In metal works, Extrusion is a process in which the metal is subjected to plastic flow by enclosing the metal in a closed chamber in which the only opening provided is through a die. Let us discuss more details about the extrusion process such as different extrusion processes, extrusion defects and the machines used for extrusion.

Extrusion Process
As we mentioned above Extrusion is a process in which the metal is subjected to plastic flow by enclosing the metal in a closed chamber in which the only opening provided is through a die. The material is usually treated so that it can undergo plastic deformation at a sufficiently rapid rate and may be squeezed out of the hole in the die.
In the process, the metal assumes the opening provided in the die and comes out as a long strip with the same cross-section as the die-opening. Incidentally, the metal strip produced will have a longitudinal grain flow.
The process of extrusion is most commonly used for the manufacture of solid and hollow sections of nonferrous metals and alloys e.g., aluminium, aluminium-magnesium alloys, magnesium and its alloys, copper, brass and bronze etc. However, some steel products are also made by extrusion.
The stock or the material to be extruded is in the shape of cast ingots or billets. Extrusion may be done hot or cold. The cross-sections of extruded products vary widely. Some of these sections are shown in the below figure.
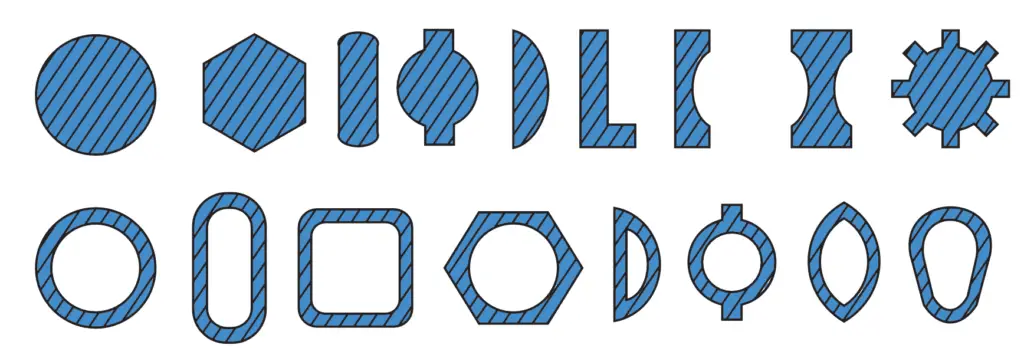
The pressure required for extrusion depends upon the strength of the material and the extrusion temperature. It will reduce if the material is hot. It will also depend upon the reduction in cross-section
required and the speed of extrusion. There is a limit to the extrusion speed. If the extrusion is done at a high speed, the metal may crack. The reduction of cross-sectional area required is also called the “extrusion ratio”. There is a limit to this also. For steel extruded hot, this ratio should not exceed 40: 1, but for aluminium extruded hot it can be as high as 400: 1.
Advantages of Extrusion Process
Let us discuss some of the advantages of the extrusion process.
- The complexity and range of parts that can be produced by the extrusion process are very large. Dies are relatively simple and easy to make.
- The extrusion process is complete in one pass only.
- This is not so in the case of rolling, the amount of reduction in extrusion is very large indeed.
- The extrusion process can be easily automated.
- Large diameter, hollow products, thin-walled tubes etc. are easily produced by the extrusion process.
- Good surface finish and excellent dimensional and geometrical accuracy is the hallmark of extruded products.
- This Extrusion process advantages cannot be matched by rolling.
Different Extrusion Processes
As we alredy mentioned above that the Extrusion can be done in hot and cold conditions. let us classify different extrusion processes in Hot and Cold extrusion processes respectively.
Hot Extrusion Processes
- Forward or Direct extrusion
- Backward or Indirect extrusion
Cold Extrusion Processes
- Hooker extrusion
- Hydrostatic extrusion
- Impact extrusion
- Cold extrusion forging
Hot Extrusion Processes
1. Forward or Direct Extrusion Process
In this process, the material to be extruded is in the form of a block. It is heated to the requisite temperature and then it is transferred inside a chamber as shown in the below figure.
