In Mechanical Engineering The material science plays a significant role. As a Design Engineer, it is necessary to understand the Classification of materials, Material Properties, and Selection of materials for engineering purpose. Selecting a suitable material base upon the condition of operation and machinability and many other factors is also a big task.

Let’s get into the subject of classification of materials and based on what factors we suggest engineering materials for the different kind of machine elements.
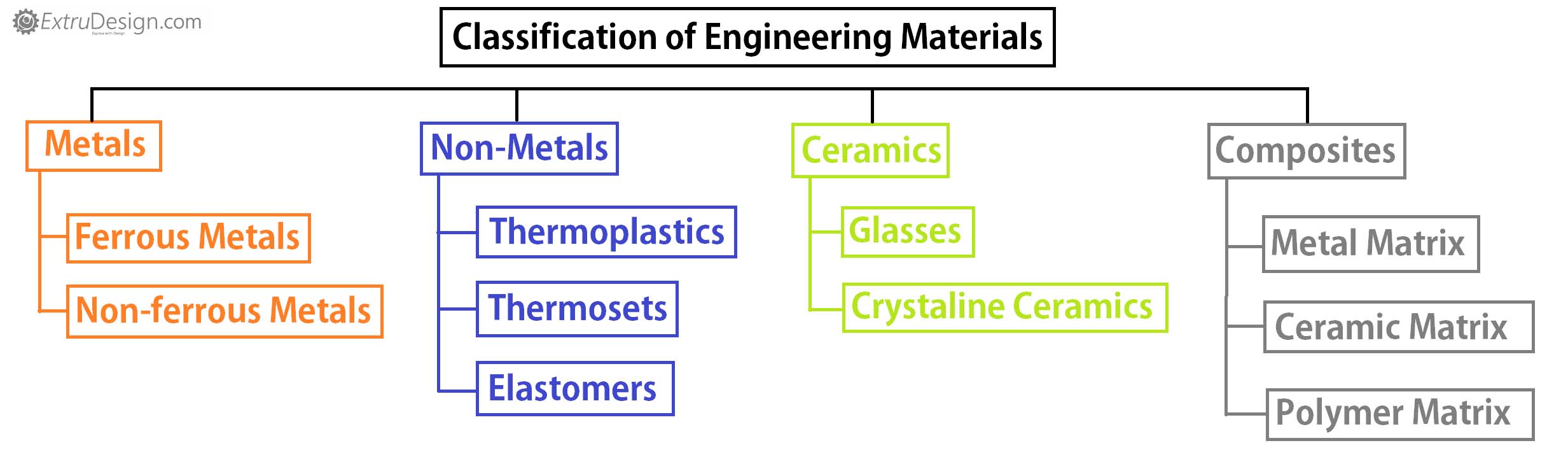
Classification of Materials/ Engineering Material Classification
In Material science engineering, the materials classified into the following categories.
- Metals
- Non-metals
- Ceramics
- Composites
There are sub-classification for these categories are also available. Follow this tree diagram to understand the subclassification of materials.
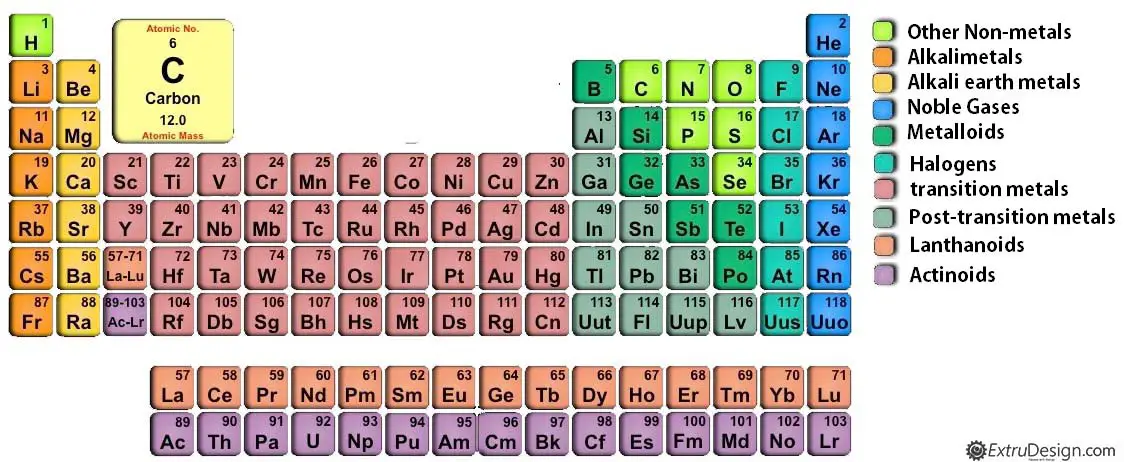
Before going into the topic it is necessary to understand the periodic table. The periodic table is a tabulation of the chemical elements according to their atomic number and electron configuration. In this periodic table, All the metals are listed on the left side and the non-metals are listed on the right side of the table. Read more about periodic table here.
