When a customer is looking for a product, they have no idea what they exactly want. Which means they do know what they want, but they fail to describe it in perfect context. So it is necessary to understand the customer needs to develop a product. This Kano Diagram model is helpful for the understanding of customer needs.

Kano Diagram
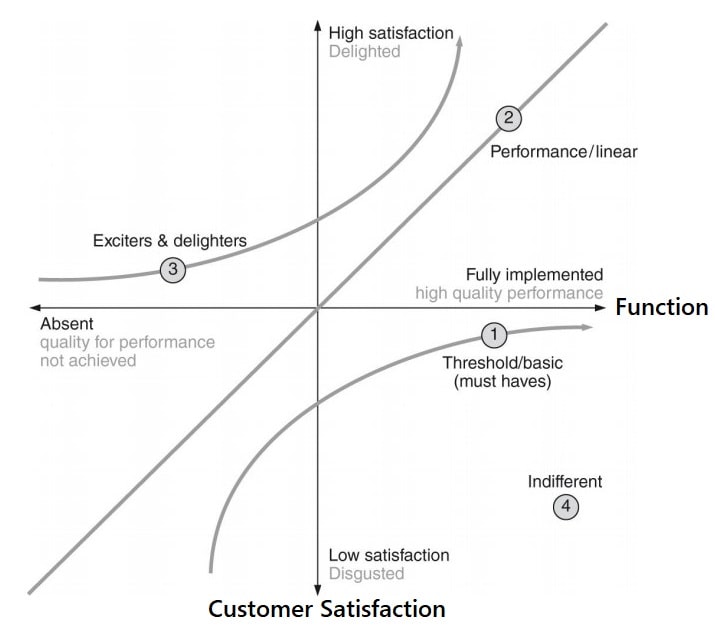
Kano diagram is the plot between customer satisfaction vs the product functions.
- Kano’s theory is that for some customer needs, customer satisfaction is directly proportional to the extent to which the product or service is fully functional.
- The horizontal axis represents how fully functional a product or service is.
- Whereas the vertical axis represents how satisfied a customer is.
There are three basic attributes that customer satisfaction can be classified.
- Basic (Threshold) – Must have
- Performance – Primary Satisfiers
- Excitement – Delighters
A competitive product meets basic attributes, maximizes performance attributes, and includes as many “excitement” attributes as possible at a cost the market can bear.
1. Basic attributes/Functions
- Threshold (or basic) attributes are the expected attributes or “musts” of a product and do not provide an opportunity for product differentiation.
- The absence or poor performance of these attributes results in extreme customer dissatisfaction. An example of a threshold attribute would be brakes on a car.
- The Must-Be curve indicates situations in which the customer is less satisfied when the product or service is less functional but is not more satisfied when the product or service is more functional.
2. Performance attributes/Primary satisfiers
- Performance attributes are those for which more is generally better, and will improve customer satisfaction.
- Conversely, an absent or weak performance attribute reduces customer satisfaction.
- Of the needs customers verbalize, most will fall into the category of performance attributes.
- The price for which a customer is willing to pay for a product is closely tied to performance attributes.
- For example, customers would be willing to pay more for a car that provides them with better fuel economy.
- Primary satisfiers are customer requirements where the level of customer satisfaction is proportional to the extent to which the product or service is fully functional.
- The horizontal axis of the diagram indicates how fully functional a product or service is.
- The vertical axis indicates how satisfied the customer is.
- The line going through the origin at 45 degrees represents the situation in which customer satisfaction is directly proportional to how fully functional the product or service is.
3. Excitement Attributes/ Delighters
- The delighted state is product performance beyond customer expectation.
- The Delighters curve indicates the situation in which the customer is more satisfied when the product or service is more functional.
- But not less satisfied with the product or service is less functional.
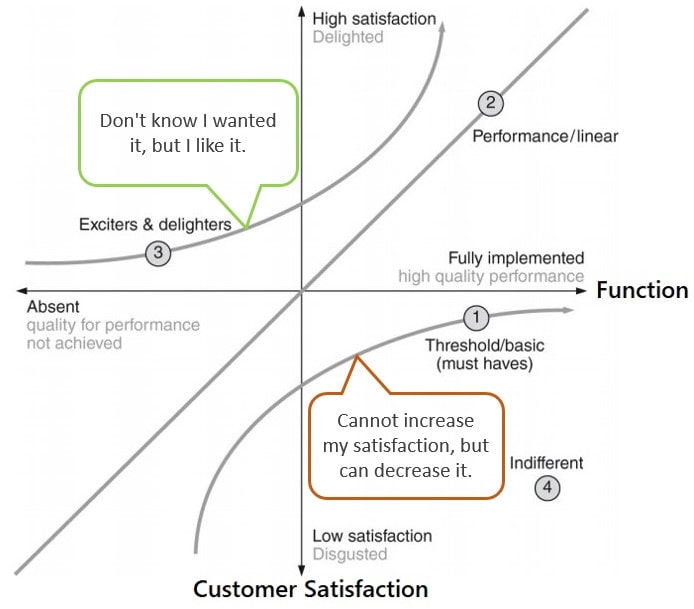
- Excitement attributes are unspoken and unexpected by customers but can result in high levels of customer satisfaction.
- However, their absence does not lead to dissatisfaction. Excitement attributes often satisfy latent needs.
So basically the Basic needs will get the firm to enter into the market, the performance needs will stay in the market for some time and excitement needs will help the firm to be the leader in the market.
4. Indifferent – Other Attributes
Other than these three attributes, we have some attributes that can not be classified into the kano Diagram model.
- These attributes are often of little or no consequence to the customer and do not factor into consumer decisions.
- A customer can be indifferent to the requirement of a product or service where it has no effect on satisfaction one way or another.
- For example, colour or logo on the credit card.
- An example of this type of attribute is a plate listing part numbers can be found under the hood on many vehicles for use by repairpersons.
Conclusion
We have discussed the Kano Diagram and the function attributes such as the basic needs, performance needs, excitement needs. If you still have any further thoughts on this topic, let us know in the comment section below.


Leave a Reply