After a few requests from my readers, I am finally writing about the introduction to the Piping system. As we all knew, Pipes are used to transporting fluids, slurries, and sometimes even very fine particles.
The most common application we see in the piping is Plumbing in our buildings, workplaces, and many places where water supply is required.
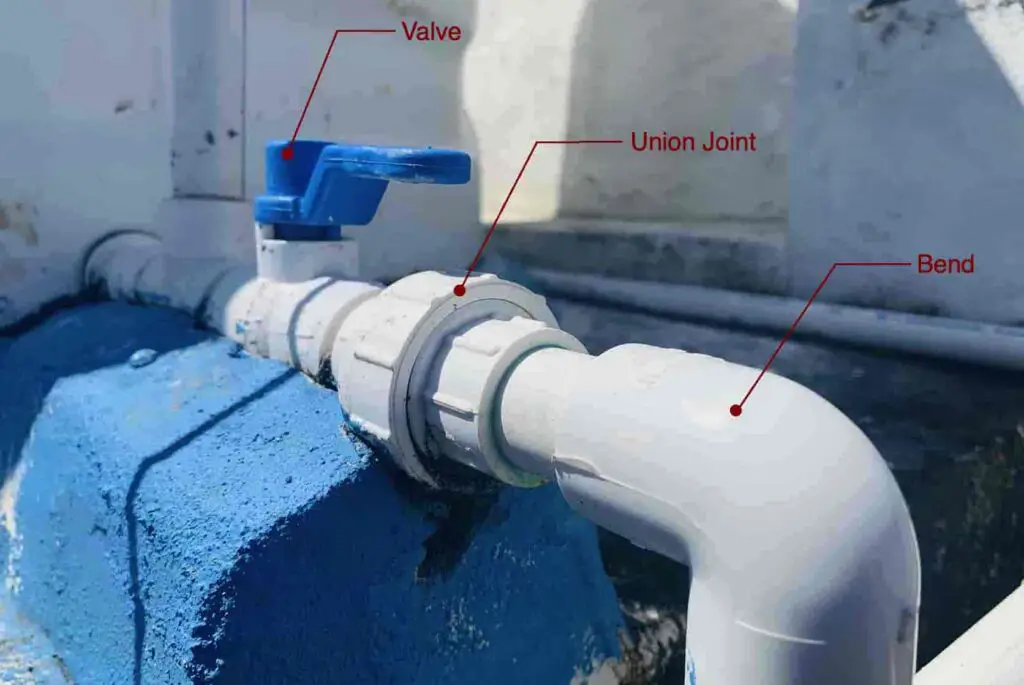
Ok, what about the industrial level piping? What are some of the applications where engineering behind the piping is necessary to understand?
Piping Applications
Following are the different industry types that use the piping system.
- Chemical Plants
- Steam Power plants
- Natural Power Plants
- Oil Refinery plants
- HVAC and Refrigeration Applications (Heating, ventilation and air conditioning)
- Water transportation, Drainage and Sewage Management
Let us have a look at some examples for the industry-level piping applications.
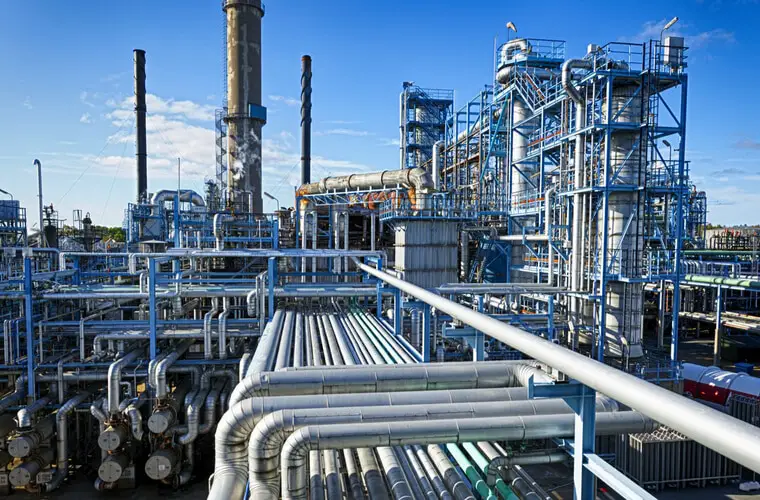

Above is the typical industrial power plant piping system. it seems the piping system is the Veins for the plant which runs the plant. Any trouble in one small pipe can cause a breakdown situation. which can result in a loss for the plant. To ensure safety and minimal breakdown situation, the plant must have piping engineers to maintain it in the proper way.
