The Heat Affected Zone is an important phenomenon of arc welding, which may result in developing cracks in the welding. so understanding the Heat Affected Zone and its effects is necessary for every welder.
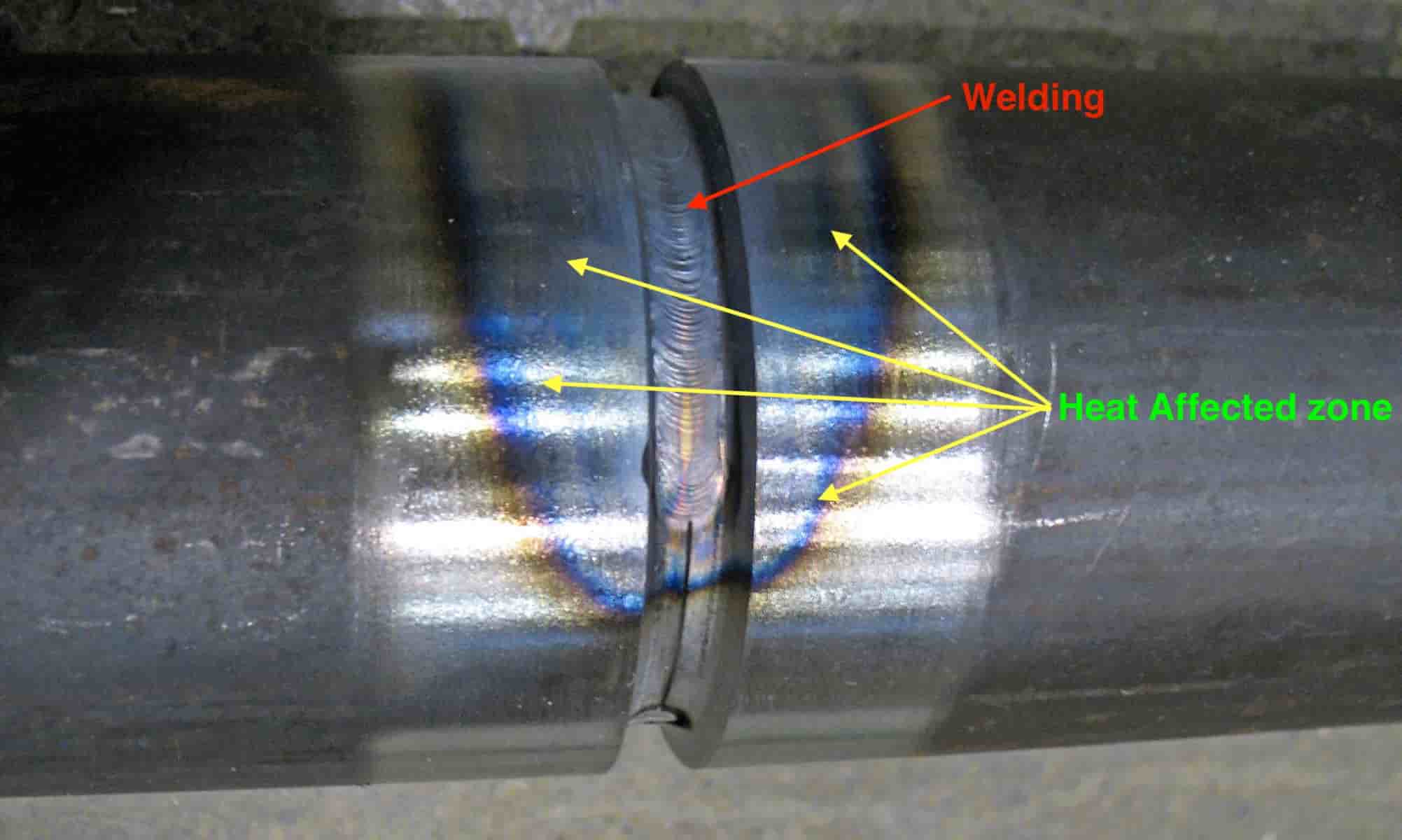
In the Arc welding process, as we have already discussed a great amount of heat is generated to produce the weld pool which melts the filler material or the electrode itself to create the weldment.
The heat is also propagated into the surrounding of the joint on either side. The temperature of the material on both sides of the weld bead may not be as high as the melting point of the metal, but, is very close to it.
