A Study on Consumer Behaviour Towards Online Shopping in Kottayam Municipality was submitted by Bijil Jacob Biju (from the Bishop Speechly College For Advanced Studies Pallom, Kottayam) to extrudesign.com.

1. INTRODUCTION
Internet is changing the way consumers shop and buy goods and services and has rapidly evolved into a global phenomenon. Many companies have started using the internet to cut marketing costs, thereby reducing the price of their products and services to communicate and disseminate information, to sell the products, to take feedback, and also to conduct satisfaction surveys with consumers. Consumers use the internet not only to buy the product online but also to compare prices, product features, and after-sales service facilities they will receive if they purchase the product from a particular store. Many experts are optimistic about the prospects of online business.
In addition to the tremendous potential of the E-commerce market, the internet provides a unique opportunity for companies to more efficiently reach existing and potential customers. Although most of the revenue of online transactions comes from business-to-business commerce, the practitioners of business-to-consumers commerce should not lose confidence. It has been more than a decade since business-to-consumer E-commerce first evolved. Scholars and practitioners of electronic commerce constantly strive to gain and improve insight into consumer behavior from different perspectives. Many of the studies have cost new emergent factors or assumptions which are based on the traditional models of consumer behavior, and then examine their validity in the internet context.
ONLINE SHOPPING IN INDIA
The birth and growth of the internet have been the biggest event of the century. ECommerce in India has come a long way from a timid beginning in 1999-2000 to a period where one can sell and find all sorts of stuff from a high-end product to a large peanut online. Most corporations are using the internet to represent their product range and services so that it is accessible to the global market and to reach out to a larger range of their audience.
Computers and the internet have completely changed the way one handles day-to-day transactions; online shopping is one of them. The internet has brought about sweeping changes in the purchasing habits of people. In the comfort of one’s home, office or cyber cafe or anywhere across the globe, one can log on and buy just about anything from apparel, books, Music, and jewelry to digital cameras, mobile phones, mp3 players, video games, movie tickets, rail, and air tickets. Ease, simplicity, convenience, and security are the key factors turning the user to buy online. There is a huge purchasing power of the youth population aged 18-40 in the urban area.
CHANGING ATTITUDE TOWARDS ONLINE SHOPPING
“Awareness, Future Demand Focus for Emerging Markets & current issues” Malls springing up everywhere, and yet people are E-shopping! And not in small numbers either. Consumers are more rational nowadays and can get choices from the market. Awareness among consumers is spread through the internet. The number of internet users is increasing day by day which attracts people who have an option to buy online. It was never thought that Indians would go in for E-shopping in such a big way. Ticketing, travel bookings, and even books and movies seem fine to buy online. Knowing that in India sizes vary from brand to brand and quality is inconsistent, even of some electronic items, how is it that people are buying these items online? In India, there are some segments of people who have not yet tried purchasing over the internet.
Here are a few reasons why internet shopping is preferable:
Convenience
Online stores are usually available 24 hours a day, and many consumers have internet access both at work and at home. Other establish such as internet café and the school provides access as well. A visit to conventional retail stores requires travel and must take place during business hours.
Information and reviews
Online stores must describe products for sale with text, photos, and multimedia files. Some stores even allow customers to comment or rate their items. There are also dedicated review sites that host user reviews for different products. Reviews and now blogs give customers the option of shopping cheaper organize purchases from all over the world without having to depend on local retailers.
Home delivery concept
In any case, home delivery is a concept that Indians are familiar with and love. The mall craze has started only now. Earlier it was a choice between setting it out in small crowded markets or asking a friendly neighborhood Kirana (grocer) to deliver groceries home and this system is still thriving.
1.1 Statement of the problem
At any given time there are millions of people online and each of them is a potential customer for a company providing online sales. Due to the rapid development of the technology surrounding the internet, accompany that are interested in selling products from its website will constantly have to search for an edge in the fierce competition. Since there are so many potential consumers, it is of the utmost importance to be able to understand what the consumer wants and needs.
The importance of analyzing and identifying factors that influence consumer when he or she decides to purchase on the internet is vital. Since the internet is a new medium for there have been new demands set by the consumer. That is why online retailers must know what influences the online consumer.