Now let us understand the different materials used for Piping in different applications.
Piping Materials Selection
Basically for the plumbing works in the household and buildings we use PVC pipes (Polyvinyl chloride pipes) for the water transportations. These PVC pipes are also used in drainage and sewage management.
But choosing the right material based on the different applications (chemical plants, power plants, oil refinery plants, HVAC, refrigeration systems) and different operating conditions for the piping system is a challenging task to the Pipe manufacturers.
This has been simplified by the international standard regulations by introducing standard piping codes to be followed by the manufacturers. This will ensure customer safety, quality of the product, and engineer productivity.
One of the most used standards for the piping system is ASME B31. Which regulates the material selection, size, and safety of the Piping systems for all the applications.
Following are the most commonly used pipe materials.
Steel Pipes
Steel is the most frequently used material for piping. Steel Pipes are manufactured in two main categories. The first one is seamless pipes and the second one is welded pipes.
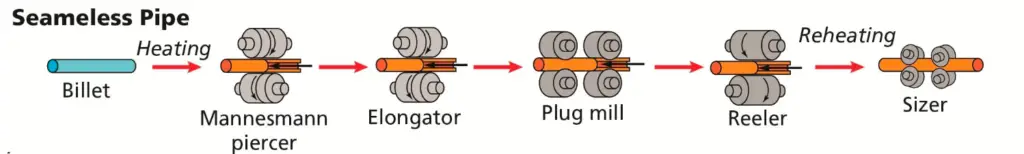
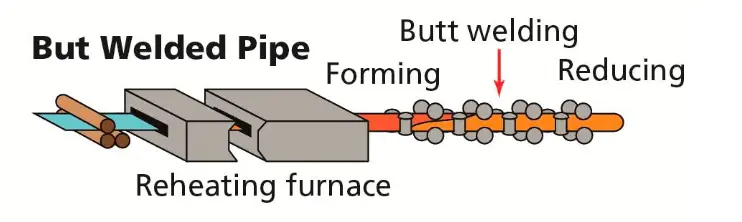
- Forged Steel: it is extensively used For Fittings.
- Cast steel: Cast steel is primarily used for special applications.
Cast Iron Pipes
Cast iron has a high resistance to corrosion and to abrasion and is used for ash handling systems, sewage lines, and underground water lines. Since Cast iron pipes are very brittle, so those are not suitable for most power plant services.
- It is made in different grades such as grey cast iron, malleable cast iron and ductile cast iron.
Brass and Copper
Non-ferrous materials such as copper and copper alloys are used in power plants in instrumentation and water services where the temperature is not a prime factor.

Concrete and Ceramic Pipes
The pipes made from concrete and ceramics are mostly used for low-pressure applications. Examples are gravity flow, sewage, and drainage underground.
These Concrete pipes required different sealing techniques to make them leakproof since they usually have a receiving bell or a stepped fitting.
On the other hand, Ceramic pipes are used for underground drainage which may be exposed to corrosive chemicals.
These concrete and ceramic pipes are relatively inexpensive for the diameters in question and allow for ease of installation in rough site conditions.
Plastic Pipes

- Plastic pipes are widely used for their lightweight, chemical resistance and non-corrosive properties.
- And they are very easy to install and make the pipe joints.
- As we mentioned above PVC pipes are the most used piping material for many applications.
- Also following are the examples of the other plastic pipe materials.
- chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC)
- polyethylene (PE)
- polypropylene (PP)
- polybutylene (PB)
- Fibre reinforced plastic (FRP)
- Reinforced polymer mortar (RPMP)
- Cross-linked high-density polyethylene (PEX)
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
Also, there are other special materials where there is a requirement such as glass or lined pipe.
Pipe Joints and Fittings
The pipe lengths are limited most of the time and to achieve suitable lengths we need a pipe joint to join them. Some of the most common types of Pipe Joints are discussed below.
- Socket or a coupler Joint
- Nipple Joint
- Union Joint
- Spigot and Socket Joint
- Expansion Joint
- Flanged Joint
- Hydraulic pipe Joint
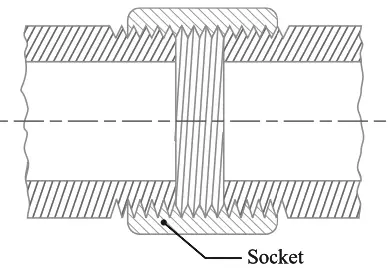
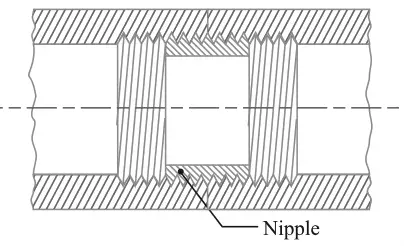
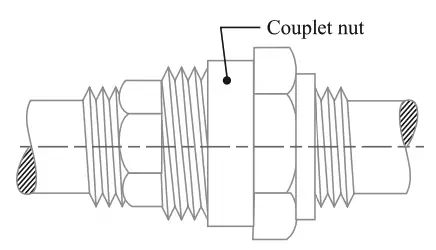
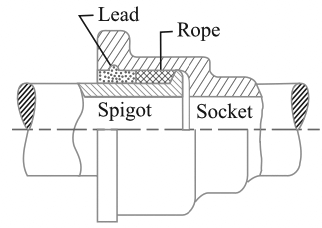
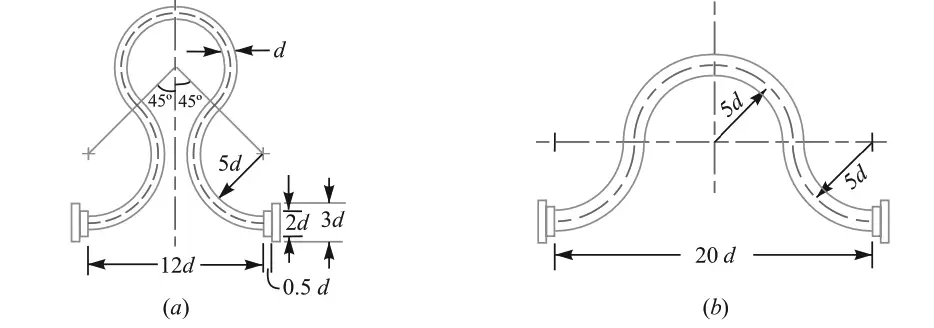
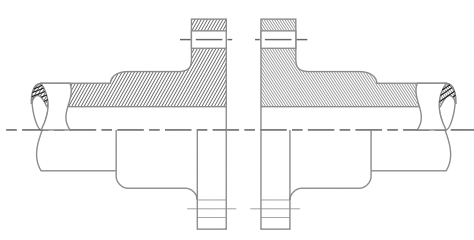
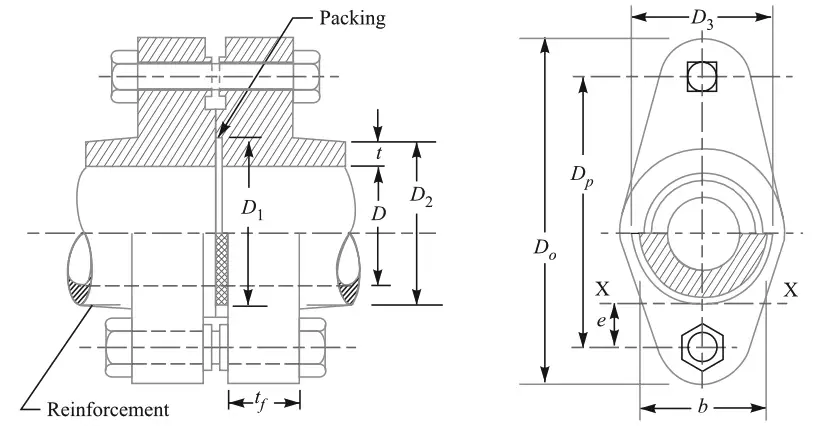
We have discussed the details about the individual pipe joints in this article here.
