A final year project on “Present And Future Trend Of Electric Vehicles” was submitted by Manjeet Kumar Gupta (from Galgotias University Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh) to extrudesign.com.
| University: | Galgotias University Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh. | |
| Project Title: | Present And Future Trend Of Electric Vehicles | |
| Submitted by: | Manjeet Kumar Gupta | |
| Authors: | Manjeet Kumar Gupta | |
| Supervised by: | Dr. Neha Dubey (Assistant Professor) | |
| Department: | Bachelor in Business Administration | |
| Academic Year: | 2021-22 |

ABSTRACT
The environmentally-friendly electric vehicles market is advancing in India. New car companies are transforming the car industry, creating innovative new models. Interest in the electric vehicles market is growing rapidly and with new pricing models, the growth is predicted to get bigger.
All Existing car makers are aware of this change and are trying to unveil new hybrid or electric vehicle Models. Developed countries like UK and France have planned to prohibit diesel and petrol car sales from 2040, and experts suggest that Europe’s new car sales will likely be all-electric five years before the deadline.
There is rising commitments and competition from leading car manufacturers and businesses within the automotive industry. Countries like Norway are experiencing rapid progression in the electric vehicles market. In Norway’s new car sales in December 2017, almost 30% sold were driven by electric battery power.
Energy experts believe that China and Indian markets will drive vehicle demand and due to fewer carbon emission challenges, electric vehicle development will be high on these countries’ political agendas. Many companies are planning to introduce electric vehicle charging points as the electric vehicle industry growth is increasing.
INTRODUCTION
In the world, fuel conservation and ecological protection concerns are growing and the electric vehicles, Research and development has hastened. The automotive industry globally is experiencing disruption by Digitization. Increasing automation, are revolutionizing the industry for a new revolution in 21sty century and India automobile industry is also experiencing its effects. Indian EV market is different compared to other global markets as Indian economy dynamics, market requirements and consumer preferences are very different.
Understanding and reinventing is important to manage the future changes in this sector. These trends will Change mobility behavior and build new avenues for competition and collaboration. The growth ahead is to Provide the required services which are expected to increase. Thirteen cities out of 20 in the world with highest Air pollution are in India and reducing the growing vehicle pollution levels is of importance. The automotive Industry is under the effects of electrification all over the world. By 2030, electric vehicles including Battery Electric Vehicles, Plug-ins / Hybrid Vehicles are to have a share up to 50 percent of new vehicle sales globally and India will be significantly impacted across the whole automotive value chain including the manufacturers.
DRIVERS OF ELECTRIC VEHICLE ADOPTION:
EV sales are comparatively less and experience from other countries indicates those push and pull factors Proper mix could decide the speed of Indian EV penetration:
- Several countries have increased e-mobility usage by providing various incentives, along with a Supportive environment with strict carbon emission regulations
- As a large constituent of the EV vehicle cost is due its high battery price which impact both Manufacturing and sales, hence advanced technology can reduce battery cost increase mileage, Making EVs more available and lucrative to potential customers.
- Easy affordable charging infrastructure for meeting customer daily needs.
- Creating a pull among customers by providing a economical cost proposal will be essential for encouraging customers to spend in EVs.
LITERATURE REVIEW
The literature search was mainly focused on topics China found that compared to gasoline vehicles there is 37.5% less energy consumption and 35% less greenhouse gas emissions. Liu and Santos (2015)
The working of electric vehicle was compared with conventional internal combustion and hybrid electric vehicle along with its advantages, disadvantages along with future technology views. Holms et al, (2010) The activities related to transportation have emphasized the highly-efficient safe transportation with reduced emissions. Electric vehicles have been proposed to replace conventional vehicles in the future and they studied how financial incentive and socio economic aspect of consumers increase electric vehicle adoption in many countries. Many governments have started financial policies to encourage electric vehicle adoption however decision makers have to take a long term perspective to get them implemented efficiently (Sierzchulaet al 2014, X Zhang et al 2014) The hybrid cars demand in metro cities of India Analyzed. Due to fossil fuel reserves depletion, environmental harms, and global warming alternative fuel is required for sustainability. The study said that people with conventional thinking, are more concerned for environment and Indian consumers are prepared to pay additional cost for an environmental friendly car.
Pros and cons of electric cars:
Electric vehicles offer many benefits, but they also have some disadvantages when compared to conventional gasoline-powered cars. One of the biggest questions prospective electric car buyers face is whether to purchase an all-electric vehicle (AEV), plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV), or a gasoline-powered car.
Top pros and cons of electric cars
Electric cars are growing in popularity every day. Just like conventional cars, there are certain benefits and drawbacks of using an electric car. Here are the top few to keep in mind:
| Pros of electric cars | Cons of electric cars |
| Electric cars are energy efficient | Electric cars can’t travel as far |
| Electric cars reduce emissions | “Fueling” takes longer |
| Electric cars require lower maintenance | Electric cars are sometimes more expensive |
On the pros side, electric cars are energy efficient, are net good for the environment, and don’t require as much maintenance as traditional gas-powered cars. On the cons side, you can’t travel as far between refueling, the actual refueling process takes longer than filling a car at a gas pump, and upfront costs are sometimes a barrier.
