Combustion is a chemical reaction which generates heat energy. The process of combustion is a very complex subject. This combustion process in an IC engine takes place in a homogeneous mixture or heterogeneous mixture based on the type of engine. In this article, we are going to discuss the Different Stages of combustion in SI engine.

In a thermodynamic cycle, we have the suction, compression, combustion, expansion and exhaust processes. The theoretical and the actual cycles are not the same in each of these processes due to several factors. Let’s see the combustion process in both Actual cycle and theoretical cycle with the help of a Pressure and crank angle diagram [p-θ Diagram].
Pressure vs Crank angle diagram
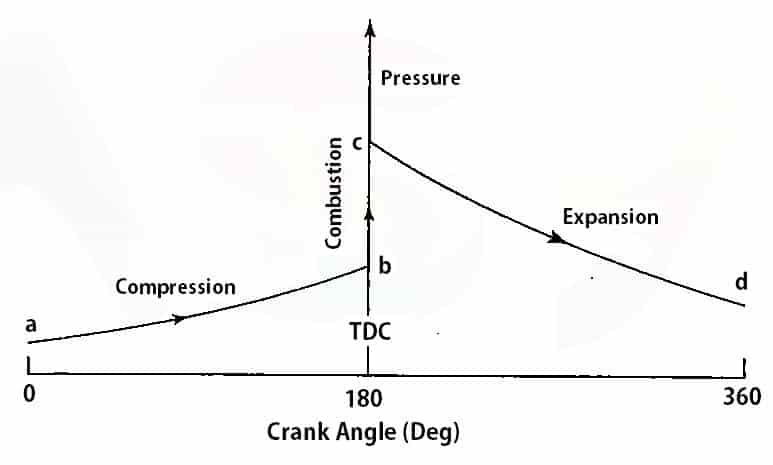
In the above Pressure vs cranks Angle diagram of the four-stroke spark ignition engine, a → b is the Compression process, and b → c is the combustion process, c → d is the expansion process.
As you can see that the pressure rise during the combustion process is at constant volume in the theoretical cycle. (i.e at top dead centre). But in the actual cycle is it not possible.
Stages of combustion in SI engine
Check the actual Pressure vs Crank angle diagram [p-θ Diagram]
![Actual Pressure vs Crank angle diagram [p-θ Diagram]](https://cdn-0.extrudesign.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Stages-of-combustion-in-SI-engine-Extrudesign.com-003.jpg)
As you can see the combustion process will be completed in the three stages in an actual engine.
- Ignition Lag
- Flame Propagation
- After burning
1. Ignition Lag
The time interval between the passage of the spark and the inflammation of the air-fuel mixture is known as ignition lag or Ignition delay. It is also referred to as the preparation phase.
There are two chances that can cause the ignition delay. Physical delay and chemical delay. Physical delay due to the atomisation, vaporization and mixing of air fuel. The chemical delay due to pre-combustion reactions.
The ignition lag depends on the heat, pressure, the nature of the fuel and the proportion of the exhaust gas residuals.
2. Flame Propagation
The flame propagation means that the propagation of combustion wave through a combustible mixture. Or simply the spread of the flame throughout the combustion chamber.
When the ignition initiated, the adjacent layer of the reaction zone also ignites and propagated to the next layer. This continued throughout the mixture in the combustion chamber. This process takes some time to spread the flame throughout the combustion chamber.
During this stage the pressure rises with very little change in the volume. But it can not be instantaneous as we claimed to be in the actual cycle.
3. After burning
This After Burning stage begins where the cylinder pressure reaches a maximum point(c) in the cylinder. Also, flame propagation gradually decreases due to the flame velocity will reduce.
The expansion stroke will starts at or before this stage. so there will be no pressure rise in this stage.
These are the different Stages of combustion in SI engine.
Conclusion
We have discussed the pressure vs crank angle diagram [p-θ Diagram] for the actual cycle and the theoretical cycle. And also the different stages of combustion in SI engine, those are ignition lag, flame propagation and the afterburning. If you have any further thoughts on this topic, let us know in the comment section below.

where is motoring curve
What do you mean by Motoring curve exactly?