Wire rope comes under the Rope drives. The rope drives are widely used where a large amount of power is to be transmitted, from one pulley to another, over a considerable distance. It may be noted that the use of flat belts is limited for the transmission of moderate power from one pulley to another when the two pulleys are not more than 8 meters apart. If large amounts of power are to be transmitted by the flat belt, then it would result in excessive belt cross-section. Let us discuss the Wire rope Classification, Properties, and Construction in detail.

The ropes drive uses the following two types of ropes:
- Fiber ropes
- Wire ropes
The fiber ropes operate successfully when the pulleys are about 60 meters apart, while the wire ropes are used when the pulleys are up to 150 meters apart.
In the previous article, we discussed the Fibre Ropes in a detailed manner. In this article, we are going to discuss only the Wire ropes.
Wire Ropes
When a large amount of power is to be transmitted over long distances from one pulley to another (i.e. when the pulleys are up to 150 meters apart), then wire ropes are used. The wire ropes are widely used in elevators, mine hoists, cranes, conveyors, hauling devices, and suspension bridges. The wire ropes run on grooved pulleys but they rest on the bottom of the grooves and are not wedged between the sides of the grooves.

The wire ropes are made from cold-drawn wires in order to increase strength and durability. It may be noted that the strength of the wire rope increases as its size decreases. The various materials used for wire ropes in order of increasing strength are wrought iron, cast steel, extra strong cast steel, plow steel, and alloy steel. For certain purposes, the wire ropes may also be made of copper, bronze, aluminum alloys, and stainless steel.
Advantages of Wire Ropes
The wire ropes have the following advantages as compared to fiber ropes.
- These are lighter in weight,
- These can withstand shock loads
- These are more durable
- The efficiency is high
- These offer silent operation
- These are more reliable,
- They do not fail suddenly
- The cost is low.
Construction of Wire Ropes
The wire ropes are made from various grades of steel wire having a tensile strength ranging from 1200 to 2400 MPa as shown in the following table:
| Grade of wire | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 |
| Tensile strength range (MPa) | 1200 – 1500 | 1400 – 1700 | 1600 – 1900 | 1800 – 2100 | 2000 – 2400 |
The wires are first given special heat treatment and then cold drawn in order to have the high strength and durability of the rope. The steel wire ropes are manufactured by special machines. First of all, a number of wires such as 7, 19, or 37 are twisted into a strand, and then a number of strands, usually 6 or 8 are twisted about a core or center to form the rope as shown in the following figure.
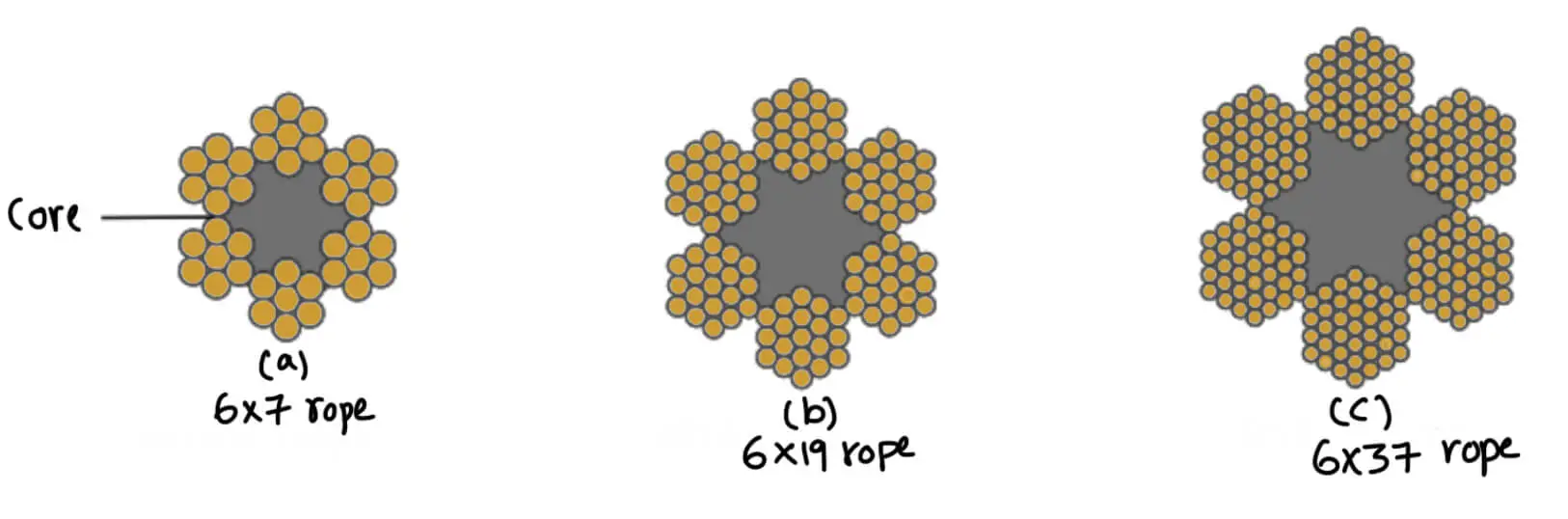
The core may be made of hemp, jute, asbestos, or a wire of softer steel. The core must be continuously saturated with lubricant for the long life of the core as well as the entire rope. The asbestos or soft wire core is used when ropes are subjected to radiant heat such as cranes operating near furnaces. However, a wire core reduces the flexibility of the rope, and thus such ropes are used only where they are subjected to high compression as in the case of several layers wound over a rope drum.