Pros and cons of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles
Many of the same benefits of all-electric cars also apply to plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. PHEVs are great vehicles for reducing emissions and reducing fuel usage. For short trips, your PHEV may not need to switch away from its all electric motor, in which case the car emits no tailpipe emissions. Even more, PHEVs use 30 to 60 percent less fuel than conventional gas powered cars. If the electricity is sourced from renewable resources, the amount of greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced even further.
PHEVs also make great vehicles for those who cannot commit to a fully electric vehicle because of driving and recharging needs. While AEVs are limited to their battery range, the fuel backup in a plug-in hybrid means that when the battery runs out the vehicle can continue to run and even recharge the battery by using fuel. PHEVs usually have a better fuel economy than their conventional gas powered counterparts.
Much like an AEV, one of the hurdles to owning a PHEV is the amount of time it takes to recharge the battery. While PHEV batteries are smaller on average than those found in AEVs, a Level 1 charger may still take several hours to charge. A Level 2 charger can take one to four hours. In addition, while fast charging does exist most PHEVs do not have this charging capability.
Another factor to consider is cost: like AEVs, PHEVs have a higher price tag than many gas powered vehicles. There are fuel savings, tax credits, and state incentives that can help offset these costs, and as the production of PHEVs expands, these prices may come down.
RESEARCH OBJECTIVES:
The objectives of the study are stated as follows.
- To Understand The Indian Automobile Production And Sales Trends
- To Understand The Emission Standards For India
- To Understand The Type Of Vehicle Standards In Various Countries
- To Investigate Structure Of Vehicle Standard By Light-Duty Vehicle Energy Consumption
- To Investigate Global Warming Emission Reduction Under Light Duty Vehicle Standards.
- To Investigate the Electric Vehicle Trends & Sales Goals country wise.
- To Understand the Indian Electric Vehicle Market Challenges and Opportunities
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research Methodology: The purpose of the methodology is to describe the process involved in research work. The research design for this study was descriptive design, Sources of data collection: – Secondary data was used for the study. Secondary Source: – Secondary data was accumulated through various sources like internet Websites and magazines, journal articles, etc. The expected contribution from the study:-The study is expected to present information about the Indian automobile market and the changes & challenges in the electric vehicle industry.
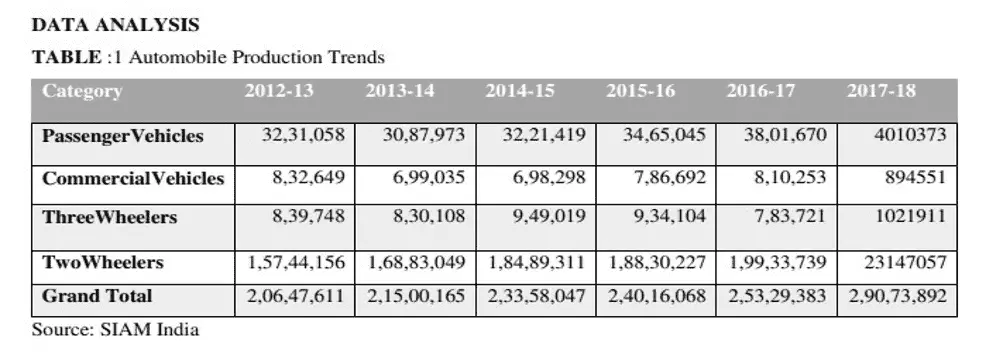
Discussion: The India automobile market by vehicle type is separated into two-wheeler, commercial passenger cars, and others. The most preferential vehicles are passenger cars and two wheelers, and this segment will dominate in the electric vehicle market. Indian passenger cars division is predicted to seize three-fourths of the electric vehicles market share by 2025.
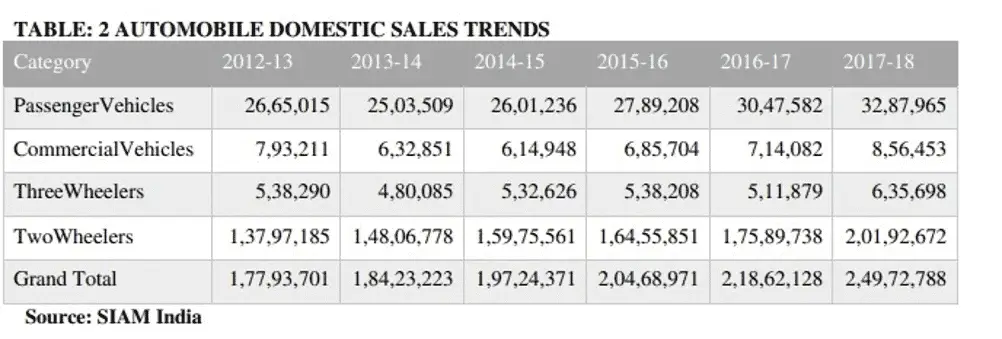
Discussion: The future of electric vehicle transportation is developing with changes in consumer preferences and environmental sustainability to reshape the automotive industry. An automobile is a connected device intelligence for driving functions. Changing consumer preferences and technological disruptions are transforming the facet of mobility, urging automakers to rethink plan and with increased strategies.