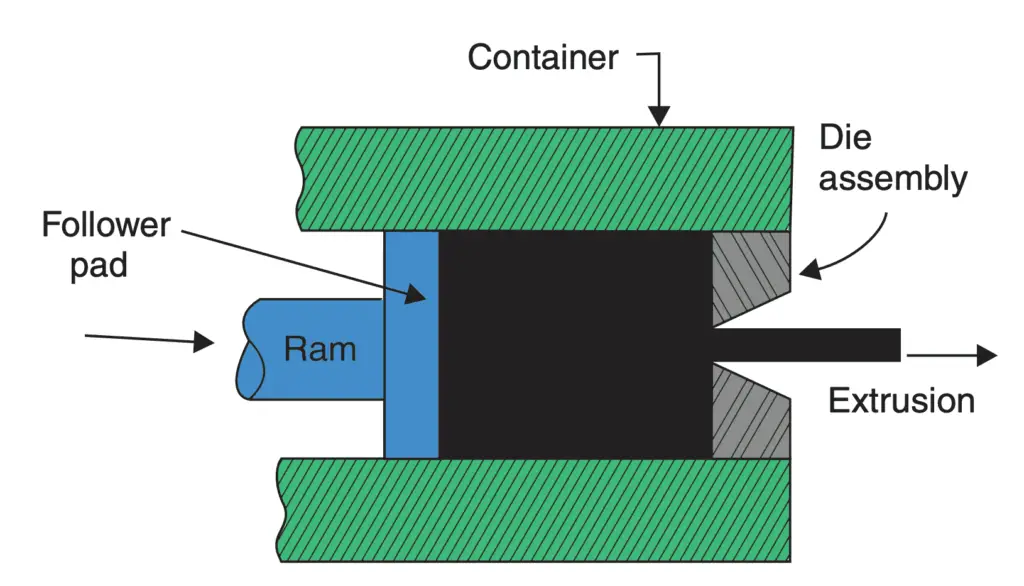
- In the front portion of the chamber, a die with an opening in the shape of the cross-section of the extruded product is fitted.
- The block of material is pressed from behind by means of a ram and a follower pad.
- Since the chamber is closed on all sides, the heated material is forced to squeeze through the die opening in the form of a long strip of the required cross-section.
- The process looks simple but the friction between the material and the chamber walls must be overcome by suitable lubrication.
- When extruding steel products, the high temperature at which the steel has to be heated makes it difficult to find a suitable lubricant.
- The problem is solved by using molten glass as a lubricant.
- When lower temperatures are used, a mixture of oil and graphite is used as a lubricant.
- At the end of the extrusion process, a small piece of metal is left behind in the chamber which cannot be extruded.
- This piece is called butt end scrap and is thrown away.
- To manufacture a tubular rod, a mandrel of diameter equal to that of the tube bore is attached to the ram.
- This mandrel passes centrally through the die when the material is extruded.
- The outside diameter of the tube produced will be determined by the hole in the die and the bore of the tube will be equal to the mandrel diameter. The extrusion process will then be called “tubular extrusion”.
2. Backward or Indirect Extrusion
This process is depicted in the below figure.