Let’s back to the subject.
Metals
Metals have good electrical and thermal conductivity and capable of malleable(able to be hammered or pressed into shape without breaking or cracking). In periodic table out of 118 elements, 90 are metals only. See the periodic table for the metals.
Examples of metals are steel, iron, copper, aluminium, zinc, silver, lead, etc. These are all alloys of metals.
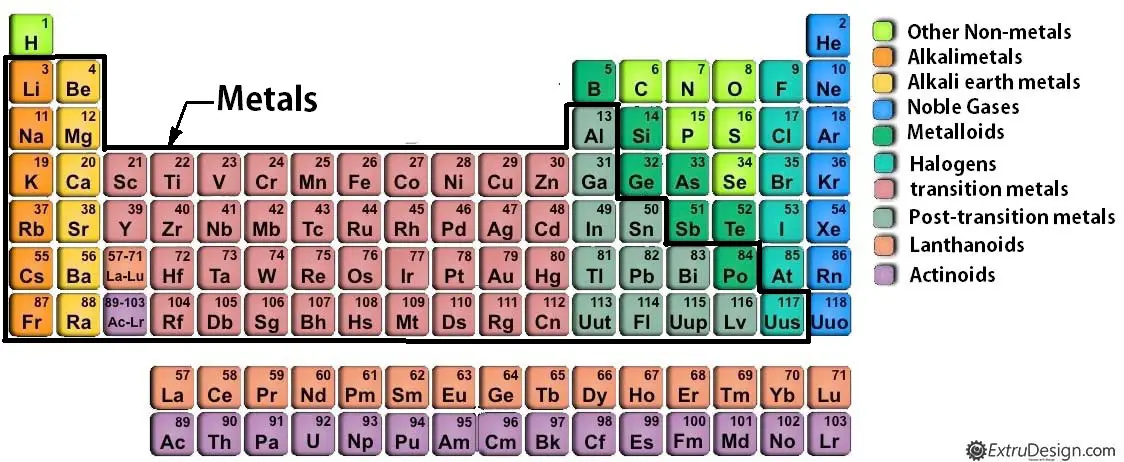
Metals are further classified into the following groups.
- Ferrous Metals
- Non-Ferrous Metals
Ferrous Metals
Ferrous metals are rich in iron. Iron such as cast iron wrought iron, steel is the main constituents in ferrous metals. Ferrous metals are magnetic and capable of little resistance to the corrosion too.
Examples for ferrous metals are cast iron, carbon steels, alloy steels, stainless steels, tool steels and die steels.
Non-Ferrous Metals
These metals have lightweight, high conductivity, corrosion resistance and non-magnetic properties are the specialities of non-ferrous metals. These metals don’t have the iron as the composition. Some amount of iron will be added in some of the Non-ferrous metals but it is not a considerable amount.
Example: aluminium, copper, lead, nickel, tin, titanium and zinc.
Some of the Non-ferrous alloys such as brass, gold, silver and platinum.
cobalt, mercury, lithium, tungsten, indium, beryllium, cadmium, niobium, tellurium, gallium, germanium, selenium, tantalum, vanadium, and zirconium are some of the rare non-ferrous metals.
Non-ferrous metals are refined thru the electrolysis process.
