A Pitot tube is a measuring instrument used to determine the velocity of the fluid in a pipe or a channel. It also works on Bernoulli’s principle as the Orifice meter and Venturimeter. Let us discuss more details on the Pitot tube, how it works and how we can find the Flow Velocity Equation of a fluid flowing through a pipe with help of the Pitot Tube.

Pitot-tube
In fluid dynamics, the Pitot tube is the flow velocity measuring instrument. Generally, this instrument is mostly used in water boats, and aircraft to determine their speed. This Pitot tube also has many industrial applications.
Construction and Working Principle of Pitot Tube
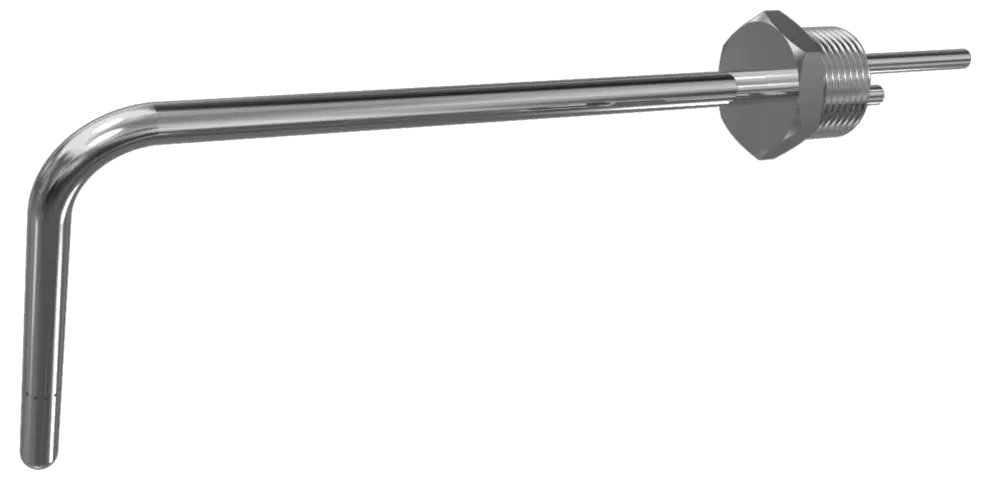

- Pitot Tube consists of a tube, bent at right angles as shown in the above figure.
- The lower end (the opening end), which is bent through 90° is directed in the upstream direction of the fluid flow.
- Inside the Pitot Tube, there will be fluid inside the vertical portion of the pitot tube.
- As the fluid flow through the entrance of the Pitot Tube, the liquid rises up due to the conversion of the kinetic energy into pressure energy.
- The velocity of the fluid can be determined by measuring the level of the fluid raise on the vertical portion of the tube.