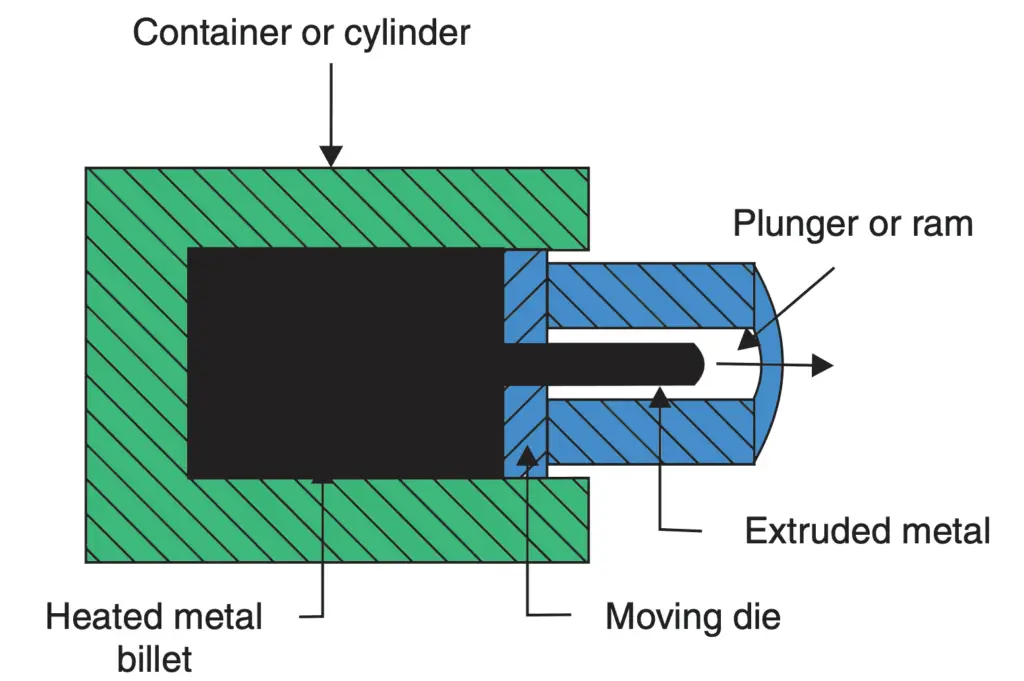
- As shown, the block of heated metal is inserted into the container/chamber.
- It is confined on all sides by the container walls except in front; where a ram with the die presses upon the material.
- As the ram presses backwards, the material has to flow forwards through the opening in the die.
- The ram is made hollow so that the bar of extruded metal may pass through it unhindered.
- This process is called the backward extrusion process as the flow of material is in a direction opposite to the movement of the ram.
- In the forward extrusion process, the flow of material and ram movement were both in the same direction.
The following table compares the forward (direct) and backwards (indirect extrusion process) with differences.
| Forward or direct extrusion | Backward or indirect extrusion |
| 1. Simple, but the material must slide along the chamber wall. | 1. In this case, the material does not move but the die moves. |
| 2. High friction forces must be overcome. | 2. Low friction forces are generated as the mass of material does not move. |
| 3. High extrusion forces are required but mechanically simple and uncomplicated. | 3. 25–30% less extruding force is required as compared to direct extrusion. But hollow ram required limited application. |
| 4. High scrap or material waste 18–20% on an average. | 4. Low scrap or material waste is only 5–6% of billet weight. |
Cold Extrusion Processes
1. Hooker Extrusion Process
This process is also known as the extrusion down method. It is used for producing small thin-walled seamless tubes of aluminium and copper. This is done in two stages. In the first stage, the blank is converted into a cup-shaped piece. In the second stage, the walls of cup one thinned and it is elongated. The process can be understood by referring to the following figure. This process is a direct extrusion process.
2. Hydrostatic Extrusion
This is a direct extrusion process. But the pressure is applied to the metal blank on all sides through a fluid medium. The fluids commonly used are glycerine, ethyl glycol, mineral oils, castor oil mixed with alcohol etc. Very high pressures are used – 1000 to 3000 MPa. Relatively brittle materials can also be successfully extruded by this method.
