When a shaft is transmitting power from driver equipment to the driven equipment, It is necessary to calculate the shaft diameter from the torque based on the maximum torque that can be transferred through the shaft or the maximum amount of twist in the shaft. Otherwise, the shaft may not satisfy the functionality of the equipment.
Inputs that we need to calculate shaft diameter
As we know Torsional equation (Read more about the torsional equation here)
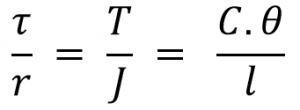
Where
τ = Torsional stress induced at the outer surface of the shaft (Maximum Shear stress).
r = Radius of the shaft.
T = Twisting Moment or Torque.
J = Polar moment of inertia.
C = Modulus of rigidity for the shaft material.
l = Length of the shaft.
θ = Angle of twist in radians on a length.
From Torsion Equation we can consider
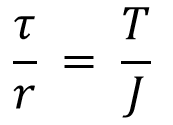
It can be written as
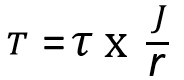
The Polar moment of inertia will be calculated from the following equation.
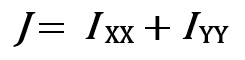
The polar moment of inertia for a circular cross-section is
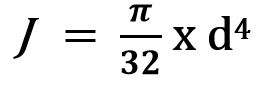
From this, the maximum torque that can be transferred thru the shaft can be written as
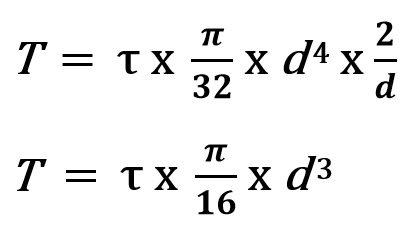
From the above equation, we can calculate the unknown factors. In our case, the shaft diameter is the unknown factor.
So we need the following input data
- The maximum torque that would be transferred thru the shaft (We can calculate torque from the Power and the speed also)
- The torsional shear stress of the material
Let’s take a sample problem to calculate the shaft diameter from the torque.
Sample Problem to calculate the shaft diameter from the torque
Problem: A shaft is transmitting 200 kW at 1200RPM. Find a suitable diameter for the shaft, if the maximum torque transmitted exceeds the mean by 30%. Take maximum allowable shear stress as 70 MPa.
Answer:
Given data
Power(P) = 200kW = 200 x 103 W
Speed (N) = 1200RPM
Operating Torque (TOperating) = ?
The maximum torque that can be operated on the shaft = 30% to the operating torque
TMax = 1.3 x TOperating
We have power(P) = (2 π N T)/60 = (2 x 3.14 x 1200 x T)/60
200 x 103 = 125.6 x T
T = 1592.36 N-m (Torque Calculator)
Operating Torque (TOperating) = 1592.36 N-m
Where TMax = 1.3 x TOperating
TMax = 1.3 x 1592.36
TMax = 2070.06 N-m
The maximum torque that can be operated on the shaft (TMax) = 2070.06 N-m
From this maximum operating torque, we can find the shaft diameter with the above equation
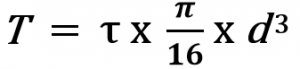
2070.06 x 103 N-mm = (70Mpa (N-mm2) x π x d3)16
d3 = 150687.075 mm
d = 53.19 mm
The required shaft diameter will be a 53 mm shaft
Here is an online calculator that Helps you Calculate the shaft diameter. Try it, it will be fun 🙂
Conclusion
Here we only consider the maximum torque that can be transferred through the shaft as the known factor to calculate the shaft diameter. We can also find the shaft diameter with the maximum angular twist that can be allowable in the shaft by considering the shaft stiffness(C) and the torque relation(Given below) from the torsional equation.
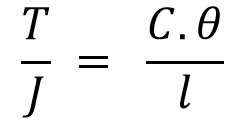
Try the following exercise problem and post your answer in the comment box below! Let’s see who can post the right answer.
Exercise problem: A shaft is transmitting 97.5 kW at 180 r.p.m. If the allowable shear stress in the material is 60 MPa, find the suitable diameter for the shaft. The shaft is not to twist more than 1° in a length of 3 meters. Take C = 80 GPa.
And if the shaft is subjected to bending, then also we can calculate the shaft diameter. check how

Not sure
a solid steel shaft transmits 100kw at 150rpm.determine the suitable diabmeter of the shaft if maximum torque exceed the mean by 20 percent in each revolution.the shear storess not to exceed 600mpa.the dia meter of the shaft is?
You want me to help me with this problem?
I will be much happier if you can solve it by using the above article and the sample problem. Let me know if you have any understanding issue with the above article.
How to calculate shaft diameter, when subjected to torsion and bending moment. Know Power is 20 kW and rpm is 400. Material of shaft is AISI 4140.
hey Pankaj,
here is the article to help you calculate shaft diameter when subjected to torsion and bending moment.
https://extrudesign.com/how-to-calculate-shaft-diameter-under-twisting-and-bending-moment/
d3 = 150687.075 mm
d = 53.19 mm
How have you got 53.19 out of d3, shouldn’t the answer be 438.01 ?
ø = 2 x √(A / π)
My friend, it is simply the (150687.075)^(1/3)
shaft dia = 103.098 mm
Yes, correct Devender Narang.
Good job
how you convert to d^3 from the formula?
can you suggest 11000 RPM of select of shaft diameter 6 and length is 600mm
Few input details are still missing for the shaft diameter calculation. If you can understand the above article you can help yourself with the calculation. If you have difficulty understanding the above article I can gladly help you.
hello
can you please explain why it is 30% of the operation torque which is the maximum torque?
This maximum torque is mentioned in the problem statement. “Find a suitable diameter for the shaft, if the maximum torque transmitted exceeds the mean by 30%”
Example Problem: A steel solid shaft transmitting 15 kW at 200 RPM is supported on two bearings 750 mm apart and has two gears keyed to it. The pinion having 30 teeth of a 5 mm module is located 100 mm to the left of the right-hand bearing and delivers power horizontally to the right. The gear having 100 teeth of 5 mm module is located 150 mm to the right of the left-hand bearing and receives power in a vertical direction from below. Using allowable stress of 54 MPa in shear, determine the diameter of the shaft.
This is a somewhat complex problem. It involves finding the bending moment and drawing bending moment diagrams as well. Try to solve it.
Check here for the answer: https://extrudesign.com/example-problem-on-calculating-shaft-diameter/
I can’t do the math, I’m sorry.
But I need to know how big of a shaft I need (we seem to keep bending the existing one) for 125kw transmitted 140 inches at 720 rpm. Material is 1144 Stressproof steel solid rod.
I should add that it is in a small hydroelectric turbine. No shock loads.
A shaft is transmitting 20 W at 3000 RPM. Find a suitable diameter for the shaft, if the maximum torque transmitted exceeds the mean by 30%. Material used is AISI 304.
What are the references for the equations