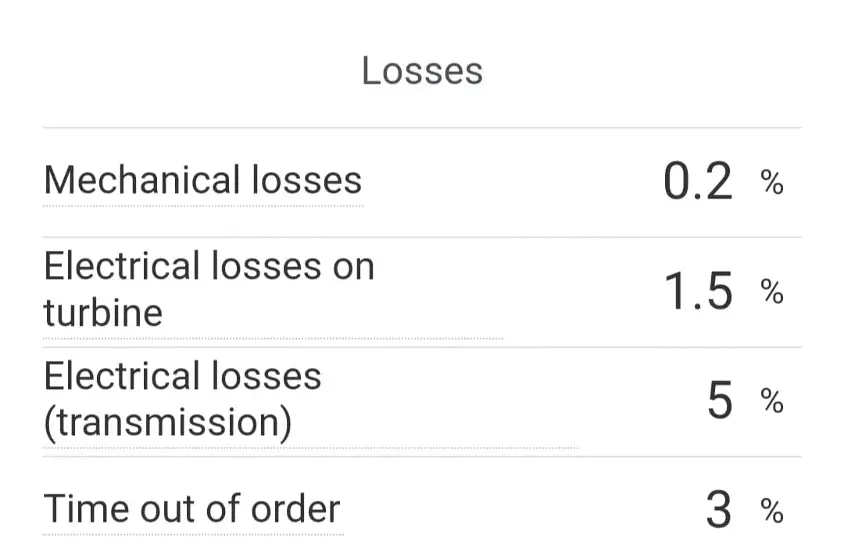
μ = (1 - kₘ) * (1 - kₑ) * (1 - ke,t) *(1 - kt) * (1 - kw) * Cₚ
where:
Cₚis the turbine efficiency. It must be lower than the Betz limit (59.3%), and is typically between 30-40%kware the wake losses due to neighbouring turbines and the terrain topography, typically 3-10%kₘare the mechanical losses of the blades and gearbox, typically 0-0.3%kₑare the electrical losses of the turbine, typically 1-1.5%ke,tare the electrical losses of transmission to grid, typically 3-10%ktis the percentage of time out of order due to failure or maintenance, typically 2-3%μis the real efficiency
Efficiency is usually expressed as a percentage, but you input it into the formula as a fraction (for example, 30% = 0.3).
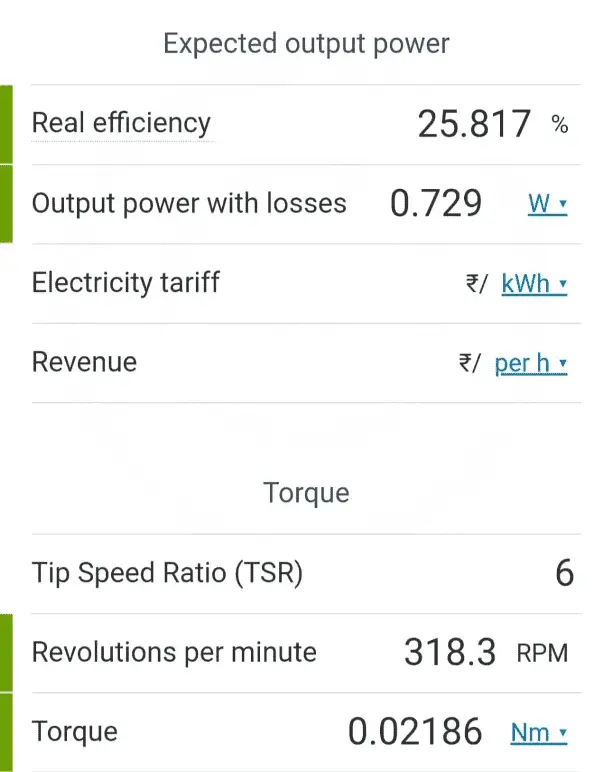
4. Calculating the output power
To find the wind turbine power, simply multiply the efficiency by the wind power available:
P out= m x Pwind
OMNI VAWT CALCULATOR:
5. CONCLUSION
The advantages of VAWT are larger than that of the HAWT regarding the performance parameters. The helical and spiral structures in VAWTs do not require special mechanisms to compensate for the air traction. This leads to a less complex design. The material of the blades must be cheap, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant. Remote monitoring can be done to detect the issues occurring in the turbines in real-time. The results in the studies showed that the design performed adequately under various analyses. The maximum stress was well under the yield strength that showed that the turbine had a strong structure and it will not fail. The drag forces were lower and generated lesser resistive forces. This became more evident when the flow trajectory showed fewer vortexes. The lift was also generated as the blades were designed like the airfoils of an airplane. Lastly, the cost of the design was not very high as some of the components used inside it could be directly purchased from the market.
6. REFERENCE:
- Non-Conventional energy sources by smt. C.K.Rai
- Wikipedia, Encyclopedia, Retrived from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/image:H-Darrieus-Rotor.png.jpg on November 28,2005.
- http://www.urbanwind.net/pdf/technological analysis.pdf
- http://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/vertical-axis-wind-turbine
- http://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation.aspx?paperid=102696
- http://www.omnicalculator.com/ecology/wind-turbine
- NiranjanaSJ “Power Generation by Vertical Axis Wind Turbine” International Journal of Emerging Research in Management &Technology ISSN: 2278-9359 (Volume-4, Issue-7).
- Mr.Mukesh Kumar Sharma. “Assessment of Wind Energy Potential from Highways”. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) Vol. 1 Issue 8, October – 2012 ISSN: 2278-0181
- Mark Paluta, Dan Reitz, Ryan Snelling, Joe Gadient “Design and Fabrication of a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine University of Notre Dame Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering”.
- H. Fernández, A. Martínez, V. Guzmán and M. Giménez. – Wind Turbine Generation System Implemented with a Car Alternator for Use in Isolated Locations. RE & PQJ, Vol. 1, No.2, April 2004
- Arvindkumar; Sandeep kumarsingh – Wind Power Generation on Highway.
Credit: This project “Residential Vertical Axis Wind Turbine” was completed by Aakash M.K, Aravindh. B, Dhanavendhan. N, and Manikanda Bharathi.T, under supervision of Dr. K. Baskaran (HOD) Department of Electrical And Electronics Engineering from Alagappa Chettiar Government College Of Engineering And Technology karaikudi.

Leave a Reply