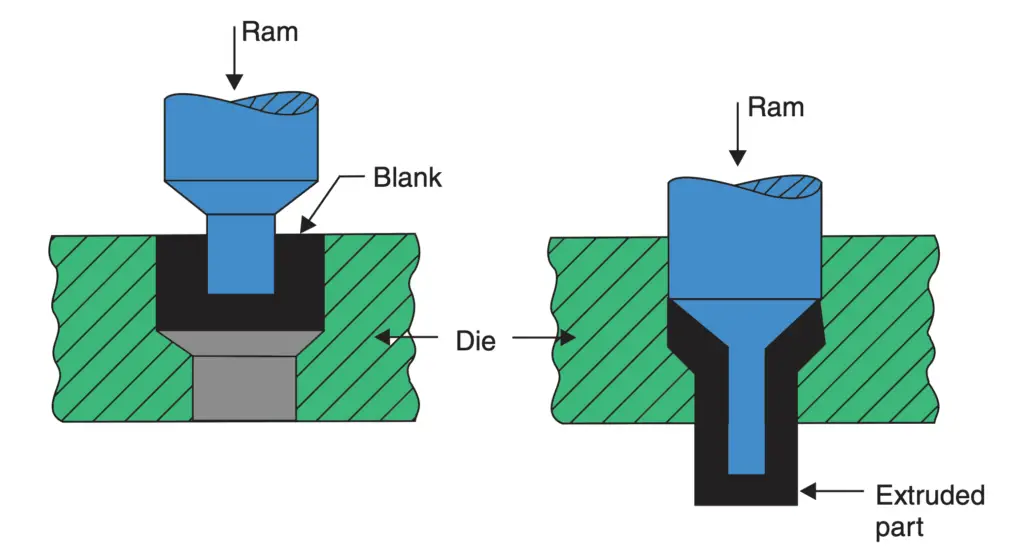
3. Impact Extrusion
In this process, which is shown in the below figure the punch descends with high velocity and strikes in the centre of the blank which is placed in a die.
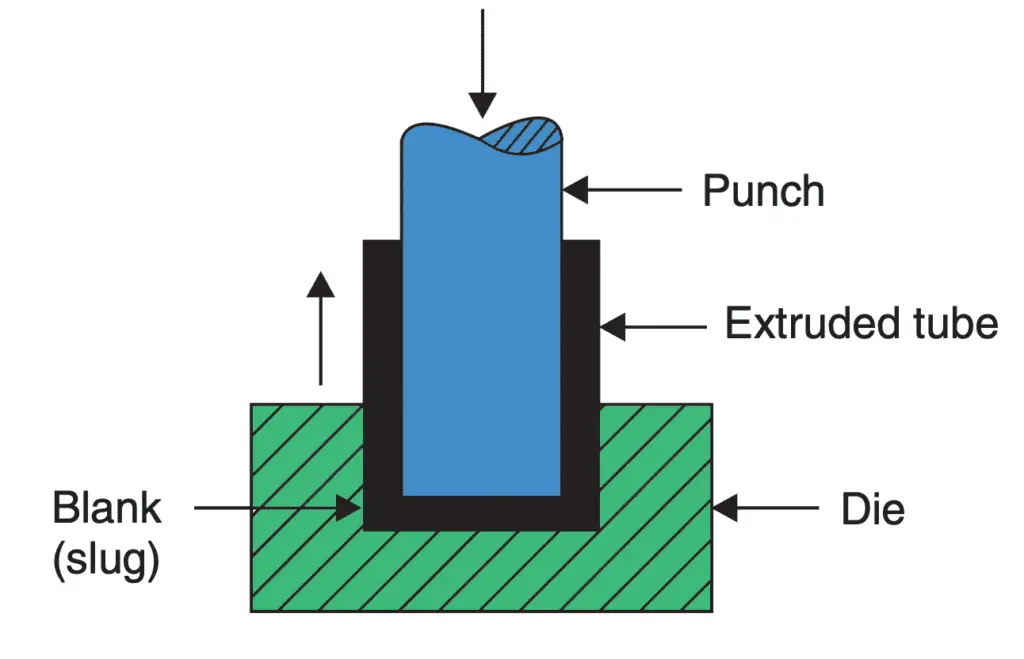
The material deforms and fills up the annular space between the die and the punch flowing upwards. Before the use of laminated plastic for manufacturing toothpaste, shaving cream tubes etc., these collapsible tubes containing paste were and are still made by this process. This process is actually a backward extrusion process.
4. Cold Extrusion Forging
This process is depicted in the following figure.