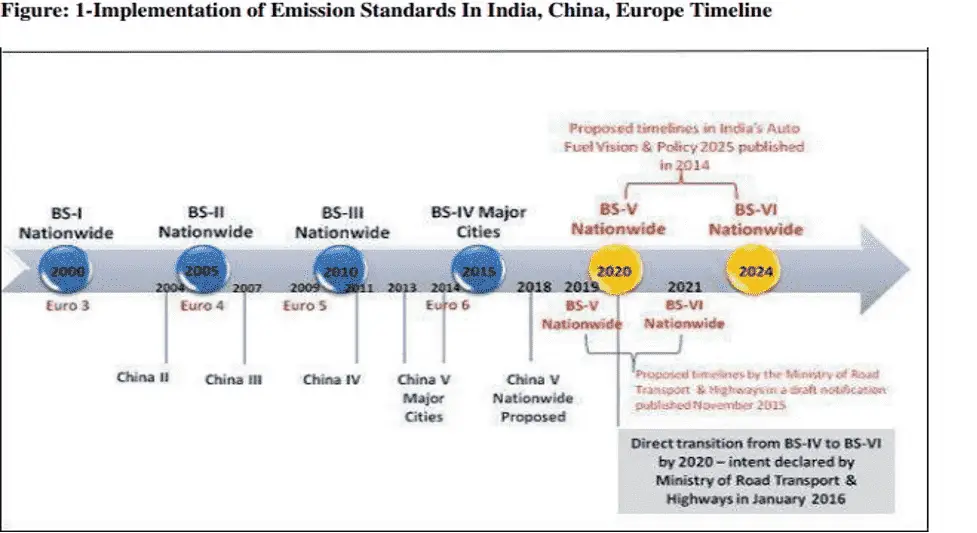
Discussion:
In the World Bank environmental quality survey among 172 countries, India is at155, and in air pollution it is last. The Auto Fuel & Vision Policy 2025 of India, published in 2014, proposed rolling out nationwide BS-IV, BS-V, and BS-VI (based on Euro 4, Euro 5, and Euro 6) over a staged timeline by 2017, 2020, and 2024 respectively. However, as air pollution worsens, India has been pondering between adopting BS-VI and directly transitioning to BS-VI up gradation. In November 2015 The Indian government published a notification for execution of BS-V and BS-VI by 2019 and 2021 . It is predicted that the proposed upgrades can lessen PM and NOx vehicular emissions to the range of 40 percent – 80 percent on the set timeline. Sector specialists are requesting direct transitioning to BS-VI as performance of Euro 5 for NOx control in diesel vehicles has been substandard, and Euro 6 rise above this as a better performing standard.
INDIA ELECTRIC VEHICLE MARKET:
DRIVERS In India, despite numerous challenges and difficulties, electric vehicles are gradually increasing due to 1. Electric vehicle incentives under FAME India launched by central government to achieve a production of ~ 7 Million EV’s by 2020 and NEMMP 2020 target 2. Low maintenance operations costs for electric vehicles 3. Rising crude oil cost as 80% of crude oil requirement is imported Although, in India’s EV market is at a very nascent stage and , currently the challenges seem to outweigh the opportunities in India but the right steps from government by support dynamics for EVs in India at various levels is anticipated to transform it as opportunities are in large numbers in future
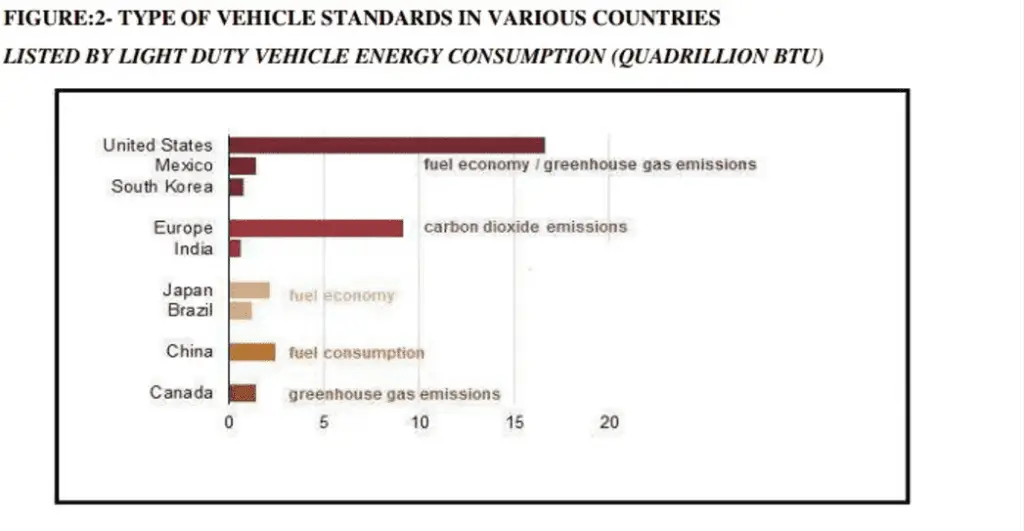
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Discussion: Light-duty vehicles of nine countries global fuel consumption is 75% and has adopted standards regarding fuel economy and greenhouse gas emissions (GHG). The Light duty vehicle emissions policy differs in the various countries and vehicle standards an important components for liquid fuels demand estimation. Emissions reductions. To decrease emission EU, India focuses on CO2 emission standard, while Canada has limitations relating to all GHGs. Fuel economy. Brazil, Japan standards is to raise fuel economy and reach a specific miles-per-gallon rating. Fuel consumption. China standard is to reduce fuel consumption and attain gallons per mile and it is inversely equal to the fuel economy standard. Light-duty vehicles must reduce the gallons consumed per mile for increasing fuel economy Combination or option. The United States, Mexico have standards of fuel saving and GHG, and manufacturers have to satisfy both. South Korea’s vehicle manufacturers have the alternative to choose either fuel economy or GHG standard.
