What is a Rivet? Well, A Rivet is a permanent fastening element mostly used for fastening light metals of plates in Boiler shells, structural works, Shipbuilding, and bridges. In this article, we are going to discuss the methods of Riveting joints and what are the materials that can be used for the Rivets.

In a permanent joint, Rivet is the fastening element. So let us have a Look at a Rivet first.
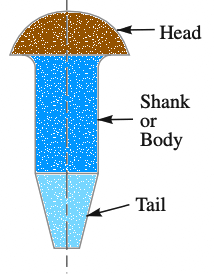
In a Rivet, the cylindrical portion of the rivet is called the body or shank, and the lower portion of the body is called the tail and the upper portion of the body is the head as shown and represented above.
Methods of Riveting
The main function of rivets in a joint is to make a connection that has strength and tightness.
- The Strength is necessary to prevent failure of the joint.
- The Tightness is necessary in order to contribute to strength and to prevent leakage as in a boiler or in a ship hull.
Following is the schematic diagram of two plates joining by a revit.
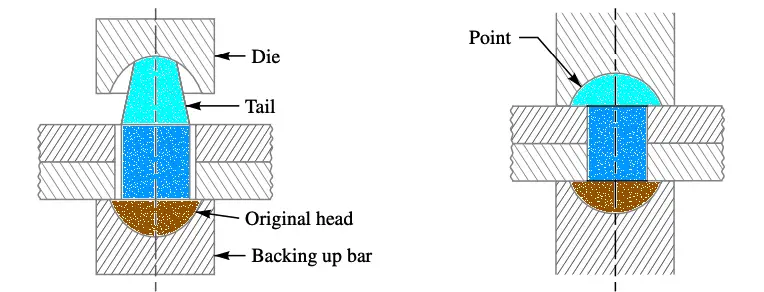
- When two plates are to be fastened together by a rivet, the holes in the plates are punched and reamed or drilled.
- Punching is the cheapest method and is used for relatively thin plates and in structural work.
- Since punching injures the material around the hole, therefore drilling is used in most pressure-vessel work.
- In structural and pressure vessel riveting, the diameter of the rivet hole is usually 1.5mm larger than the nominal diameter of the rivet. YOu can observe the clearance between the rivet body and the holes in the plates as in the above schemtatic diagram(left).
- To make the holes in the plates, they can be drilled together and then separated to remove any burrs or chips so as to have a tight flush joint between the plates.
- A cold rivet or a red hot rivet is introduced into the plates and the point (i.e. the tail) is then formed as shown in the above schematic diagram(right).
- When a cold rivet is used, the process is known as cold riveting and when a hot rivet is used, the process is known as hot riveting.
- The cold riveting process is used for structural joints such as the bridges ans metal structures to attain more strength. Cold reviting is used for steel rivets upto 12mm diameter.
- Where as the hot riveting is used to make leak proof joints by for boiler shells, boat hulls and ship buidling to attain more tightness. Hot Riveting is used for the rivets greater then 12mm diamter.
- When the Rivet body/shank is long, then only the tail is heated and Riveted. Whole rivet is not required to be heated.
- The riveting can be done by hand or by a riveting machine.
- In hand riveting, the original rivet head is backed up by a hammer or heavy bar and then the die or set, as shown in above left figure, is placed against the end to be headed and the blows are applied by a hammer.
- This causes the shank to expand thus filling the hole and the tail is converted into a point as shown in above figure (right).
- As the rivet cools, it tends to contract. The lateral contraction will be slight, but there will be a longitudinal tension introduced in the rivet which holds the plates firmly together.
- Where as in machine riveting, the die is a part of the hammer which is operated by air, hydraulic or steam pressure.
This is how the Riveting is done. Let us understand what materials can be used for the Rivets.
Materials used for Rivets
The material of the rivets must be tough and ductile. They are usually made of
- Steel (low carbon steel or nickel steel),
- Brass,
- Aluminium
- Copper
When strength and a fluid-tight joint is the main consideration, then the steel rivets are used.
Indian Standard for Rivets materials specification
The rivets for general purposes shall be manufactured from steel conforming to the following Indian Standards :
- IS : 1148–1982 (Reaffirmed 1992) – Specification for hot rolled rivet bars (up to 40 mm diameter) for structural purposes.
- IS : 1149–1982 (Reaffirmed 1992) – Specification for high tensile steel rivet bars for structural purposes.
- IS : 1990 – 1973 (Reaffirmed 1992) – Specification for steel rivets and stay bars for boilers. (The rivets for boiler work must be acc. this standard)
- IS : 2100 – 1970 (Reaffirmed 1992) – Specification for steel billets, bars and sections for boilers. (The steel for boiler construction should conform acc. to this standard)
These are the materials and the standards used for the Rivets.
But what makes a good Rivett Joint? What are the essential qualities of a Rivet?
Qualities of Rivet
- According to Indian standard, IS: 2998 – 1982 (Reaffirmed 1992), the material of a rivet must have a tensile strength not less than 40 N/mm2 and elongation, not less than 26%.
- The material must be of such quality that when in cold condition, the shank shall be bent on itself through 180° without cracking and after being heated to 650°C and quenched, it must pass the same test.
- The rivet when hot must flatten without cracking to a diameter 2.5 times the diameter of shank.
How Rivets are made?
Cold heading and hot forging are the two manufacturing methods for making Rivets according to Indian standard specifications.
- If rivets are made by the cold heading process, they shall subsequently be adequately heat-treated so that the stresses set up in the cold heading process are eliminated.
- If they are made by the hot forging process, care shall be taken to see that the finished rivets cool gradually.
Conclusion
As we have discussed above there are two ways of Riveting Cold Riveting and Hot Riveting. Also, the Riveting can be done by hand or with a machine based on the above specification. And how a revit can be manufactured and what makes a good Rivet joint. Let us know what do you think about this article in the comment section below.

I feel so fortunate to have come across this post. It’s like striking gold in terms of valuable information. Thank you!