- In the above picture, the Pitot tube is installed on an Aircraft to determine the speed of the aircraft from the airflow velocity calculated from the pitot tube’s vertical fluid level.
Flow Velocity Equation in Pitot Tube
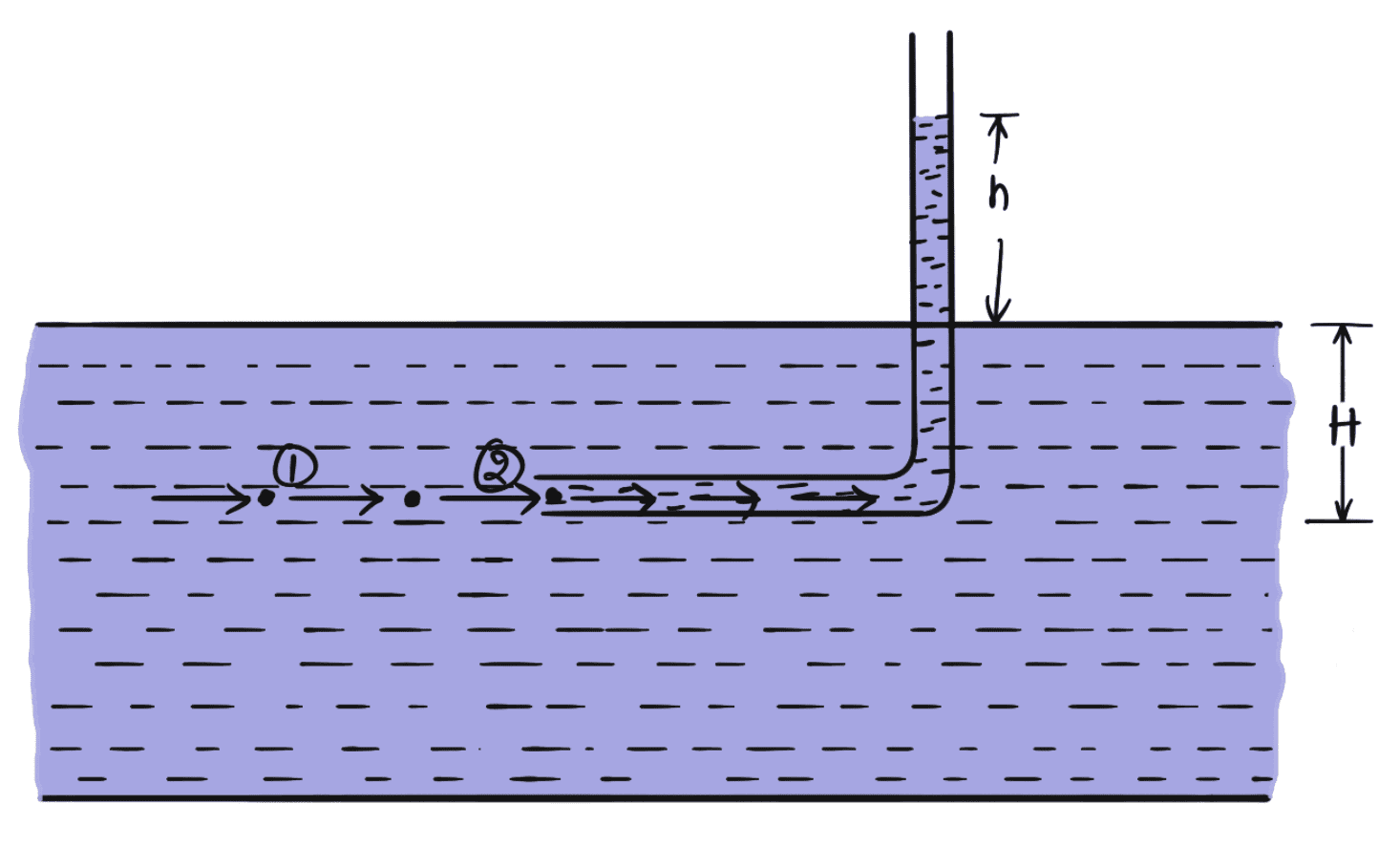
Let us Consider two points (1) and (2) at the same level in such a way that point (2) is just like the inlet of the pitot tube and point (1) is far away from the tube.
Now
p1 = Intensity of pressure at point (1)
v1 = Velocity of flow at (1)
p2 = Pressure at point (2)
v2 = Velocity at point (2) which is zero
H = Depth of tube in the liquid
h = Rise of liquid in the tube above the free surface
Applying Bernoulli’s equation at points (1) and (2), we get
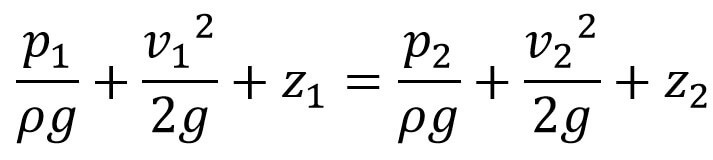
Byt z1 =z2 as points (1) and (2) are on the same line and v2 =0


Let us substitute these values, we get,
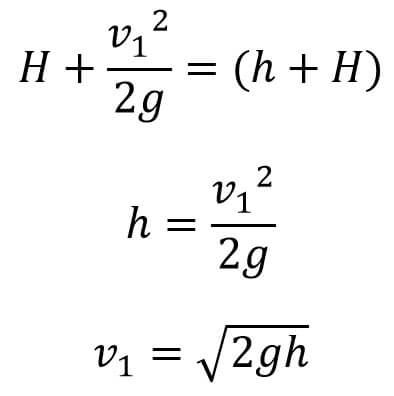
This is the Theoretical velocity. The Actual Velocity has given by
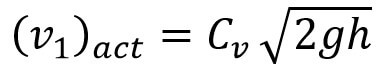
Where Cv =Coefficient of Pitot Tube
Velocity at any point of the fluid flow that can be determined by the pitot tube is
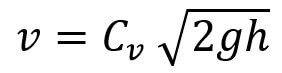
This is the Flow Velocity Equation to calculate velocity measured by the Pitot Tube.