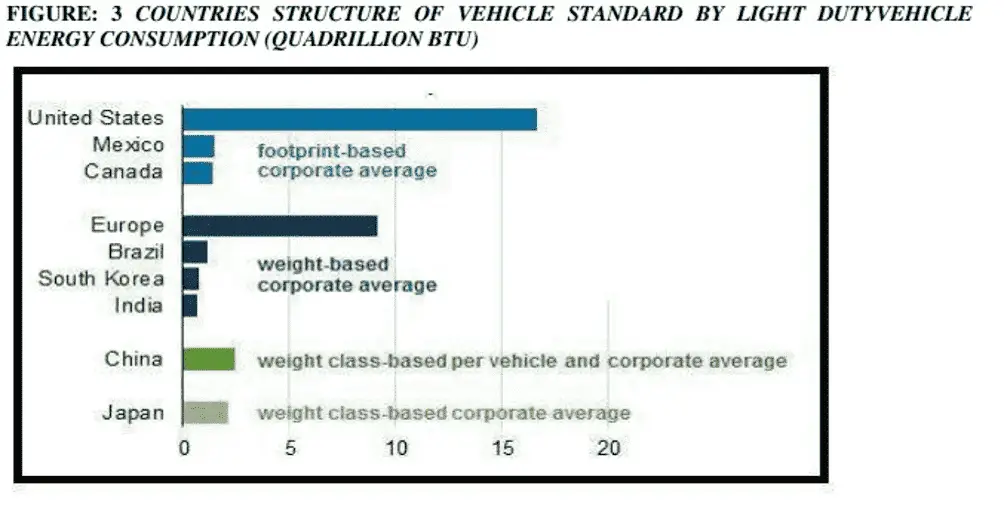
Discussion: The vehicle standards by light duty vehicle energy consumption structure also differ. Footprint- corporate average based. In US , Mexico the standard has GHG release , fuelsaving targets and in Canada it is on vehicle footprint, (wheelbase * by average track width). The general GHG emission targets of the manufacturer are obtained by averaging footprint target produced. Weight- corporate average based. Brazil, EU, India, and South Korea have the standards of weight-based corporate average. Weight-class corporate per vehicle average based. China has this standard and is more severe than the weight-based corporate average standard. Vehicle manufacturers in China must meet standard of fuel consumption for every weight class level along with overall corporate average fuel consumption standard. Weight-class corporate average based. Japan has a corporate average standard based on weight class and has to fulfill the standard for weight class relatively to overall manufacture standard. Light-duty vehicle manufacturers have to fulfill different standards in diverse countries, and these standard differences likely to persist because of variations in policy goals and consumer preferences. Fuel economy and emissions standards of vehicles have to be fulfilled if the company has to sell its products in that country, e.g. U.S manufactured vehicles have to meet European standards for vehicles sold in Europe.
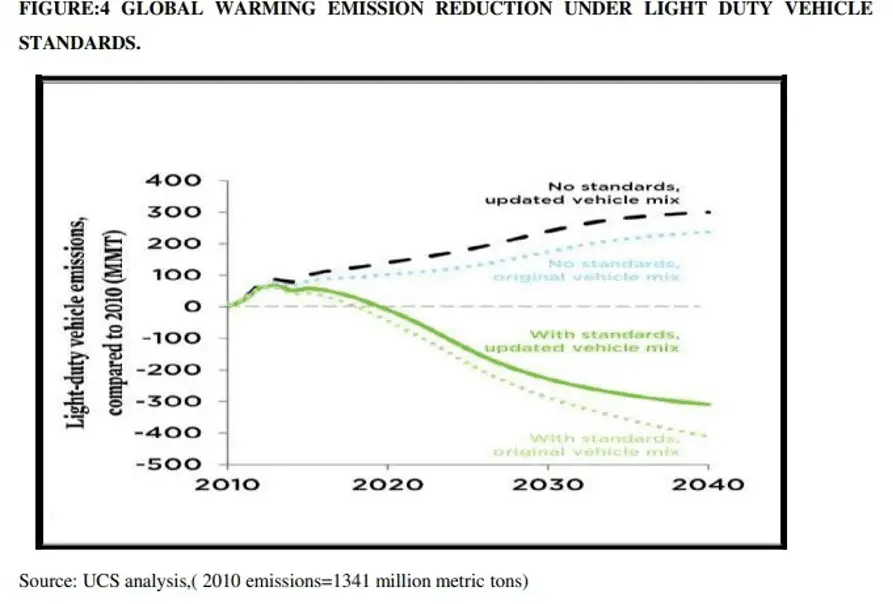
Discussion: Light-duty vehicles (LDVs) Global greenhouse gas and fuel economy emissionstandards have improved significantly in the last decade. Only four governments had introduced mandatory GHG emission/fuel economy standards ten years ago, ( Japan , China ,South Korea, and the United States). At present, 10 more governments (Brazil, Canada, India, Japan, Mexico, China, the European Union, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, and the United States) have established GHG emission standards. Nearly 80% of new LDVs sold globally have some kind of GHG emission fuel economy standards and the above said countries are among the top 15 vehicle markets worldwide.
