Yes, it is not possible to measure the true value of an object, there will be definitely an existence of error either it can be very small (Negligible) or considerable based on application. This error can be evaluated as either an absolute error or a relative error. let’s discuss different sources of errors in measurement.
This is a Video tutorial on this topic: sources of errors in measurement. If you would like to read the full article, scroll down below.
Error in Measurement
Basically, the error can be defined as the difference between the measured value and the true value. This error can be evaluated as following types
- Absolute Error
- Relative Error
Absolute Error
Absolute error = |True value-Measured Value|
Relative Error
Relative error = Absolute Error/Measured value
They are as simple as that.
While measuring a parameter with a measuring instrument there are so many factors that determine the accuracy of the measurement, these factors are the sources of the errors in measurement. Let’s discuss different sources of errors in measurement.
Sources of Errors in measurement
sources of errors in measurement are nothing but the different error possibilities in the measurement. the different types of errors are listed as a tree diagram below.
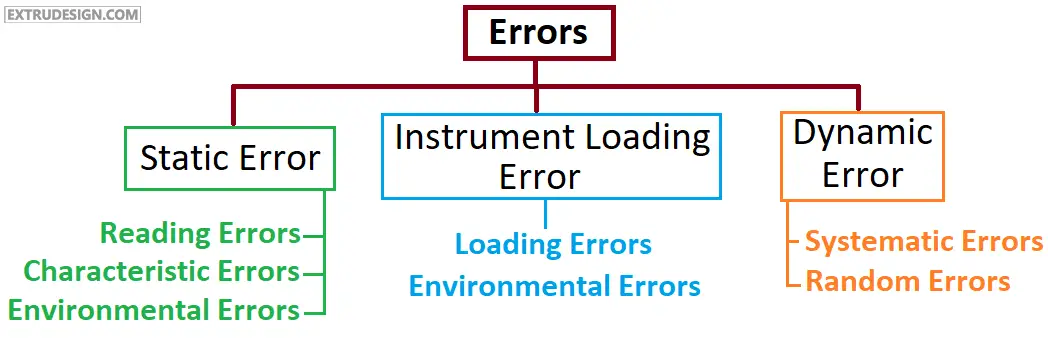
Static Errors
There are three static errors those are Reading errors, Characteristic errors, Environmental errors. The static error means no relation to the time variation in the measurement, only related to the physical nature of the measuring instrument. That is what a static Error means.
i) Reading error: Reading errors such as reading with
- parallax error: Observing the readings from the dial without putting it normal to the eye.
- Interpolation error: Taking correct interpolation when the indicator is in between two graduations.
ii)Characteristic Error:
- Not able to attain the theoretical performance of the Instrument in taking an actual measurement.
iii) Environmental Errors:
- Environmental factors such as wind, surrounding temperature, humidity, effects the on measuring instruments.
- Even the electrical and the magnetic field also influence the error in the measuring instruments while in static measurement.
- This environmental error is also a source of an error under instrumental loading errors.
Instrumental Loading Errors
- Instrument loading errors mean, due to the measuring instrument the object which needs to be measured tends to change. For example, due to applying overpressure on the object by using the measuring instrument forcibly, the object may tend to change its shape and gives us an error.
- The environmental factor also affects the object to change in its parameter and becomes a source of an error as we said earlier.
Dynamic Errors
Dynamic errors mean the error caused by the time variation in the measurand(the object being measured). The main factor causes the dynamic error are the inertia, damping, friction in the sensing system or the display system of the measuring instrument.
There are two different dynamic errors. They are
i) Systematic Errors:
These systematic errors are
- Regular or repeats in nature and also can be controllable. (Repeats after a certain amount of time)
- Can be eliminated sometimes.
- Calibration errors, variation in the contact pressure, variation in the atmospheric pressure, Parallax error, misalignment errors are the sources of Systematic errors.
ii) Random Errors:
These Random Errors are
- Errors randomly occurred with the measuring instrument. (Unable to predict the when the error going to happen)
- Hard to control.
- Can be corrected in the final results.
- Error due to the variation of in the setting of the workpiece and the instrument, Due backlash and friction in the components of the measuring instruments are the sources of the Random errors in measurement.
Conclusion
Those are the different sources of errors in measurement. If you have any thoughts about the sources of errors in measurement please let us know in the below comments.

Thank you, I used to write for msc instrumentation assignment