The pulleys are used to transmit power from one shaft to another by means of flat belts, V-belts, or ropes. Since the velocity ratio is the inverse ratio of the diameters of driving and driven pulleys, the pulley diameters should be carefully selected in order to have the desired velocity ratio. Let us discuss Different Types of Pulleys for Flat Belts for your application.
The pulleys must be in perfect alignment in order to allow the belt to travel in a line normal to the pulley faces.
The pulleys may be cast iron, cast steel, pressed steel, wood, and paper. The cast materials should have good friction and wear characteristics. The pulleys made of pressed steel are lighter than cast pulleys, but in many cases, they have lower friction and may produce excessive wear.
Types of Pulleys for Flat Belts
Following are the various types of pulleys for flat belts:
- Cast iron pulleys
- Steel pulleys
- Wooden pulleys
- Paper pulleys
- Fast and loose pulleys
Cast iron pulleys
The pulleys are generally made of *cast iron, because of their low cost. The rim is held in place by a web from the central boss or by arms or spokes. The arms may be straight or curved as shown in the following (a) and (b) and the cross-section is usually elliptical.
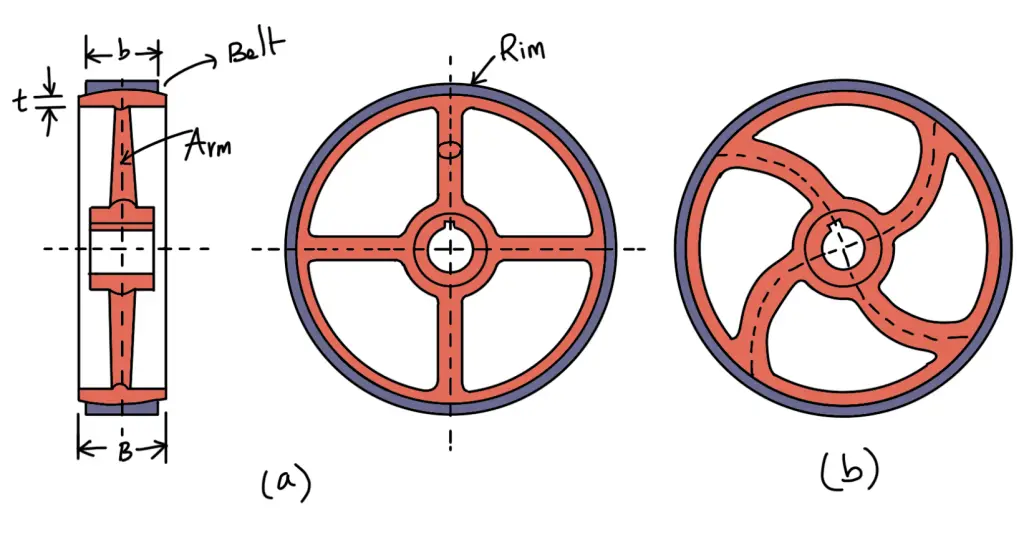
When a cast pulley contracts in the mold, the arms are in a state of stress and are very liable to break. The curved arms tend to yield rather than to break. The arms are near the hub.
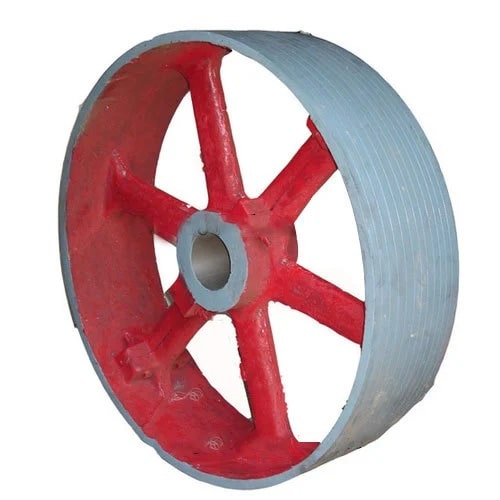

The cast iron pulleys are generally made with rounded rims. This slight convexity is known as crowning. The crowning tends to keep the belt in the center on a pulley rim while in motion. The crowning may be 9 mm for 300 mm width of the pulley face.