Classification of Wire Ropes
According to the direction of twist of the individual wires and that of strands, relative to each other, the wire ropes may be classified as follows:
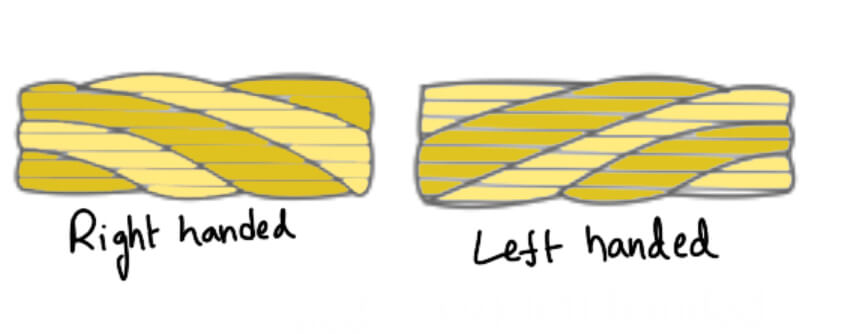
- Cross or regular lay ropes. In these types of ropes, the direction of the twist of wires in the strands is opposite to the direction of the twist of the stands, as shown in the following figure (a). Such types of ropes are the most popular.
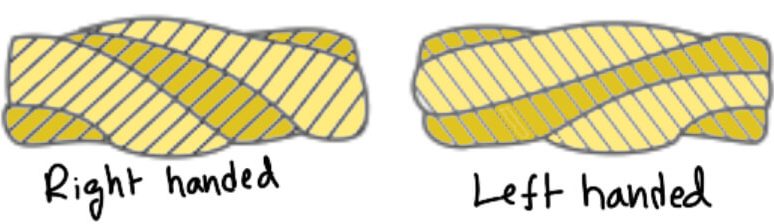
- Parallel or lang lay ropes. In these types of ropes, the direction of the twist of the wires in the strands is the same as that of strands in the rope, as shown in the following figure (b). These ropes have better bearing surface but are harder to splice and twists more easily when loaded. These ropes are more flexible and resist wear more effectively. Since such ropes have the tendency to spin, therefore these are used in lifts and hoists with guideways and also as haulage ropes.
- Composite or reverse-laid ropes. In these types of ropes, the wires in the two adjacent strands are twisted in the opposite direction, as shown in the following figure (c).
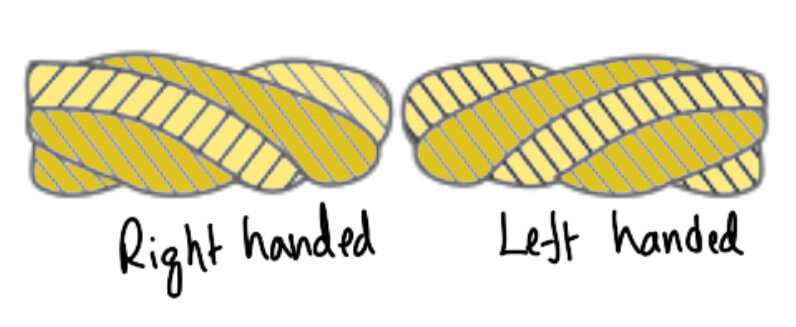
Note: The direction of the lay of the ropes may be right-handed or left-handed, depending upon whether the strands form right-hand or left-hand helixes, but the right-hand lay ropes are most commonly used.
Designation of Wire Ropes
The wire ropes are designated by the number of strands and the number of wires in each strand. For example, a wire rope having six strands and seven wires in each strand is designated by 6 × 7 rope.