Velocity at any point Velocity of Flow in a pipe by Pitot Tube
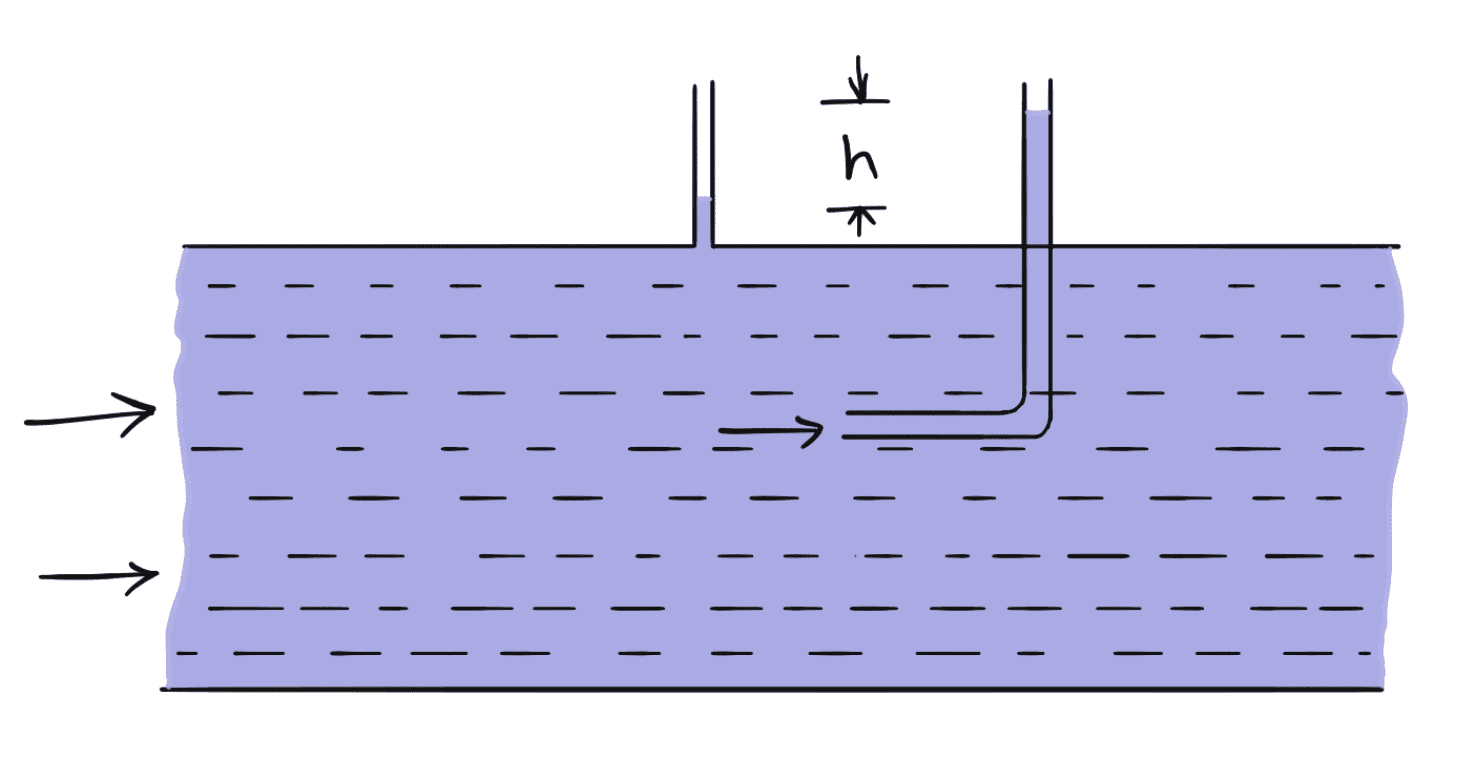
For finding the velocity at any point in a pipe by pitot tube, the following arrangements of the pitot tubes can be adopted.