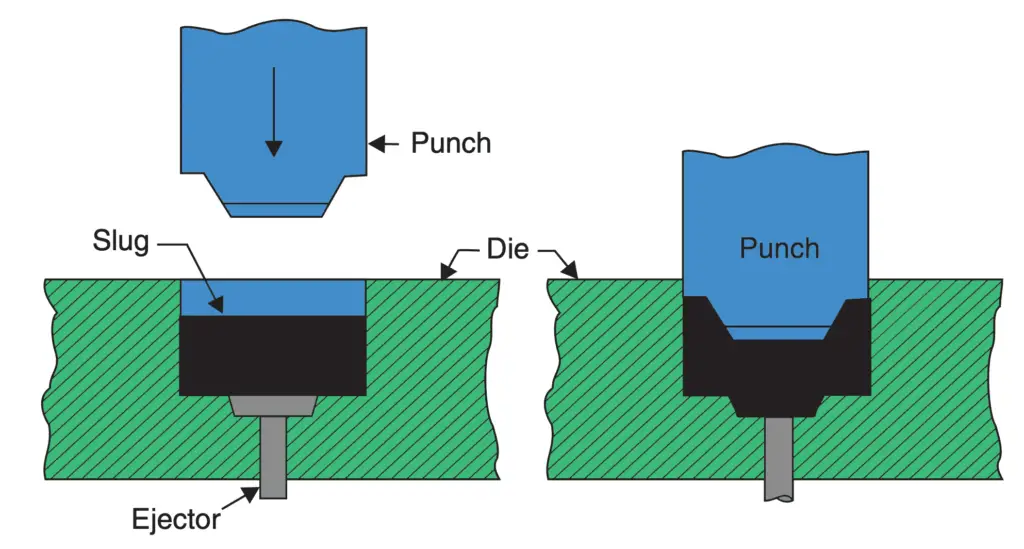
This is generally similar to the impact extrusion process, but there are two differences:
- In this process the punch descends slowly
- The height of the extruded product is short and the side walls are much thicker than the thin-walled products produced by the impact extrusion process.
In essence, this process is one of backward extrusion.
Comparison between Hot and Cold Extrusion
This is given in the following table:
| Cold extrusion | Hot extrusion |
| 1. Better surface finish and lack of oxide layers. | 1. The surface is coated with oxide layers. The surface finish is not comparable with cold extrusion. |
| 2. Good control of dimensional tolerance no machining or very little machining required. | 2. Dimensional control is not comparable to cold extrusion products. |
| 3. High production rates at low cost. Fit for individual component production. | 3. High production rates but process fit for bulk material, not individual components. |
| 4. Improved mechanical properties due to strain hardening. | 4. Since processing is done hot, recrystallisation takes place. |
| 5. Tooling is subjected to high stresses. | 5. Tooling is subjected to high stresses as well as to high temperatures. Tooling stresses are however lower than for cold extrusion. |
| 6. Lubrication is crucial | 6. Lubrication is crucial. |
Machines For Extrusion
- Both hydraulic and mechanical presses of horizontal and vertical configurations are used for extrusion.
- They should be capable of exerting high forces and their rams should have long strokes.
- To reduce friction between metal and extrusion chamber walls, lubricants are used.
- The dies and punches are made from good quality alloy steels which are known as hot and cold die steels.
- Extrusion speed is of the order of 0.5 m/sec for light alloys and 4.5 m/sec for copper alloys.
Extrusion Defects
- Sometimes the surface of extruded metal/products develops surface cracks.
- This is due to heat generated in the extrusion process.
- These cracks are especially associated with aluminium, magnesium and zinc alloy extrusions.
- The extruded product can develop internal cracks also.
- These are variously known as centre burst, centre cracking and arrowhead fracture.
- The tendency for centre cracking increases with increasingly angles and material impurities.
Conclusion
We have discussed different Extrusion process under Hot Extrusion and cold extrusion processe also discussed the differences between Hot and Cold extrusion processes. given some clues about the extrusion porocesses defects. THe machine used for the extrusion proocesses also discussed. Let us know what do you think about this article in the comment section below.

Simple articles about extrusion technology contains good information.