We have been discussing the different thermodynamic cycles and the Law of thermodynamics, so far we understand what is a Thermodynamic system. A thermodynamic system is a group of material which is having properties such as the temperature, pressure, volume, internal energy etc. This thermodynamic system can be a closed system or an open system or isolated system. Let’s discuss the different Thermodynamic Processes in detail.

Thermodynamic Processes
When there is a change in the thermodynamic system due to a change in its properties such as the temperature, pressure, volume, etc. then there will be four different thermodynamic processes will come into the picture. Those are the isothermal process, adiabatic process, isochoric process, isobaric process.
- Isothermal process – Constant Temperature
- Adiabatic process – Energy transfer without the transfer of heat or mass
- Isochoric process – Constant Volume
- Isobaric process – Constant Pressure
Isothermal process (Constant Temperature Process)
When a thermodynamic System is changed from one state to another without a change in its temperature during the process, then this process is called the Isothermal process.
For the given number of moles of an Ideal Gas, we have
PV = nRT
Where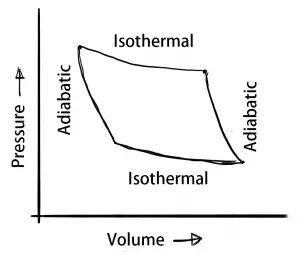
P = Pressure
V = Volume
n = Number of Moles
R = Universal Gas Constant
T = Temperature
Where the temperature is constant, then
PV = Constant
During the isothermal Process, there will be no change in the internal energy. So from the first law of the thermodynamics, the change in the internal energy is equal to the algebraic difference between the amount of heat supplied to the system and the Amount of the Work done by the system
dU = δQ – δW
Where Change in internal energy (dU) = 0
0 = δQ – δW
δQ = δW
In the Isothermal process, the amount of heat supplied to the system is equal to the Amount of the Work done by the system.
Adiabatic process
In the Adiabatic process, there will be no transfer of the Heat or mass between the system and the surroundings. Only the energy can be transferred in the form of work.
ΔQ = 0
from the First law of thermodynamics,
dU = 0 – δW
dU = – δW
There will be Change in the internal energy due to the work is done on the system by the surroundings. For example, a gas is compressed in the cylinder with the piston.
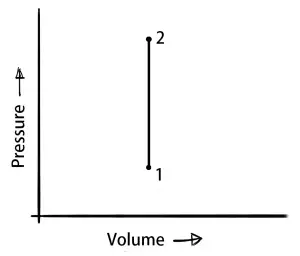
Isochoric process (Constant Volume Process)
In the isochoric process, the volume of the system remains constant. So obviously the work done will be zero.
ΔV = 0 (∴ ΔW = P×ΔV = 0)
From the First law of thermodynamics,
δQ = dU
This means the heat supplied to the system will increase in the internal heat energy.
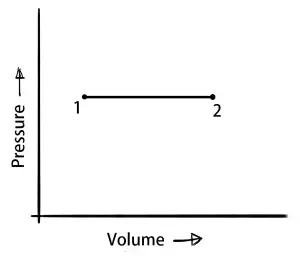
Isobaric process (Constant Pressure Process)
In the Isobaric Process, the pressure of the system remains constant.
∴ ΔW = P×ΔV
From the First law of the thermodynamics,
dU = δQ – δW
δQ = dU+(P×ΔV)
A little amount of heat is used to raise the temperature and brings a change in the internal energy and also some work output under the constant pressure.
Conclusion
We have discussed the different process in the thermodynamic system such as the isothermal process, adiabatic process, isochoric process, isobaric process in details with the P-V diagrams. If you still have any doubts please let us know in the comment section below.

Leave a Reply