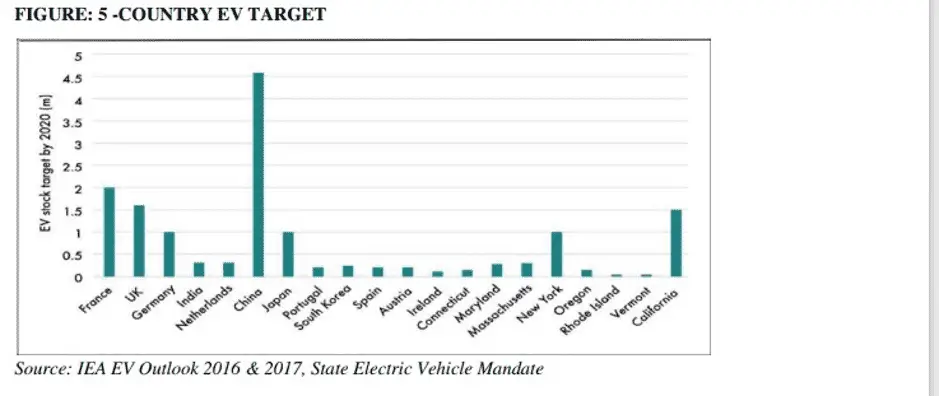
Discussion: This region expected projection is 15.2 million EVs, by 2020. These targets provide policy assurance from major national governments to enact policies regarding the speed of shift to EVs which will help to provide OEMs to invest and develop new EV models and build the future business models. Indian policymakers should also decide regarding the phase-out of ICEs.
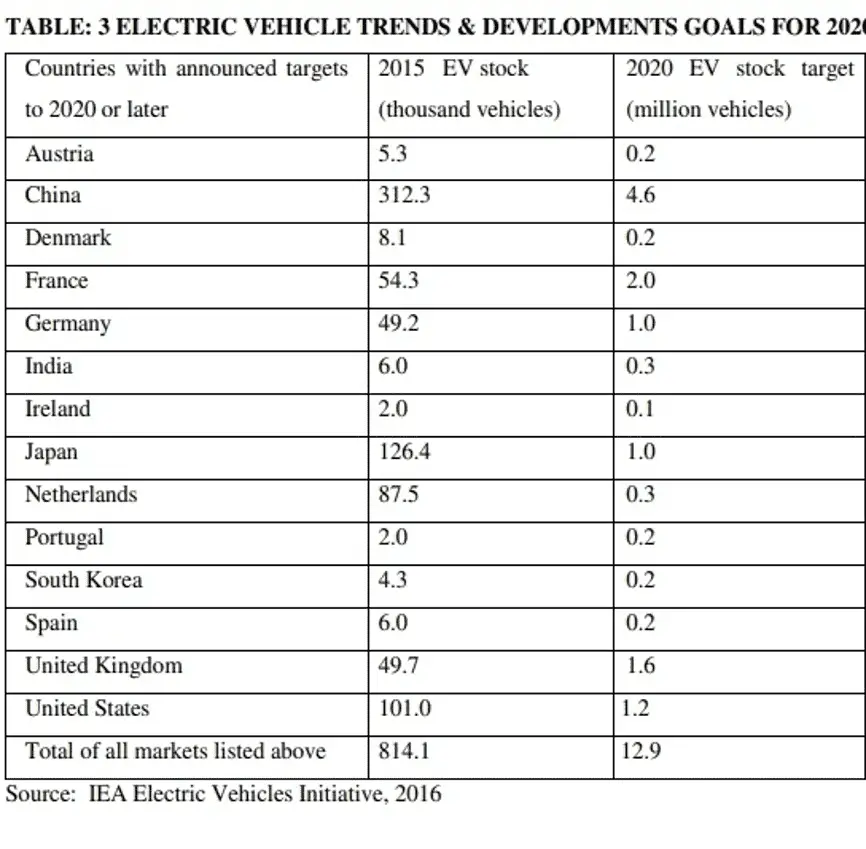
Discussion:
The Paris declaration has asked for consumption of 100 million electric cars worldwide by 2030 to control climate change (UNFCCC, 2015). Electric Vehicles (EVs) are a technology for drastically reducing the road transport CO2 emissions worldwide. However, EVs are still an evolving technology and there exist many doubts relating to battery, energy capacity (relative to vehicle range), charging speed, robustness, its availability and environmental impacts of materials used. Most EV manufacturers are serving European, North American and East Asian markets and are also manufacturing from these regions. However, there is a significant share of Chinese and Indian car manufacturers, and one South African company. Chinese, South American, South Asian (esp. India) and Middle East markets have an important role for EV penetration and increased usage, whereas African, Central American and Central Asian markets usage is predicted less.