All the above-mentioned pipe joints make the pipe joined together in a straight direction. But we have situations where we need to make angular turns or need to reduce the pipe cross-section or need to split into branches. Then the following fittings will help.
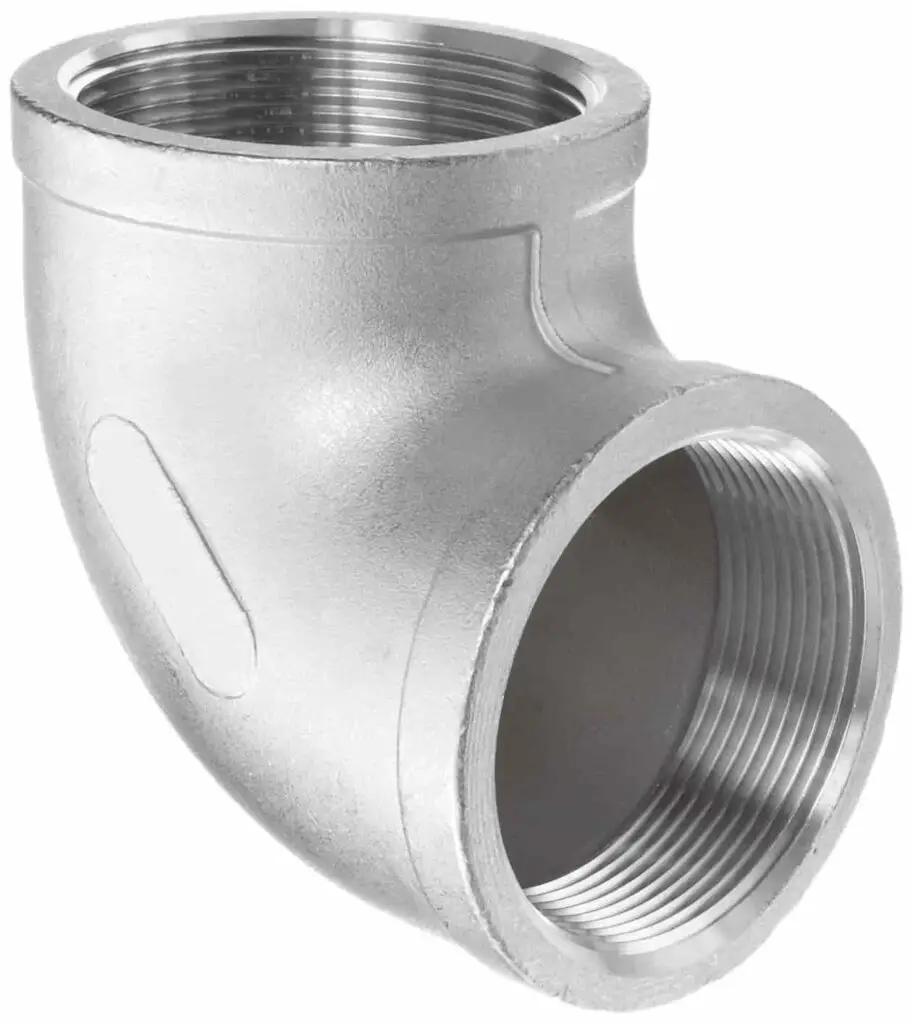
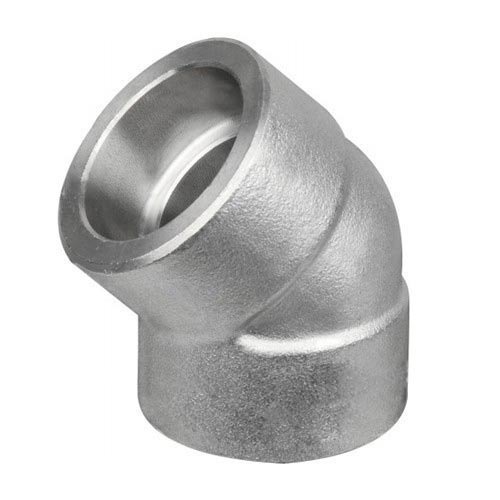
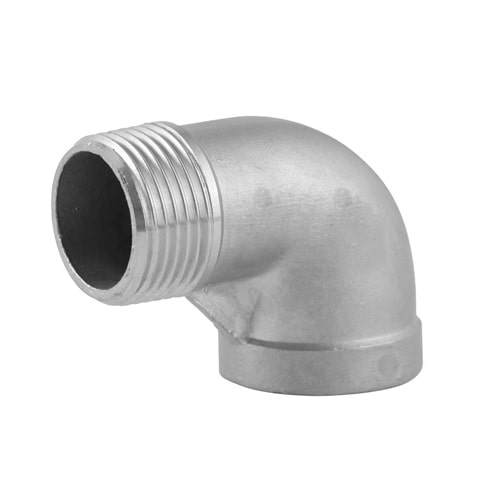
Elbows Pipe Fittings
Elbow fitting makes it easier for the pipes to make angle turns.



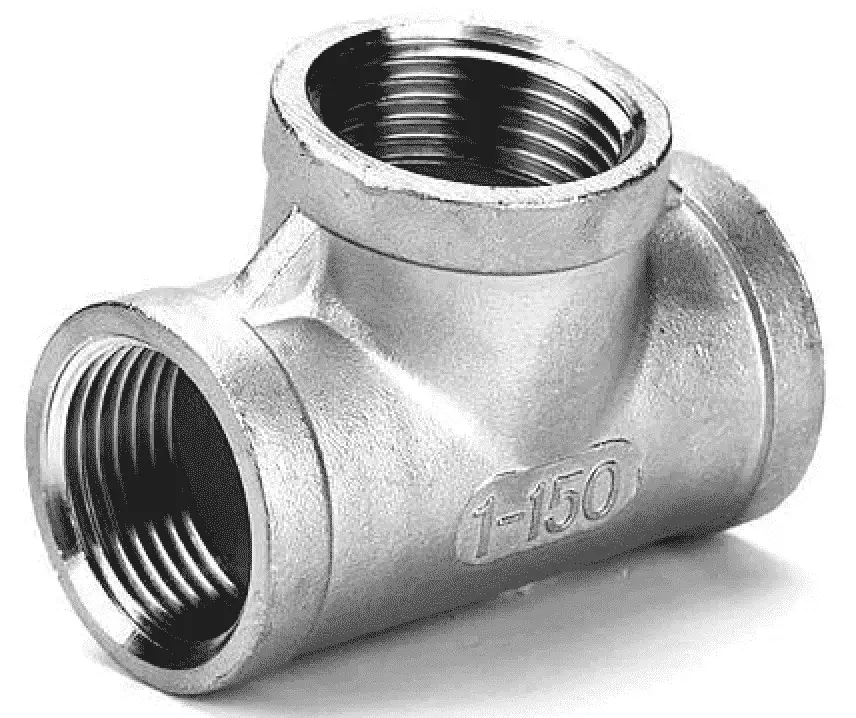
Junction Bends
Junction bends help to make the branched connections
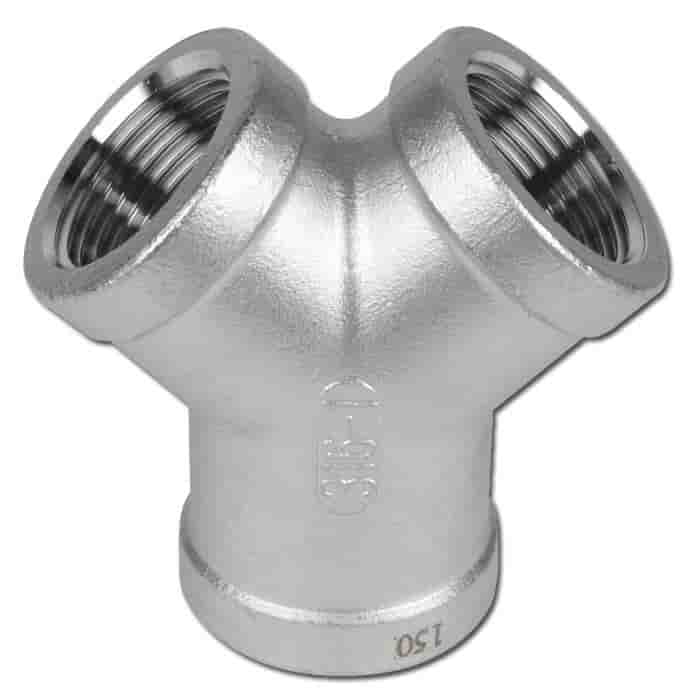
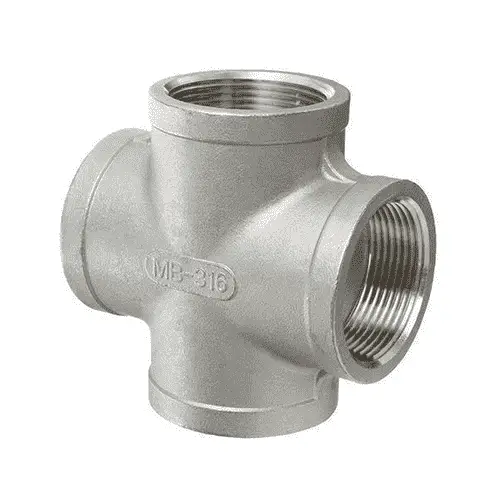



With the above pipe joints and pipe fitting elements, it’s easy to make the piping for any application.
We have already discussed how to design pipes and pipe joints based on the fluid pressure inside the pipe.
- How to design a Pipe to transfer fluids?