Analyzing consumer behavior is not a new phenomenon. The renowned marketing expert Philip Kotler has published several works on the topic of consumer behavior theories. These theories have been used for many years not only to understand the consumer but also to create a marketing strategy that will attract the consumer efficiently. Hence, understanding and identifying the consumer is closely related to the directions a company will take with its marketing strategies. These theories can also be applied to identify the online consumer and to create certain consumer segments.
Since online retailing is a new retailing medium and online consumer behavior is diverse from traditional consumer behavior, one must identify what influences the online consumer. Analyzing the process that the online consumer goes through when deciding and making a purchase over the internet, shows some factors that consumers consider. These factors need to be identified and taken into account by online retailers to satisfy consumer demands and compete in the online market.
1.2 SCOPE OF THE STUDY
At any given time there are millions of people online and each of them is a potential customer for a company providing online sales. Due to the rapid development of the technologies surrounding the internet, a company that is interested in selling products from its website will constantly have to search for an edge in the fierce competition. There are so many potential consumers, it is of the utmost importance to be able to understand what the consumers want and need. The importance of analyzing and identifying factors that influence the consumer when he or she decides to purchase on the internet is vital. Since the internet is a new medium for there have been new demands set by the consumer. The online retailers must know what influences the online consumer behavior is diverse from traditional consumer behavior, one must identify what influences the online consumer.
1.3 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
This project research helps to find out what are the main factors that affect consumer behavior towards online shopping. The following are the objectives of the study;
- To study consumer behaviour towards online shopping.
- To know the factors which affect decision making process of customer while purchasing the online shopping product.
- To examine whether customer prefer online shopping or offline shopping.
- To identify their preference towards different E-shopping websites and the features of websites in general.
- To know the problems they face during online shopping.
1.4 METHODOLOGY
The research is based upon both primary and secondary data both. The primary data was collected through a questionnaire designed exclusively for the study. Secondary data was taken from Research papers, journals, magazines, and websites.
1.4.1 SAMPLE SIZE
Samples were collected from consumers and buyers of online shopping in the Kottayam Municipality region. The sampling size is 50, the sampling technique used for the study is Random Sampling.
1.4.2 SAMPLE DESIGN
In particular research, a procedure that is being followed for selecting a sampling unit is called sample design. The procedure that is being followed by the researchers to select a sampling unit is simple random Sampling. In simple random sampling, each sample unit has an equal chance to get selected. The population selected by the researchers for the study is citizens in Kottayam municipality.
1.4.3 COLLECTION OF DATA
PRIMARY DATA
Primary data are those, which are collected for the first time, and are original. A suitable combination of Questionnaires and interview techniques is used to collect the required primary data. By using a questionnaire, data has been collected from 100 sample respondents residing in Kottayam municipality.
SECONDARY DATA
The secondary data are those which are already collected by someone for some purpose and are available for the present study. Secondary data was collected from magazines, websites, and other such sources.
1.4.4 TOOLS OF ANALYSIS AND PRESENTATION
The collected data has been analyzed and interpreted by using different statistical tools such as percentages, pie charts, bar charts, etc.
1.4.5 LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY
The study suffers from the following limitations:
- The study is based on the opinion on only 100 respondents. It cannot be generalised.
- The data was collected through structured questionnaire and analysed based on the information given by respondents.
- The study largely based on the perception of the respondents.
2. REVIEW OF LITERATURE AND THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 REVIEW OF LITERATURE
INTRODUCTION
This dissertation aims at finding factors that affect online consumers’ buying behavior. By reading literature concerning consumer characteristics and online consumer characteristics I believe to find implications for certain factors that are of importance for the online consumer.