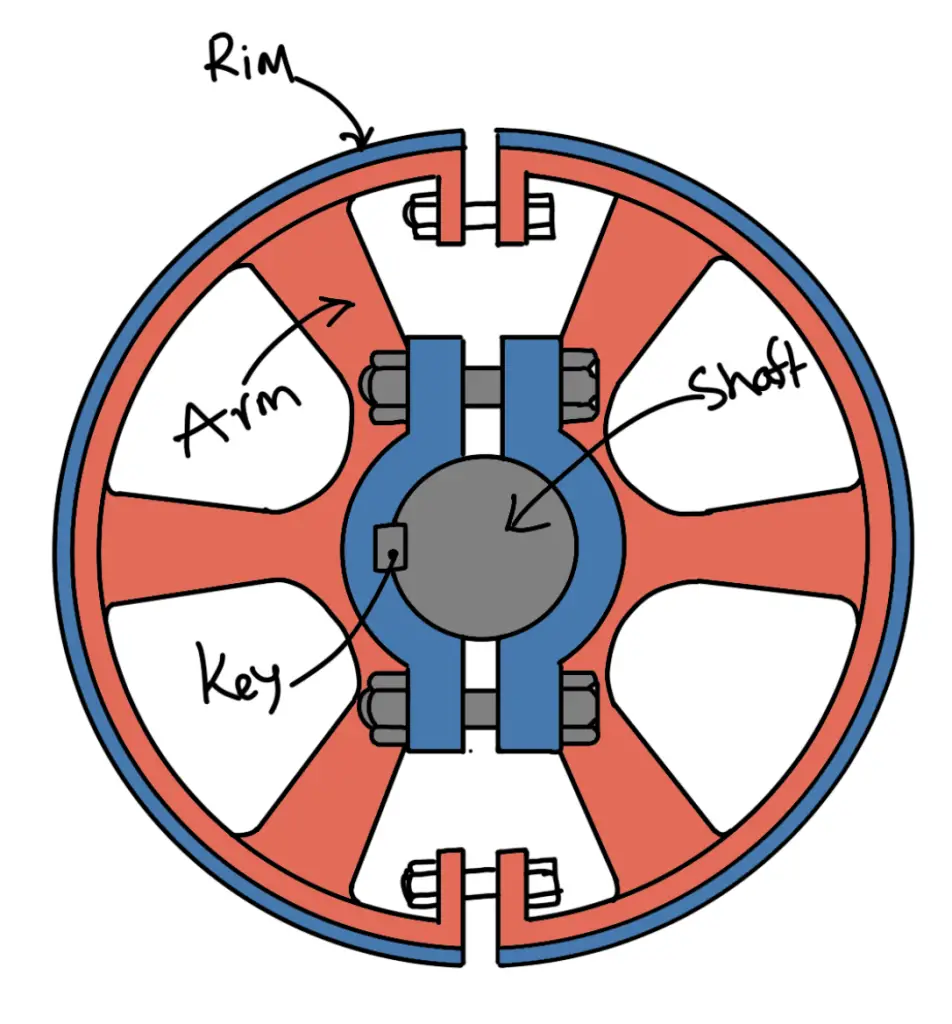
The cast iron pulleys may be solid as shown in the above figure or split type as shown in the following figure. When it is necessary to mount a pulley on a shaft that already carries pulleys etc. or have its ends swelled, it is easier to use a split pulley. There is a clearance between the faces and the two halves are readily tightened upon the shafts by the bolts as shown in the following figure. A sunk key is used for heavy drives.
Steel Pulleys
Steel pulleys are made from pressed steel sheets and have great strength and durability. These pulleys are lighter in weight (about 40 to 60% less) than cast iron pulleys of the same capacity and are designed to run at high speeds. They present a coefficient of friction with leather belting which is at least equal to that obtained by cast iron pulleys.
Steel pulleys are generally made in two halves which are bolted together. The clamping action of the hub holds the pulley to its shaft, thus no key is required except for most severe service. Steel pulleys are generally equipped with interchangeable bushings to permit their use with shafts of different sizes. The following table shows the number of spokes and their sizes according to Indian Standards, IS 1691 – 1980 (Reaffirmed 1990).
| Diameter of pulley (mm) | No. of spokes | Diameter of spokes (mm) |
| 280 – 500 | 6 | 19 |
| 560-710 | 8 | 19 |
| 800 – 1000 | 10 | 22 |
| 1120 | 12 | 22 |
| 1250 | 14 | 22 |
| 1400 | 16 | 22 |
| 1600 | 18 | 22 |
| 1800 | 18 | 22 |
Other proportions for the steel pulleys are :
Length of hub = Width of face / 2
The length of the hub should not be less than 100 mm for 19 mm diameter spokes and 138 mm for 22 mm diameter spokes.
Thickness of rim = 5 mm for all sizes
A single row of spokes is used for pulleys having widths up to 300 mm and a double row of spokes for widths above 300 mm.