As we move away from the joint or weld bead, the metal may be heated to lesser and lesser temperatures. As the electrode travels over the joint and moves away, the heated metal cools as quickly as it was heated.
Thus, we can conclude, that the metal adjacent to the weld bead has been subjected to a heat treatment.
If steel is being welded, this heating and quick cooling may result in the formation of martensitic and other structures which may be prone to cracking and hardness.
The area so affected by welding is called the Heat Affected Zone.
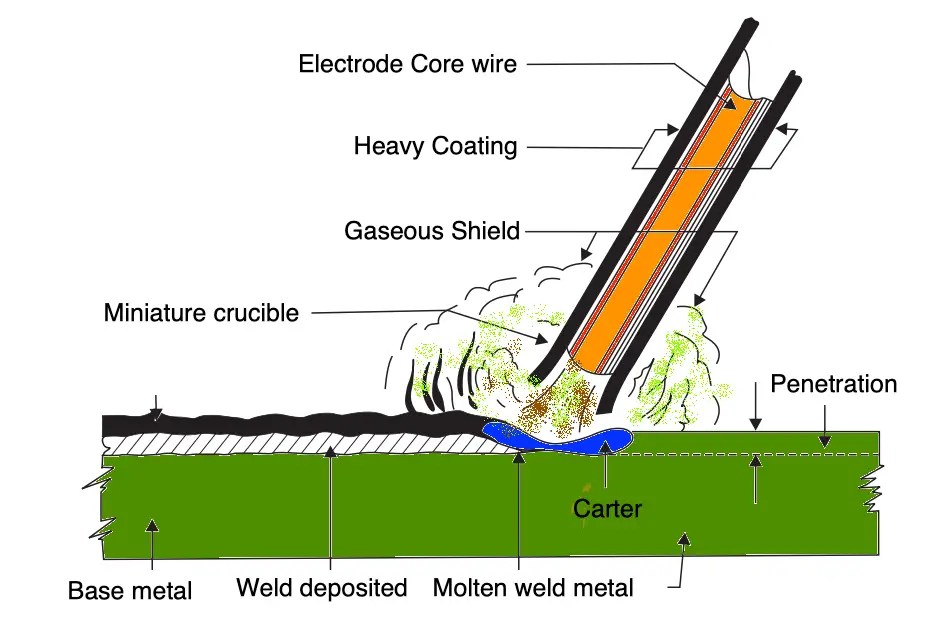
Causes of Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
- Slow heat input rate can casue more HAZ than the high rate of heat input.
- Welding speed also influence the heat affected zone.
- HAZ area may vary depends on the material properties, material thickness also. Thermal conductivity of the material plays an important role for the size of heat-affected Zone.
- Geometry of the welding infleunce the size of HAZ.
- More heat-affected zone results faster cooling of the weldment.
- Not only welding, Thermal cutting process also develop HAZ.
- The laser cutting the heat effected zones are very less since laser hase more concentrated heat on very small area.
Effects of Heat Affected Zone
Many of the welding failures occur due to the heat-affected zones. Due to the heat-affected zones, the surrounding material will undergo heat treatment and possess changes in its microstructure. The change in the microstructure of the material may differ in the material properties such as the material strength, material corrosion resistance, and increased brittleness.
Due to changes in the material properties, the region becomes weak among the weldment area. Due to this weakness in the material crack may develop in the weldment, once the crack is developed this leads to the failure of the joint.
Can we reduce Heat Affected Zone?
Yes, we can reduce it to some extent by doing the following.
- As we have discussed the so many causes, welding speed is the one that can cause the HAZ, so better welding speeds result in smaller HAZ.
- By performing a pre and post heat treatment of the weld can also reduce change of the microstructure of the material. which results very small change in the material properties change.
- If possible choosing the proper weld geometry can help reduce the HAZ.
- More concentrated heat on smaller area of the weld joint can reduce the HAZ.
- A professional welder can apply the above techniques in an efficent manner so get a skilled welder.
Conclusion
Heat Affected zones can not be completely avoided but can be controlled to some extent by taking the above precautions to achieve a good and strong weld with a crack-free weld joint. Let us know what do you think about this in the comment section below.

Leave a Reply