The internet is a worldwide accessible series of computer networks that transmit data by packet switching using the standard internet protocol. It is a “network of networks” that consists of millions of smaller domestic, academic, business, and government networks, which together carry various information and services, such a select, file transfer, the interlinked Webpages, and other documents of the World Wide Web. Originally the internet was mainly used by academics, research scientists, and students; however, that scenario has changed as commercial organizations have moved to incorporate the World Wide Web into their promotional campaigns, and by offering the facility of online purchasing (Jobber & Fahy, 2003). The internet has evolved into a worldwide accessible marketplace for information exchange and eCommerce. The strategic importance to be available for consumers on the World Wide Web, with information and services has become particularly relevant to firms According to Vesterby and Chabert (2001) the Internet can make it easier for companies to have information about their products or services available to their customers or potential customers. A company can satisfy the consumers’ individual need for information at a low cost in comparison to sending out product brochures for example. As the user can choose information from websites, which implies that the information provider can achieve a better understanding of the user’s needs and wants by collecting data. On the other hand, the Internet is a place with hardly any structure or rules: therefore, large efforts are needed to show the consumer where a specific site is located, and what services are available on that site. Vesterby and Chabert (2001) claim that companies with no physical presence must market themselves considerably, both online and offline, for the consumer to remember their name.
Whether it is the traditional market or the online market, the marketer must understand the consumer and how he makes his decisions and purchasing choices (Hollensen, 2004), because the consumer is under a constant flow of stimuli from the marketer’s advertisements. The marketer can decide and control the output that will be forwarded to the consumers, but when the advertisement reaches the consumer that control ends. The consumer then interprets the information that has been sent out in his way based on specific factors for every consumer. Therefore marketers have developed different theories that can explain why consumers interpret information in a certain way, and thereby understand certain behaviors (Kotler & Armstrong, 2007). Several articles have set out to identify the characteristics of the online consumer. Allred, Smith, and Swinyard (2006) identify the online consumer to have the following characteristics: younger, wealthier, better educated, having a higher “computer literacy” and are bigger retail spenders. Donuthouand Garicia (1999) identify the online consumers: older, make more money, convenience seeker, innovative, impulsive, variety seeker, less risk-aware, less brand and price-conscious, and with a more positive attitude towards advertising and direct marketing. Some of these characteristics are similar, while others are the opposite.
Trying to identify the online consumer is difficult since the rapid development of e-commerce has also led to an increase of both technologies and different types of consumers. It is also known that the type of product has a significant influence on online consumer behavior which makes it more difficult to identify consumer characteristics (Christopher & Huarng, 2003).
- Solomon (1998) studied the Consumer behaviour and said that it is the study of the processes involved when an individual selects, purchases, uses or disposes of products, services, ideas, or experiences to satisfy needs and desires. In view for the Internet to spread out as a retail channel, it is imperative to realize the consumer’s mind-set, intention and conduct in light of the online buying practice.
- Lepkowska -White, and Rao (1999) referred vendor characteristics, security of transactions, content for privacy and customer characteristics as factors influencing electronic exchange.
- Donthu and Garcia (1999) proposed that risk aversion, innovativeness, brand consciousness, price consciousness, importance of convenience, variety-seeking propensity, impulsiveness, attitude toward adverting, attitude toward shopping, and attitude toward direct marketing would influence online shopping behaviour.
- Schiffman, Scherman, & Long (2003) in his study researched that “yet individual attitudes do not, by themselves, influence one’s intention and/or behavior. Instead that intention or behavior is a result of a variety of attitudes that the consumer has about a variety of issues relevant to the situation at hand, in this case online buying. Over time the Internet buyer, once considered the innovator or early adopter, has changed. While once young, professional males with higher educational levels, incomes, tolerance for risk, social status and a lower dependence on the mass media or the need to patronize established retail channels (Ernst & Young, 2001; Mahajan, Muller & Bass, 1990),
- Sultan and Henrichs (2000) in his study concluded that the consumer’s willingness to and preference for adopting the Internet as his or her shopping medium was also positively related to income, household size, and innovativeness.
- Vijay, Sai. T. & Balaji, M. S. (May 2009), revealed that Consumers, all over the world, are increasingly shifting from the crowded stores to the one-click online shopping format. However, in spite of the convenience offered, online shopping is far from being the most preferred form of shopping in India. A survey among 150 internet users, including both users and non-users of online shopping, was carried out to understand why some purchase online while others do not. The results suggested that convenience and saving of time drive Indian consumers to shop online; while security and privacy concerns dissuade them from doing so.