Non-metals
Non-Metal is referred to the chemical elements which are volatile, insulated to heat and electricity and lack of the metallic attributes. Most of the non-metals are gasses. In the periodic table, they are represented under Polyatomic nonmetal, Diatomic non-metal, Noble gases. carbon, phosphorus, sulfur, selenium, and iodine are the solid non-metals. See the Periodic table below.
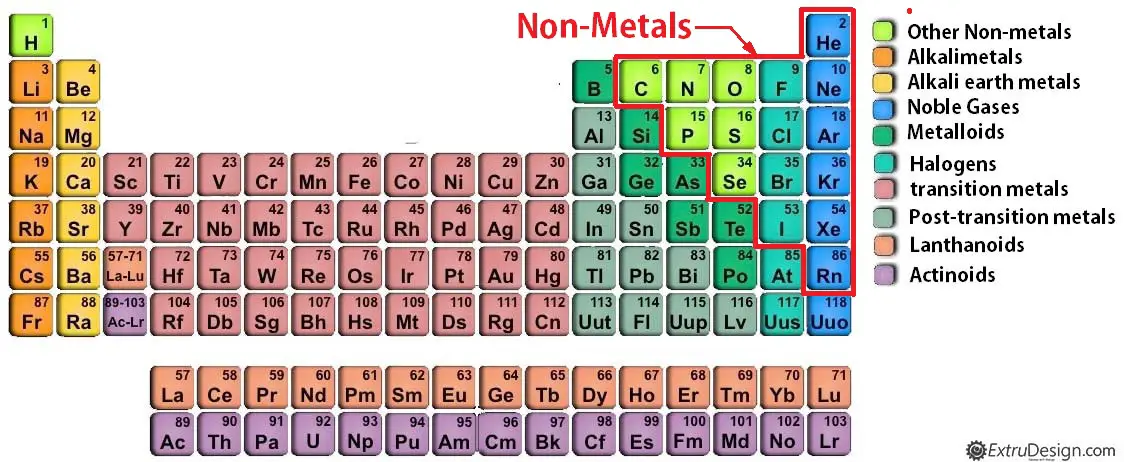
Non-metals are further classified into the following groups.
- Thermoplastics
- Thermosets
- Elastomers
Thermoplastics
A polymer that can become moldable to a specific heat and the get solidify upon cooling are known as the thermoplastics. These thermoplastics can be remoulded or reshaped many times as we want. so they are recyclable polymers.
Thermosets
These are the polymers which are capable to resist to high temperatures. Once thermosets get harden they will not be remoulded or reshaped. So these are not able to recycle. Capable of resistance to the high temperatures.
Elastomers
The elastomer is a polymer that can be deformed under stress and regain its original shape when the stress is removed. Simply a polymer which is having an elastic property called as the elastomer.
Ceramics
Ceramics are the inorganic and nonmetallic compounds. Ceramics have high strengths and hardness properties. Following examples gives the quick idea of ceramic materials.
Examples of Ceramics are plates, tiles, toilets. Not only in home appliances they are also can be used in so many other industries like automobile industries, aerospace industries.
Ceramics are Further classified into two groups
- Crystalline ceramics
- Glasses
Crystalline ceramics
Crystalline ceramics are more brittle and harder than the metals but when it comes to the tensile strength of the crystalline ceramics, it is very less. They tend to fail at very less stress.
Glasses
Glasses are also inorganic and non-metallic compounds. Glasses don’t have the crystalline structure as like Crystalline ceramics do. One special property of the glasses is the transparency.
Composite Materials
A composite material is a material formed from two or more materials to attain required properties like high strength with light in weight.
Example of the composite material is a plywood. Plywood is a composite material from a composite of different wood materials. Fibreglass is also one example of the composite material from reinforced plastics.
Composite materials are Further classified into three groups.
- Metal Matrix
- Ceramic Matrix
- Polymer Matrix
The above groups of composite materials are the different composition of materials in metal, ceramics and the polymers respectively.
Conclusion
In the machine design subject, we will deal with the most of metals only. After the classification of materials, we should focus on the selection of engineering materials for the machine members based on the type of function and many other factors.





need may you send me some of notes on my e-mail
it is very helpful…especially as a university students
Glad it helped you.