- What Pipe Flange should I use based on Steam pressure?
- How to design a Circular Flanged Pipe Joint?
Piping System Standards
Most people follow the ASME B 31 standard code for designing piping and this varies based on the geographical location.
In addition to the ASME(American Society of Mechanical Engineers), there are other standards as well. Those are mentioned below.
- ASTM (A252) – American Society for Testing and Materials
- API (5L)- American Petrolium Institute
- EN (13480) – European metallic industrial piping code
- GOST – Russian National Standards
- AWS – American Welding society
- AWWA – American Water works association
- ANSI – American national Standard Institute
- CWB – Canadian Welding Beuro
Piping System Special Equipments
Along with the pipes and the joints and fittings, there are several pipe special instruments used such as Valves, Filters, Actuators, Piping traps, Steam separators, Drainage systems, and piping insulations. These are the special equipment that is used for special applications such as transporting steam, highly volatile chemicals, and substances that are at very high temperatures in the power plants.
Conclusion
We have discussed the different industrial piping applications, materials selections, Pipe joints, and fittings along with the piping special equipment. Let us know what do you think about this article in the comment section below.

the information you have updated is very good and useful, please update further.
Great. We do have further details about the piping system. I have made a few list for you.
What are different Pipe Joints?
How to design a Pipe to transfer fluids?
ASME Codes for Piping System
What Pipe Flange should I use based on Steam pressure according to Indian Boiler Regulation?
How to design a Circular Flanged Pipe Joint?
How to design an Oval Flanged Pipe Joint?