- The work of Kim and Park (2005) using U.S. samples suggests that their positive attitudes as well as willingness to search for pre-purchase information leads to a strong likelihood that they will buy online. Online shoppers, are required to have computer skills in order to use the Internet for shopping. Hence, those who are not comfortable with using the computer, will likely do their shopping at the traditional store, modern shop, or discount store (Monsuwe , 2004) because it will be faster shopping there than in the Internet shop.
- Goldsmith and Flynn (2004) state that the home catalog is another traditional selling channel where people can shop at home because of the varieties of products offered in the catalog. They can order through the phone or by mail. It is convenient except that they are not able to touch and feel products before purchasing.
- Dr.V Vijayalakshmi & Dr.R.Lakshmi (2018) Mostly youngsters and youth generation (19-30 age group) are very much interested in online buying because they know about technology and e- shopping.
- As per an ASSOCHAM-Resurgent joint study,(2018) online shopping is expected to clock annualised growth of 115 percent this year, aided by fast-increasing data consumption and improvement in logistics, along with a number of offers presented by e- commerce platforms.
- Jarvenpaa journal of Electronic Commerce Research, VOL.6, NO.2, (2015) it is an early stage in internet development in terms of building an appropriate dedicated model of consumer buying behaviour.
- Ahmed, (2012) Concerns of price, quality, durability and other product-related aspects are the main drivers of buying decision in developed countries but the considerations could be vary from the developing countries.
- Sylke et al, (2004) the growth rate of electronic commerce in India, however, has yet been much below anticipation; its proportion of total retail business is still small due to its certain limitations.
- Garbarino & Strahilevitz (2004), Korgaonkar & Wolin (1999), Van Slyke et al (2002) previous researches suggested that men are more likely to purchase products and/or services from the Internet than women.
- Na Li & Ping Zhang (2002) found that men are more adopting in online shopping, Female shoppers are found to prefer using catalogues to shop at home. It is found once female showed preference in online shopping, they will shop more frequently online than their male counterparts.
- Zhang, Dran, Small, and Barcellous (1998), indicated that website design features of the website are important and influencing factors that leads consumer‘s satisfaction and dissatisfaction with a specific website.
2.2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
MEANING OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR
Consumer behavior is the study of individuals, groups, or organizations and all the activities associated with the purchase, use, and disposal of goods and services, and how the consumer’s emotions, attitudes, and preferences affect buying behavior. Consumer behavior emerged in the 1940–the 50s as a distinct sub-discipline of marketing but has become an interdisciplinary social science that blends elements from psychology, sociology, social anthropology, anthropology, ethnography, marketing, and economics (especially behavioral economics).
The Galeries Royales Saint-Hubert shopping arcade in Belgium. Consumer behavior, in its broadest sense, is concerned with how consumers select, decide and use goods and services.
The study of consumer behavior formally investigates individual qualities such as demographics, personality lifestyles, and behavioral variables (such as usage rates, usage occasion, loyalty, brand advocacy, and willingness to provide referrals), in an attempt to understand people’s wants and consumption patterns. Also investigated are the influences on the consumer, from social groups such as family, friends, sports, and reference groups, to society in general (brand-influencers, opinion leaders).
Research has shown that consumer behavior is difficult to predict, even for experts in the field; however, new research methods, such as ethnography, consumer neuroscience, and machine learning[1] are shedding new light on how consumers make decisions. In addition, customer relationship management (CRM) databases have become an asset for the analysis of customer behavior. The extensive data produced by these databases enables detailed examination of behavioral factors that contribute to customer re-purchase intentions, consumer retention, loyalty, and other behavioral intentions such as the willingness to provide positive referrals, become brand advocates or engage in customer citizenship activities. Databases also assist in market segmentation, especially behavioral segmentation such as developing loyalty segments, which can be used to develop tightly targeted, customized marketing strategies on a one-to-one basis. (Also see relationship marketing).
DEFINITION OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR
According to Engel, Blackwell, and Mansard, ‘consumer behavior is the actions and decision processes of people who purchase goods and services for personal consumption.