- Pitot-tube along with a vertical piezometer tube as shown in the following figure
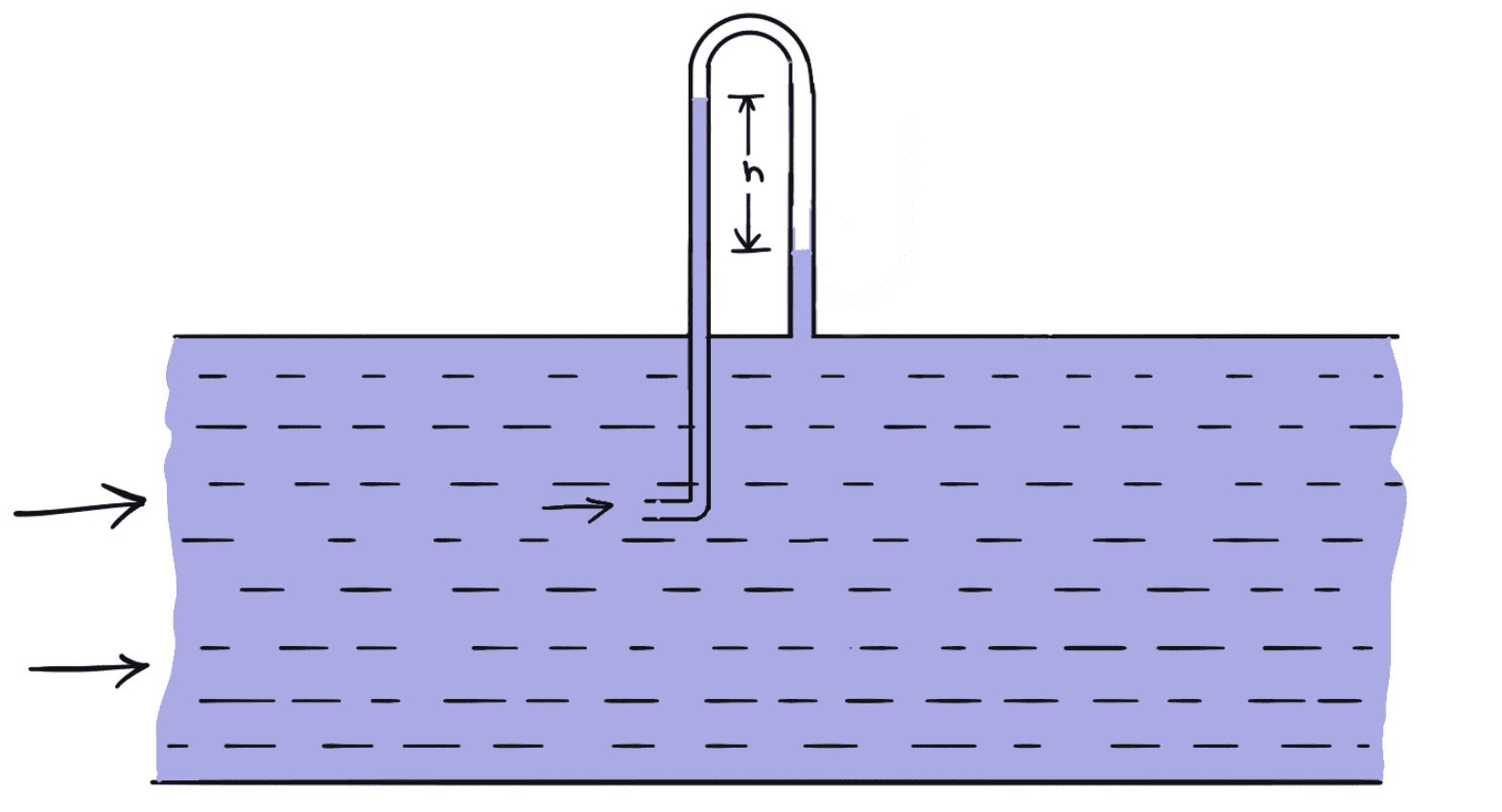
- Pitot-tube connected With piezometer as shown in the following figure.
- Pitot-tube and vertical piezometer tube connected with a differential V-tube manometer as shown in the following figure.