Wooden Pulleys
Wooden pulleys are lighter and possess a higher coefficient of friction than cast iron or steel pulleys. These pulleys have 2/3rd of the weight of cast iron pulleys of similar size. They are generally made from selected maple which is laid in segments and glued together under heavy pressure. They are kept from absorbing moisture by protective coatings of shellac or varnish so that warping may not occur. These pulleys are made both solid or split with cast iron hubs with keyways or have adjustable bushings that prevent relative rotation between them and the shaft by the frictional resistance setup. These pulleys are used for motor drives in which the contact arc between the pulley face and belt is restricted.
Paper Pulleys
Paper pulleys are made from compressed paper fiber and are formed with metal in the center. These pulleys are usually used for belt transmission from electric motors when the center-to-center shaft distance is small.
Fast and Loose Pulleys
A fast and loose pulley, as shown in the following figure, used on shafts enables the machine to be started or stopped at will. A fast pulley is keyed to the machine shaft while the loose pulley runs freely. The belt runs over the fast pulley to transmit power by the machine and it is shifted to the loose pulley when the machine is not required to transmit power. In this way, the stopping of one machine does not interfere with the other machines which run by the same line shaft.
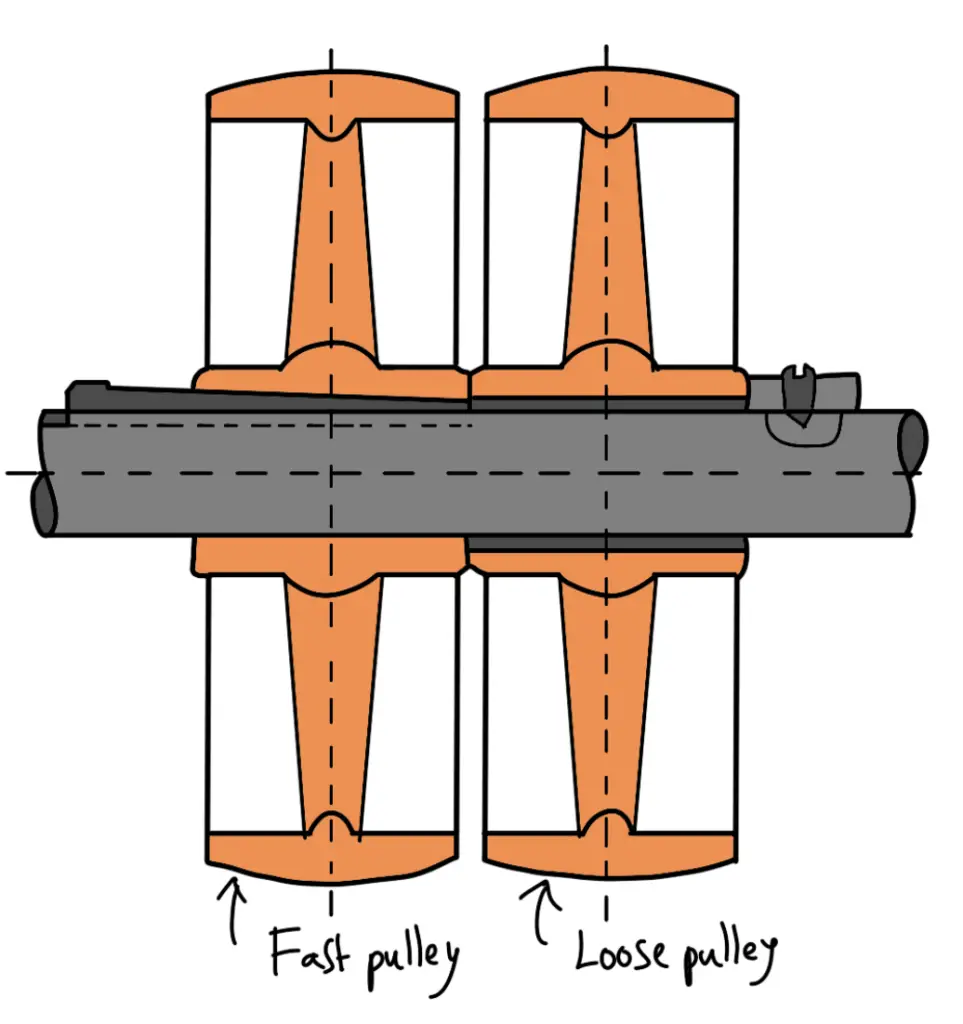
The loose pulley is provided with a cast iron or gun-metal bush with a collar at one end to prevent axial movement.
The rim of the fast pulley is made larger than the loose pulley so that the belt may run slackly on the loose pulley. The loose pulley usually has a longer hub in order to reduce wear and friction and it requires proper lubrication.

Leave a Reply