Have you ever wondered why most of the time you have seen many applications involve hollow shafts instead of solid ones? How the Hollow Shaft is better than a Solid shaft? Let us see how the hollow shafts are better than the solid ones.

Differentiating the Hollow shaft and solid shaft can be done with two main mechanical properties. Those are the resistance to bending and torsion. Following are the comparison points assuming both shafts should have the same weight.
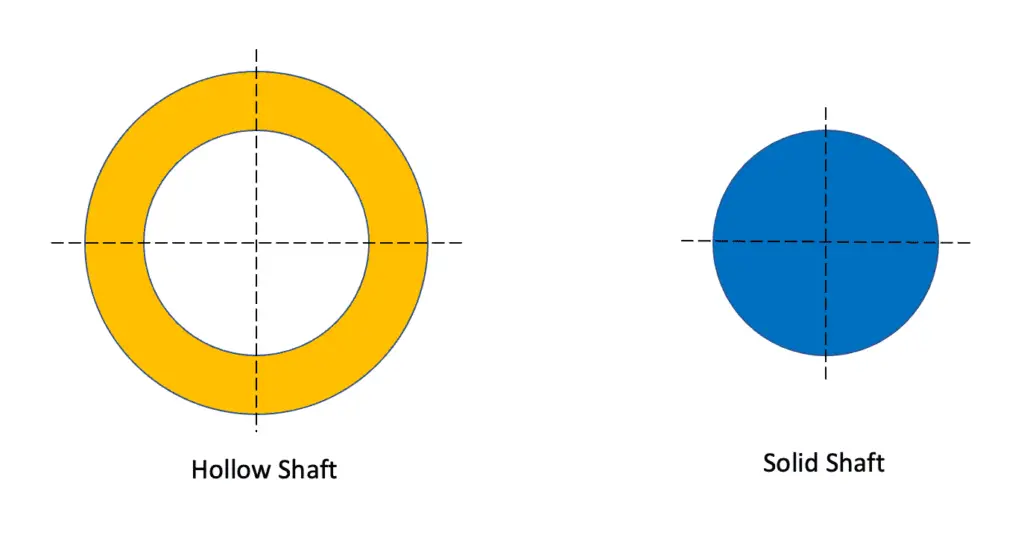
- As you can see the above hollow shaft and solid shaft cross-section representations, the diameter of the hollow shaft is more than a solid shaft and require more space to match with the same weight.
- Hence the hollow shaft will have more strength than the solid shaft with the same amount of weight of shaft.
- Hollow will be much stiffer than the same weight solid shaft.
- Hollow shaft natural frequency will be higher than the solid shaft with the same weight.
- Hollow shaft manufacturing is costlier than the solid shaft production.
- Hollow shafts have a more polar moment of inertia, which enables them to transmit more torque than solid shafts.
- Hollow shafts can not transfer more power but the power to weight ratio of hollow shafts is more as compared to the solid shaft.
- Solid shafts, when subjected to bending, are stronger than that of the hollow shaft.
As you can see, many of the advanced are on the hollow shaft side… except one which is the on the bending resisting strength of solid shafts is better compared to the hollow shafts.
Which shaft you should choose? Hollow shaft or Solid shaft?
Hollow shaft Applications
For structural applications like a Rollcage of offroad vehicles, the hollow shaft is better than the solid shafts because it can beat the same loads as a solid shaft for lesser weight.
Ans also hollow shafts preferred where the load-bearing type of shaft is required because it has higher stiffness and rigidity and can resist slightly higher bending moments compared to the solid shaft of the same wight.
Solid shaft Applications
Whereas the solid shaft is better for power transmission applications such as driveshafts when compared to the hollow shaft.
You must have observed all the shafts used for transmission of torque like crankshafts, driveshafts, are solid shafts. Since the solid shaft is always better because it has higher torsional stiffness.
Also, The applications require very less critical bending moment, then solid shafts are preferred, otherwise, most of the shafts are hollow.
Let us solve an example to compare the weight, strength, and stiffness of the solid shaft and the hollow shaft of the same external diameter and see which design is better.
Example problem to compare Hollow Shaft with Solid shaft of Same diamter
Compare the weight, strength, and stiffness of a hollow shaft of the same external diameter as that of a solid shaft. The inside diameter of the hollow shaft is half the external diameter. Both the shafts have the same material and length.
Answer:
Let us say
do = Outer diameter of the hollow shaft
di = Inner diameter of the hollow shaft
d = Diameter of the solid shaft
Given that both the hollow shaft and solid shaft are the same external diameter. We can write
do = d
di = do / 2
k = di / do = 1 / 2 = 0.5
1. Comparing of weight of Hollow shaft with solid shaft of same diameter
We know that weight of a hollow shaft
WH = Cross-sectional area × Length × Density
WH= (π/4) × [ ( do )-( di )2 ] × Length × Density
The weight of the solid shaft
WS = (π/4) × d2 × Length × Density
Since we are comparing the weight of the same diameter of the hollow shaft and solid shaft, and also we assumed that both shafts were made of the same material and have the same length.