The following table shows the standard designation of ropes and their applications:
Table: Standard designation of ropes and their applications.
| Standard designation | Application |
| 6 × 7 rope | It is a standard coarse-laid rope used as haulage rope in mines, tramways, and power transmission. |
| 6 × 19 rope | It is a standard hoisting rope used for hoisting purposes in mines, quarries, cranes, dredges, elevators, tramways, and well drilling. |
| 6 × 37 rope | It is an extra flexible hoisting rope used in steel mill laddles, cranes, and high-speed elevators. |
| 8 × 19 rope | It is also an extra flexible hoisting rope. |
Properties of Wire Ropes
The following tables show the properties of the various types of wire ropes. In these properties, the diameter of the wire rope (d ) is in mm.
Table: Steel wire ropes for haulage purposes in mines.
| Type of rope | Nominal diameter (mm) | Average weight (N/m) | Tensile strength (N) | |
| Tensile strength of wire | ||||
| 1600 MPa | 1800 MPa | |||
| 6×7 | 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 24, 25 26, 27, 28, 29, 31, 35 | 0.0347 d2 | 530 d2 | 600 d2 |
| 6 × 19 | 13, 14, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21 22, 24, 25, 26, 28, 29, 32 35, 36, 38 | 0.0363 d2 | 530 d2 | 595 d2 |
Table: Steel wire suspension ropes for lifts, elevators, and hoists.
| Type of rope | Nominal diameter (mm) | Average weight (N/m) | Tensile strength (N) | |
| Tensile strength of wire | ||||
| 1100–1250 MPa | 1250–1400 MPa | |||
| 6 × 19 | 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16 18, 20, 22, 25 | 0.0383 d2 | 385 d2 | 435 d2 |
| 8 × 19 | 8, 10, 12, 14,16 18, 20, 22, 25 | 0.034 d2 | 355 d2 | 445 d2 |
Table: Steel wire ropes used in oil wells and oil well drilling
| Type of rope | Nominal diameter (mm) | Approximate weight (N/m) | Ultimate tensile strength (N) | ||
| Tensile strength of wire | |||||
| 1600 – 1800 MPa | 1800 – 2000 MPa | 2000 – 2250 MPa | |||
| 6×7 | 10, 11, 13, 14, 16, 19, 22, 25 | 0.037 d2 | 550 d2 | 610 d2 | – |
| 6 × 19 | 13, 14, 16, 19 22, 25, 29, 32, 35, 38, | 0.037 d2 | 510 d2 | 570 d2 | 630 d2 |
| 6 × 37 | 13, 14, 16, 19, 22, 25, 26, 32, 35, 38 | 0.037 d2 | 490 d2 | 540 d2 | 600 d2 |
| 8 × 19 | 13, 14, 16, 19, 22, 25, 29 | 0.0338 d2 | – | 530 d2 | – |
Table: Steel wire ropes for general engineering purposes such as cranes, excavators etc
| Type of rope | Nominal diameter (mm) | Approximate weight (N/m) | Average tensile strength (N) | ||
| Tensile strength of wire | |||||
| 1600 – 1750 MPa | 1750 – 1900 MPa | ||||
| 6 × 19 | 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 32, 36, 38, 40 | 0.0375 d2 | 540 d2 | 590 d2 | |
| 6 × 37 | 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56 | 0.038 d2 | 510 d2 | 550 d2 | |
Diameter of Wire and Area of Wire Rope
The following table shows the diameter of wire (dw) and area of wire rope (A) for different types of wire ropes:
Table: Diameter of wire and area of wire rope
| Type of wire rope | 6 × 8 | 6 × 19 | 6 × 37 | 8 × 19 |
| Wire diameter (dw) | 0.106 d | 0.063 d | 0.045 d | 0.050 d |
| Area of wire rope (A) | 0.38 d2 | 0.38 d2 | 0.38 d2 | 0.35 d2 |
Factor of Safety for Wire Ropes
The factor of safety for wire ropes based on the ultimate strength is given in the following table.
| Application of wire rope | Factor of safety | Application of wire rope | Factor of safety |
| Track cables Guys Mine hoists: Depths up to 150 m 300 – 600 m 600 – 900 m over 900 m Miscellaneous hoists | 4.2 3.5 8 7 6 5 5 | Derricks Haulage ropes Small electric and air hoists Overhead and gantry cranes Jib and pillar cranes Hot ladle cranes Slings | 6 6 7 6 6 8 8 |
This is all about Wire Rope Classification, Properties, and Construction. We also provided some of the wire designations and the sizes for different applications. We provided some of the safety factors for the different applications.

Leave a Reply