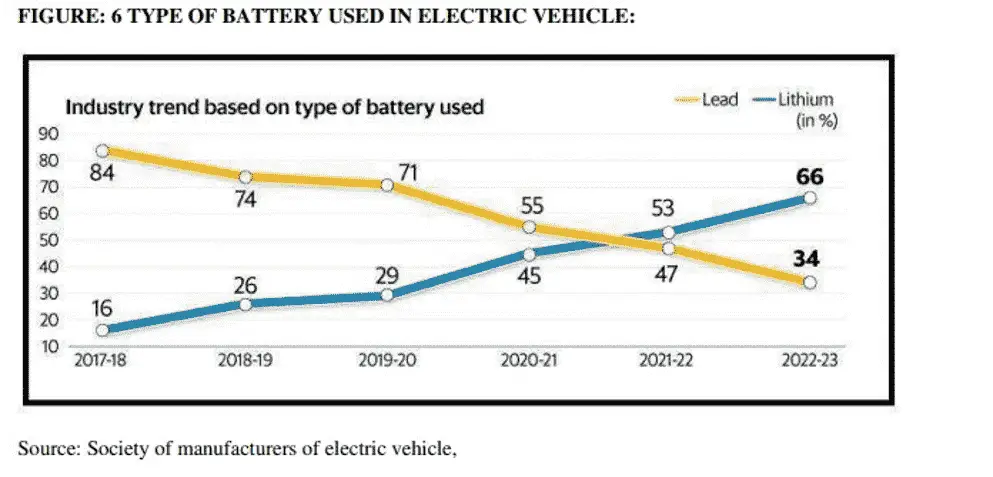
Discussion: Improvement in energy source increases the electric vehicle value due to more drive per charge. important factors behind low electric vehicle penetration rate is because Consumers are concerned over the inadequate charging facilities availability and time-consuming charging periods. Batteries used in electric vehicles are Lithium ion batteries, Lead Acid batteries ,Nickel Hydride batteries ,Zebra batteries,. The Leadacid and Lithium ion batteries are more used in the automotive sectors. (Del Duce et al. 2013 ; Roesky et al. 2015, Tran-Quoc et al 2017, Moghaddam et al 2018)
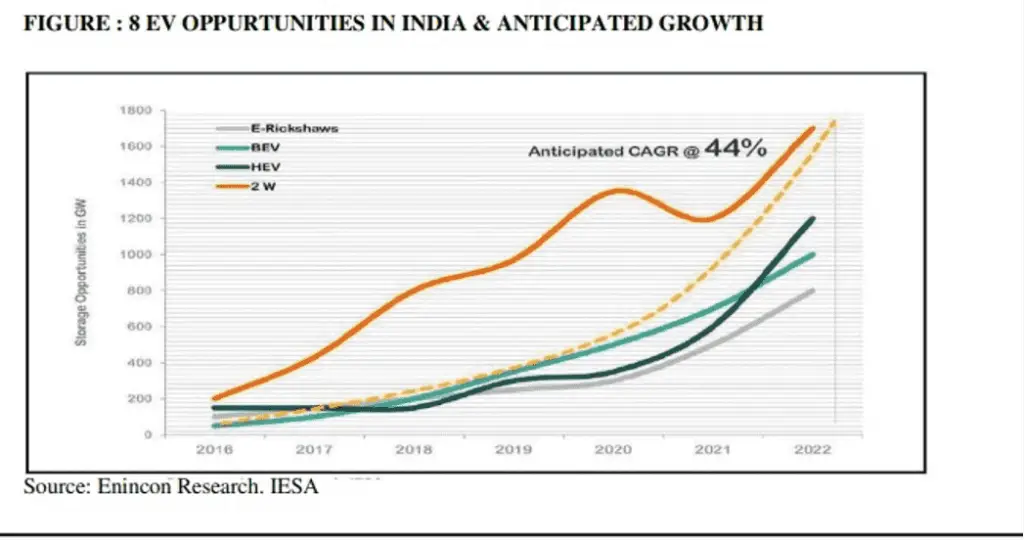
INDIA ELECTRIC VEHICLE MARKET:
EV vehicles present an important prospect for smart cities to harness cleaner fuel technologies in urban mobility. According to the Persistence Market Research report India’s electric vehicles market is forecasted to expand at a CAGR of 77% in value during 2017 – 2025 and forecasted are By Vehicle Type Forecast India electric vehicle market is anticipated to increase during FY 2018-FY2023 at 37% CAGR , market growth is anticipated on account of increasing government initiatives and growing consumer inclination, concerns over harmful effects of air pollution, and huge investments by various OEMs for developing more affordable premium electric vehicles and passenger cars and two wheelers are the main segments By Technology Forecast The technology comprises hybrid electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid and battery electric vehicles. In India Hybrid and battery electric vehicles is expected to dominate the market. A large market share of the battery electric vehicles about 85% in 2025 is expected to be sales of two wheelers in India. By Power Source Forecast The power sources comprise of stored and on-board electricity. The stored electricity is expected to be the most important in India electric vehicles market and is anticipated to dominate .The electric vehicle storage market in India is expected to be 4.7 GW by 2022. By Power train Forecast The Indian market for electric vehicles is segmented into series hybrid, parallel hybrid and combined hybrid. Parallel hybrid is the most preferred owing to its advantages above other power train types but this is not included in electric vehicle battery as it involves both internal combustion engine and an electric motor.