Therefore let us divide the weight of the hollow shaft with the solid shaft weight and put do = d, we get
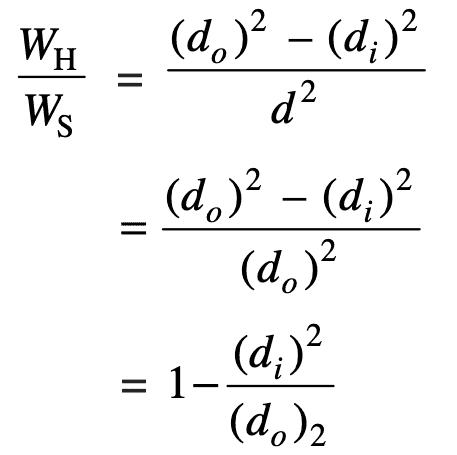
= 1 – k2
= 1–(0.5)2
= 0.75
The weight ratio of the hollow shaft to the solid shaft is 0.75: 1
In simple words, the hollow shaft is 25% less weight than the solid shaft of the same outer diameter, length, and both shafts are made of the same material.
2. Comparing of Strength of Hollow shaft with solid shaft of same diameter
We know that strength of the hollow shaft
Th = (π/16) × τ (do)3 (1 – k4)
and strength of the solid shaft,
TS = (π/16) × τ ×d3
Since we are comparing the strength of the same diameter of the hollow shaft and solid shaft, and also we assumed that both shafts were made of the same material and have the same length.
Therefore let us divide the strength of the hollow shaft with the solid shaft strength and put do = d, we get
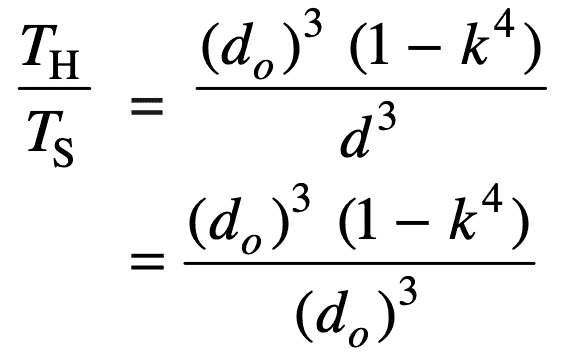
= 1 – k4
= 1 – (0.5)4
= 0.9375
The strength ratio of the hollow shaft to the solid shaft is 0.9375: 1
In simple words, the hollow shaft is almost has a strength of 93.75% of the solid shaft strength of the same outer diameter, length, and both shafts are made of the same material.
3. Comparison of stiffness of Hollow shaft with solid shaft of same diameter
We know that stiffness relation from the torsion equation
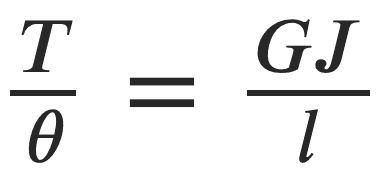
The Stiffness of a hollow shaft will be
SH = G/L × (π/32) [ (do)4– (di)4]
The stiffness of a solid shaft
SS = G/L × (π/32) × d4
Since we are comparing the stiffness of the same diameter of the hollow shaft and solid shaft, and also we assumed that both shafts were made of the same material and have the same length.
Therefore let us divide the stiffness of the hollow shaft with the solid shaft stiffness and put do = d, we get
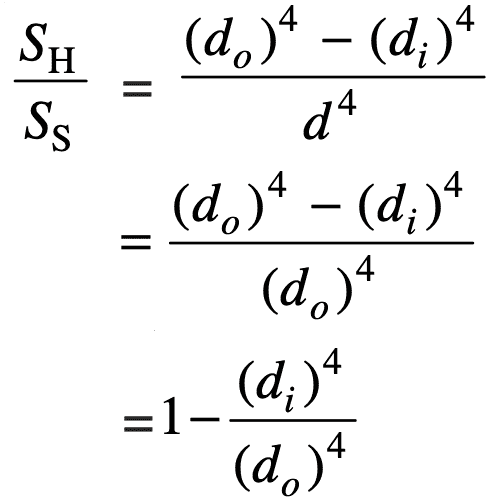
= 1 – k4
= 1 – (0.5)4
= 0.9375
The stiffness ratio of the hollow shaft to the solid shaft is 0.9375: 1
In simple words, the hollow shaft is almost has a stiffness of 93.75% of the solid shaft stiffness of the same outer diameter, length, and both shafts are made of the same material.
Conclusion
A hollow shaft is not always better than a solid shaft. but the Hollow shaft has very serious advantages over the solid shaft which we need to consider. That is the reason we think that the hollow shaft is better than the solid shaft for many applications.

Yes I agree. Hollow shaft is better than solid shaft. Last time, I used this hollow shaft. I never regretted instead of solid shaft.