The third law of Thermodynamics is one of the laws from the three laws of thermodynamics. Where the first law states about the Quantity of energy. Which means the energy cannot be created nor it can be destroyed, It can be transferred from one form to another. This is the law of Law of Conservation Energy. The second law of the thermodynamics is all about the quality of the energy. Which means an increase in the Entropy. In this article, we are going to discuss the Third law of the Thermodynamics.
Third Law of Thermodynamics
The Third Law of Thermodynamics states that when the temperature of the system becomes the absolute zero then the Change in the entropy will also be zero or it will be constant.
Δ S = 0 when T → 0
The third law of thermodynamics predicts the properties of a system and the behavior of entropy in a unique environment known as absolute temperature.
What do you mean by Absolute temperature?
The absolute temperature means the temperature is 0° in Kelvin Scale. Which is the possible lowest temperature in the universe. This 0 K is equal to the -273.15° C (Celsius) or -459.7 F (Fahrenheit).
The absolute temperature is the lowest temperature known and sets a lower limit to the Universe’s temperature range.
This Third Law of Thermodynamics is the lesser known than the other two thermodynamic Laws, First Law and the Second Law. because it is rarely applied to our day to day life.
Hold on. There is an implication in this Third law of Thermodynamics. Reaching the Absolute Temperature for the Sink would take an
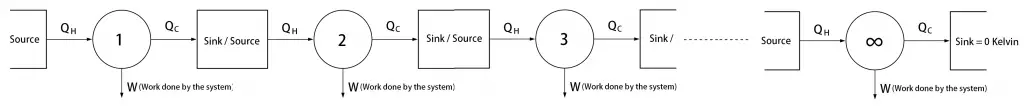
So infinite number of steps means we can not get to there.
And it also violates the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Because sink temperature is 0 Kelvin that means it the system converts all the input into work output. So we can not build a machine that can deliver a 100% efficiency.
Conclusion
We have discussed the statement of the Third Law. Also, we have discussed the implications of this law. Let us know your thought on this in the comment section below.

Leave a Reply