Discussion: A number of companies are manufacturing electric vehicle in Indian market Mahindra Electric Mobility Limited, Tata Motors Limited, Toyota Kirloskar Motor Pvt. Ltd., Volvo India Private Limited, BMW AG, Kinetic Green Energy & Power Solutions Ltd., Okinawa AutotechPvt. Ltd but as there are less charging stations across India it makes it difficult for EV owners and are mostly used within city limits
INDIA THE WAY AHEAD
Besides the end-user customer, other key stakeholders who play an important role in India’s transition towards EVs are government, Incentives and subsidies and automotive value chain industry. The government helps by defining the regulations relating to emission norms, fuel efficiency, strategic intent and direction, exploring incentives and subsidies, and developing a supportive ecosystem. The Indian government’s current CO2 emission target based on the Paris Climate Treaty is to continue at 113 g/km by 2021. Aligned with Corporate Average Fuel Consumption standard the fuel efficiency average target is 22 km/litre by 2035. The Indian government also has planned to reduce crude oil imports and indirect dependence on certain trade partners. The Indian government could focus on these areas: The government could also set up committees to provide guidance as and when industry stakeholders need any support to achieve their targets. As it drives EV penetration through policy and long term direction, the government could also define its level of participation in the means employed to meet the policies and targets. Incentives and subsidies: According to an OECD report, India is providing few subsidies, compared to other major markets. Various state governments and cities provide their own subsidies. The government may need to drive adoption, through schemes like recurring incentives, tax breaks, funding for infrastructure and innovation, support for technology localization and skill development. The automotive value chain industry: By changing the product mix, building the right service skill sets, improving the performance of batteries and electric vehicles and building scale, the industry can drive the EV disruption in India. The fuel and charging infrastructure companies: can innovate on business models (e.g., leasing of batteries, swapping infrastructure, deploying fast chargers), providing stable power supply and grid stability, can enable easy and rapid charging to increase EV adoption. 4. Charging stations: The charging stations are required for the increased usage of electric vehicles. The Leadacid and lithium ion batteries are used in automotive sectors The process of charging can take anywhere between 30 minutes (fast charging) up to 24 hours, depending on the specifications of the battery and the charger. at present, there are two main types of plug-in EV charging stations: AC and DC. An AC charging station supplies current to on-board charger and normally offers 8 to 24 km range per 30 minutes of charging. A DC charging station supplies current directly to the vehicle battery and is capable of providing up to 129 km of electric range for every 30 minutes charge.
FINDINGS, The automobile industry is important and plays a pivotal role in country’s economic and industrial development. Electric vehicles are a segment of growth and innovation as it facilitates improvement in various infrastructure transportation facilities along with ecological sustainability. Due to its forward and backward associations with many industrial segments it has a strong constructive multiplier result and is very important for national progress. Indian automobile sector is important for the country’s economy. Demographic Factors like increasing purchasing power, new environmental friendly vehicle launches, flourishing exports and easy finance accessibility have resulted in increased automobile sale volumes. The various infrastructure developments in road, power, and testing certification facilities, trained manpower availability, facilitating government policies. Indian automotive industry has become a favorable investment destination by global auto industry major manufacturers. At present India is the world’s second main manufacturer of two wheelers, fifth major commercial vehicle manufacturer. It is the fourth chief passenger car market in Asia and largest motor cycle manufacture hence the opportunities for electric vehicle are very large. The Indian automobile market is encouraging alternative fuels with advanced technologies including battery powered electric, hybrid vehicles, etc To boost the Indian automobile sector, the Indian government has encouraged new initiatives, incentives and policies. Modernization and Phased manufacturing programme, Auto policy 2002, National Automotive Testing and Research & Development Infrastructure Project (NATRIP) Project, Automotive Mission Plan 2006-2016.are a few.
A review of barriers and challenges of electric vehicles in India and vehicle to grid optimization
Highlights
- Vision for 100% electric vehicle by 2030 in the Indian vehicle market.
- Recent initiatives and various subsidies by the Indian government could promote battery technology.
- The Battery Electric Vehicle could reduce the carbon dioxide emission from the light-duty vehicle fleet and dependency on fossil-fueled vehicles.
- Barriers can be addressed from various prospective such as market, technical policy and infrastructure.
- Vehicle-to-Grid is an important aspect of energy security, renewable energy and giving a great impact to deal with global warming issues.
The objective of this study is
- To identify the essential methods, barriers, and challenges of using a battery-operated vehicle in a developing country like India.
- To identify the reasons why electric vehicles could not get much attention in India.
- To create awareness about the added advantages of battery-operated vehicles over conventional fossil-fueled vehicles in India.
- To study different Government initiatives taken in promoting Electric/Hybrid Vehicles.
