In the Design of any machine elements, it is necessary to follow the Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing for the Holes or shafts. The Regardless of feature size(RFS) is the feature of the size where it can be called out for a hole or a shaft when there is no need for MMC or LMC.
Regardless of feature size
Regardless of Feature size is also referred to as RFS. RFS is a material modifier used in the GD&T callout
This means that it does not matter whether the size is at the low or high limit of its noted tolerance and that the GD&T limit does not change.
Example for Regardless of feature size
Following is an example representation of regardless of feature size is applicable since there is no material modifier specified.
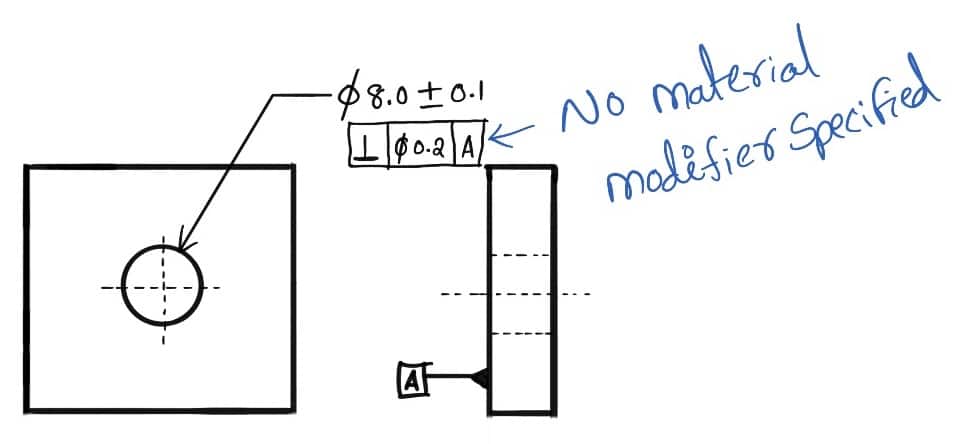
The hole on a given part can be made to its smallest size (7.9 mm) or to the largest size (8.1mm)
The worst-case allowable variation that could be allowed for the position of the hole axis would be 0.2mm regardless of the size of the hole.
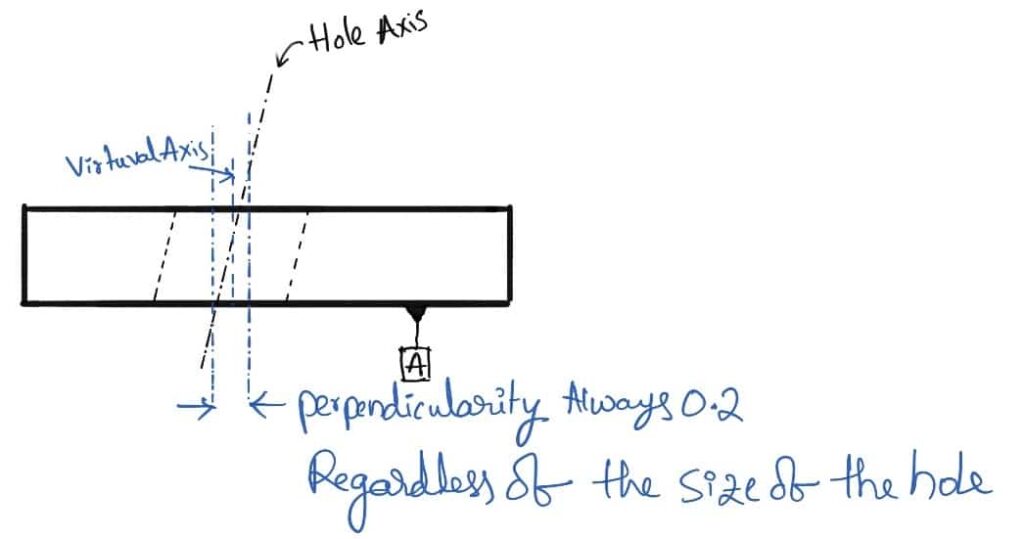
The above figure represents an example of the manufactured part, where the hole size was already made within the given specified tolerances. But irrespective of the hole size Regardless of feature size will ensure that the actual hole axis is within the Geometric Perpendicular tolerance of 0.2mm no matter the size of the hole.
The following table will illustrate this RFS scenario in a detailed manner for the above drawing.
| Size of the Hole | Perpendicular Tolerance acc. to RFS |
| 7.90 | 0.2 |
| 7.95 | 0.2 |
| 8.00 | 0.2 |
| 8.05 | 0.2 |
| 8.10 | 0.2 |
It is shown that the perpendicular tolerance is not changed with the hole size.
We will do this same for the MMC and LMC condition for the same drawing above and see how this works for MMC and LMC
| Material Condition for Hole | Size of the Hole | Perpendicular Tolerance acc. to MMC | Perpendicular Tolerance acc. to LMC |
| MMC | 7.90 | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| MMC | 7.95 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| True size | 8.00 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| LMC | 8.05 | 0.35 | 0.25 |
| LMC | 8.10 | 0.40 | 0.20 |
in the above table, it is clear that there is an additional tolerance has been added to the perpendicular tolerance (position control) with MMC and LMC material modifiers for a Hole feature.
But for the RFS table, there is no additional tolerance has been added to the perpendicular tolerance.
How and where Regardless of the Feature of size (RFS) is used?
Regardless of the Feature of size (RFS) is used for press-fit applications.
RFS does not need any symbol representation on the Drawing GD&T. By default if there is no callout for LMC or MMC on the drawing GD&T, which means it is obvious that there is an RFS callout.
If we do not need an RFS callout for a feature, then it needs to be specified to ignore the RFS callout.
Regardless of feature size eliminates any potential bonus tolerance, allowing the GD&T tolerances to be more tightly controlled.
RFS requires the hole axis to be measured separately from the size of the hole and cannot be gauged easily. However, there is no bonus tolerance allowed in this condition so the perpendicularity would be much better controlled regardless of the size of the hole.
The Feature of Size Callouts in GD&Ts
The feature of size callouts is also known as material modifiers.
- Maximum Material Condition
- Least Material Condition
- Regardless of Feature of size
These are the 3 material modifiers.
We have mentioned that the RFS is used for press-fit applications.
Whereas the MMC is used for clearance applications. MMC clears the biggest size of bolt.
And LMC is used where the wall thickness is important, like holes on gaskets and flanges, and minimum machining is required.

Leave a Reply