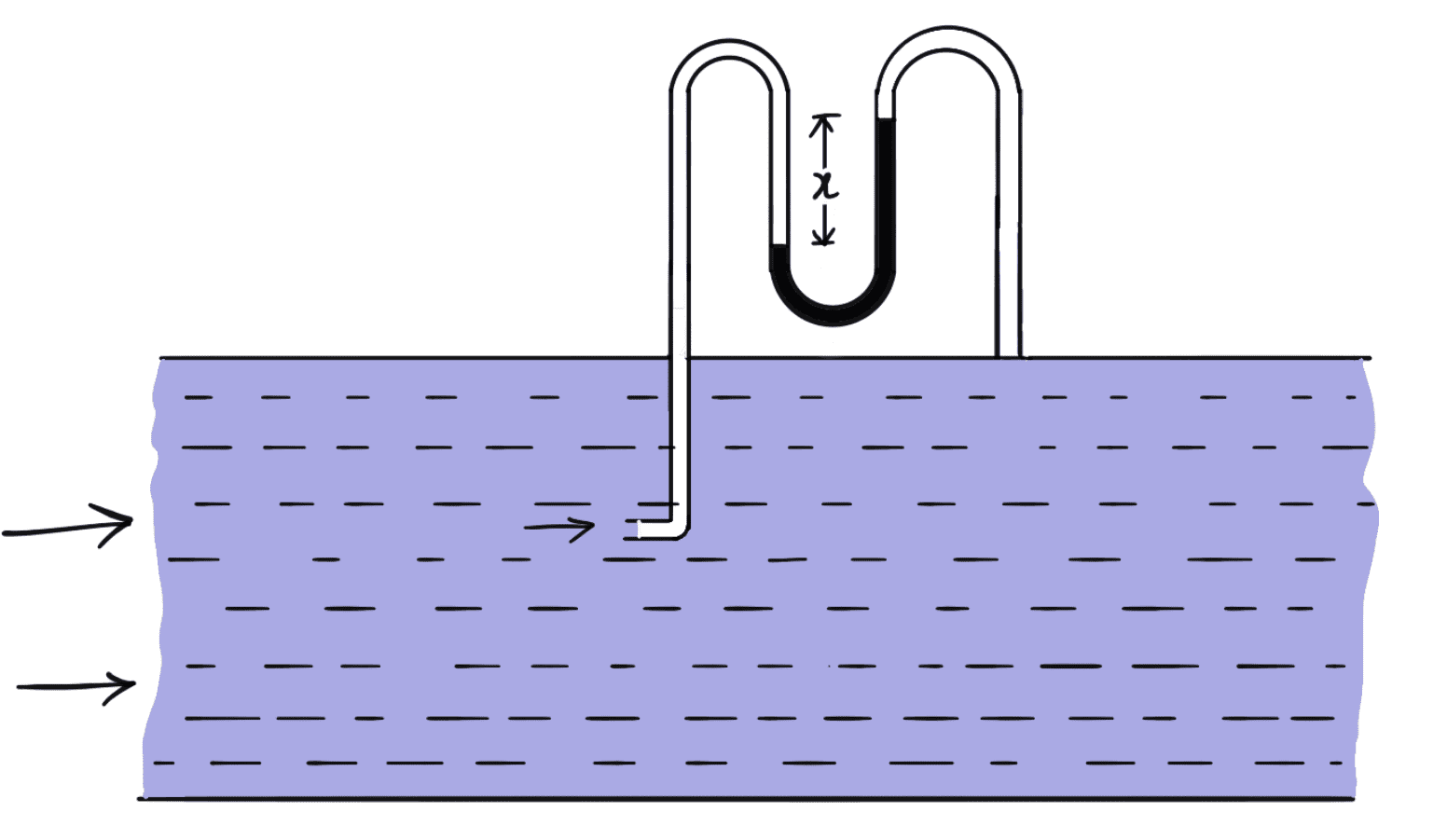
- A pitot-static tube consists of two circular concentric tubes one inside the other with some annular space in between as shown in the following figure
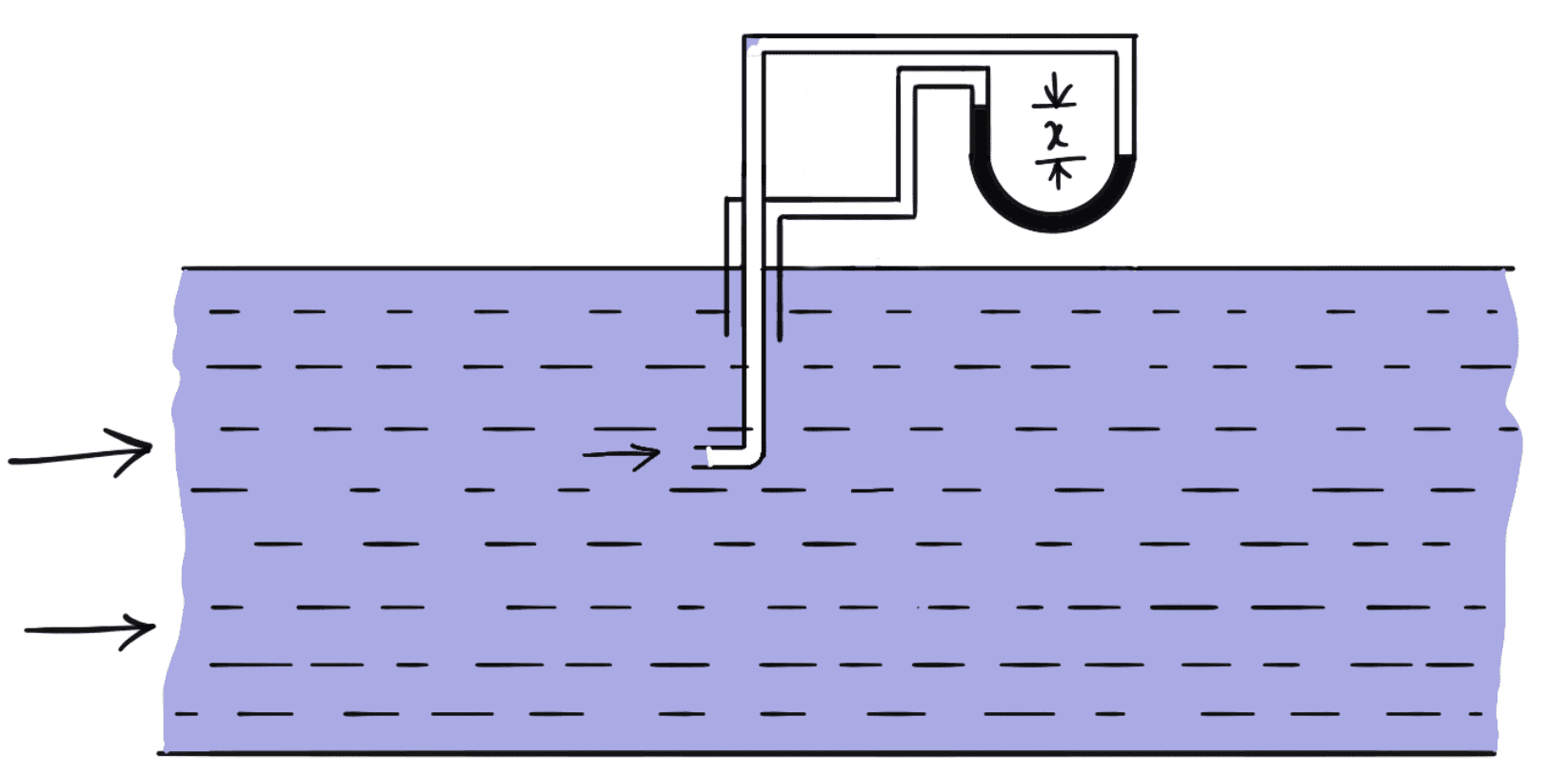
The outlet of these two tubes is connected to the differential manometer where the difference of pressure head ‘h’ is measured by knowing the difference of the manometer liquid ‘x’ then,
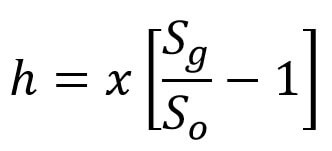
Advantages of Pitot Tube
- Pitot Tube is portable and does not contain any moving parts.
- Pitot Tube is economical.
- Permanent pressure loss is low.
- Pitot tube can be easily installed on an existing system as you can see it is installed on an Aircraft Wing.
Disadvantages of Pitot Tube
- Foreign materials in a fluid can easily obstruct the pitot tube and disrupt normal reading.
- Measuring the velocity of fluid with Pitot Tube is Less accurate compared to other instruments.
- Pitot Tube has very Low range for measuring Velocity.
Applications of Pitot Tube
- The pitot tube is used in utility streams.
- It is used in the air duct and pipe system.
- It is used in aircraft to measure airflow velocity.
- Pitot Tube is used for mapping flow profiles in a channel or duct.
This is all about the Pitot tube. Let us know what you think about this article in the comment section below.

Leave a Reply