RECOMMENDATIONS
The present study suggests following recommendations to increase EV penetration In the study it is observed that, manufacturers should provide the best and value added Services with product availability hence companies should try to tap customers by providing attractive financial incentives and offers To boost the sales, it is also recommended that the companies in association with government, banks and financial institutions should provide vehicle loans to middle class customers with low interest rate to increase usage. Today youths are very environment conscious and also decision takers in family decision making. Hence the companies should promote and advertise their vehicles in this regard, companies should give some additional discounts, incentives or special offers for college students who plan to buy an electric vehicle. In order to promote electric vehicle government and manufacturers should increase its awareness among consumers. In India, consumers are still lagging to be an electric vehicle owner; because of queries relating to charging, service stations and less awareness for this the companies can start free awareness campaigns in association with their dealers. In current scenario, petrol and diesel prices are continuously increasing due to which the customer is very much conscious towards fuel efficient environmental sustainable vehicles.
CONCLUSION AND FUTURE SCOPE
Electric vehicles are a means of worldwide sustainable transportation and its usage is increasing rapidly. The Indian government has also started to accelerate the EVs penetration. However, many hurdles should be dealt with for wider and easy adoption of EVs in India. Being a nascent player in EV transportation, the most important barriers identified include state Government Incentives and Consumer Characteristics. All Consumers are enthusiastic to reduce pollution reduction but the various costs is high (purchasing cost, minimum operating cost, vehicle cost, payback period, operating cost, maintenance cost and electricity cost, resale) .hence, a cost-effective vehicle is required for the Indian markets. Participants in industry meets arranged by the Center for Future Mobility in Delhi and Chennai mentioned high acquisition cost as the top restraint to EV penetration. The charging infrastructure, the electric vehicle performance safety concerns and new user anxiety affect EV adoption strongly Thus, in the perception of researcher, penetration pricing strategy is more suitable for Indian automobile sector which has a lot of middle class consumers . This indicates that Indian automobile policymakers must act on it to take advantage of the growth in this sector as a lot of national fuel can be conserved by using these electric vehicles along with reduced emissions.
REFERENCES
- ENERGY SAGE – SMARTER ENERGY DECISION – PROS AND CONS
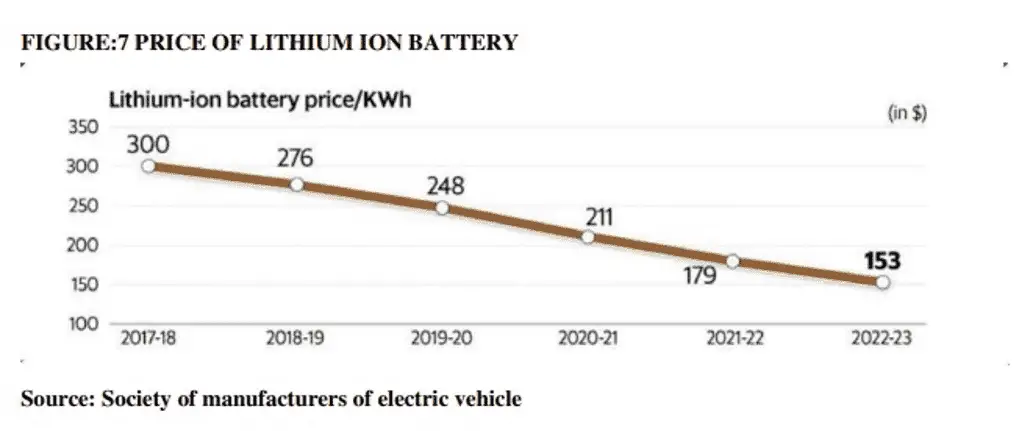
- Berckmans, G.; Messagie, M.; Smekens, J.; Omar, N.; Vanhaverbeke, L.; Mierlo, J. Van. Cost Projection of State of the Art Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles up to 2030. Energies 2017,10
- Das, Debabrata& Srinivasan, R & S. Dhankar, Raj. (2011). Demand for hybrid cars in Indian metro cities. Int. J. of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles. 3. 1 – 19. 10.1504/IJEHV.2011.040470
- Del Duce A, Egede P, Öhlschläger G, Dettmer T, Althaus H, Bütler T, Szczechowicz E (2013) Guidelines for the LCA of electric vehicles. eLCAr Enincon research, IESA. Refer https://enincon.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Flyer-EV-Market-in-India_enincon.pd
- US Energy Information Administration 2015 Annual Energy Outlook (http://eia.gov/forecasts/aeo/er/index.cfm)
- IEA. Technology Roadmap, Electric and Plug-in Hybrid. Electric Vehicles (EV/PHEV); International Energy Agency:Paris, France, 2009.
- IEA, 2013. Global EV Outlook – Understanding the Electric Vehicle Landscape to 2020. International Energy Agency, Electric Vehicles Initiative and Clean Energy Ministerial.
- IEA, 2015. Energy and Climate Change: World Energy Outlook Special Report. International Energy Agency.
- IEA, 2016. Global EV Outlook 2016. Beyond one million electric cars. International Energy Agency, Electric Vehicles Initiative and Clean Energy Ministerial.
- India Electric Vehicles Market : TOC by Persistence Market Research, Dec-2017.
- Jian Liu & Georgina Santos (2015) Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles’ Potential for Urban Transport in China: The Role of Energy Sources and Utility Factors, International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 9:2, 145-157,
Credit: This final year project on “Present And Future Trend Of Electric Vehicles” was completed by Manjeet Kumar Gupta Under the Supervision of Dr. NEHA DUBEY from Galgotias University Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh.


Leave a Reply