According to Louden and Bitta, ‘consumer behavior is the decision process and physical activity, which individuals engage in when evaluating, acquiring, using or disposing of goods and services
FACTORS AFFECTING CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR
The factors which influence consumer behavior
- Psychological (motivation, perception, learning, beliefs and attitudes)
- Personal (age and life-cycle stage, occupation, economic circumstances, lifestyle, personality, and self-concept)
- Social (reference groups, family, roles, and status)
- Cultural (culture, subculture, social class system)
3. INDUSTRIAL PROFILE
3.1 HISTORY OF ONLINE SHOPPING
Online shopping is a form of electronic commerce whereby consumers directly buy goods or services from a seller over the Internet without an intermediary service. An online shop, e-shop, e-store, Internet shop, web-shop, web-store, online store, or virtual store evokes the physical analogy of buying products or services at a bricks-and-mortar retailer or shopping center. The process is called business-to-consumer (B2C) online shopping. When a business buys from another business it is called business-to-business (B2B) online shopping.
1979
Videotext was being researched much earlier for supplying the end-users with textual information. Much work was done in the UK on videotext, it was a two-way message service and developed basically for information sending where “many companies” were interested in but on the backdrop of all that Michael Aldrich in 1979 gave the “concept of teleshopping” (today online shopping) which revolutionized the way businesses happen. The same happened in the US around that year with services like The Source and CompuServe.
1982
Mintel succeeded Videotext as an online service making online purchases, checking share market, searching telephone directory and could even chat. This is one of the most successful services before WWW using telephone lines; it was launched in France successfully but in the UK as well but to less access.
1987
With Swag (an offshoot of CompuServe) the community of software developers and shareware authors got an online market where they could sell their products using “Merchant account”. Thus, online shopping started for then software industry people.
1990
Tim Berners-Lee wrote the World Wide Web and gave the first browser to view the web which changed most of the things; a whole new revolution started, which till date is ON.
1992
Revolutionary book by J.H. Snider and Terra Ziporyn namely; Future Shop: How New Technologies Will Change the Way We Shop and What We Buy. St. Martin’s Press.
1994
Netscape released Navigator browser, later introduced Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption for secure transactions. Pizza Hut started online ordering on their webpage, cars, bikes, and adult content as well started selling on the internet.
1995
Amazon.com started selling each and everything online, and along with that Jeff Bezos starts the first commercial-free 24-hour internet-only radio stations. Then Radio HK and Net Radio start broadcasting. Companies like Dell and Cisco started using the internet in all their transactions. Online auction started by eBay.
1998
The United States started selling Electronic postal stamps online wherein they could be purchased and downloaded for print.
1999
Acquisition of Business.com by e-companies in the US $7.5 million. Napster the peer-to-peer files sharing software launches. Home decorative items started selling on ATG Stores.
2000
The dot-com bust as we know it today wasn’t something that happened in a day, over speculation for some time (approx. 1995-2000) where just the prefix “e-” or “.com” in names could make stock prices rise at great rates. This saw a great many companies rise and fall.
Many entrepreneurs came up with brilliant plans and most got pretty “generous” venture capitalists, most of these firms started working on the principle “expand the market and later profits will cover all present debts and losses.” This speculation was constantly taking the market upwards with NASDAQ at a peak of 5132.52 points. March 10, 2000. After this, the market goes down and with them, the over speculating ones have just wiped off the market.
2002
PayPal the company which offered an alternative (through the internet) to cash or check payment was acquired by eBay for $1.5 billion. CSN Stores and NetShops were founded with the concept of domain-specific commodity and spring with many online stores, going for one item on each website
2003
Online shopping matures showing to the world their confidence Amazon.com posted its first yearly profit and thus again made a presence on the stock market.
2007
Acquisition of Business.com by R.H. Donnelley for $345 million, making way for bigger players in the technology domain.
2012
The tremendous growth in the US in eCommerce with sales figures touching $204 billion, a decent 17% rise from the previous year.
2014
Online Retailer- Amazon.com has an estimated turnover daily is over US $2.5 trillion with a growth rate of 14% annually. eBay has sales of US $1.89 billion, these numbers alone speak.
2016
Average online purchases are expected to increase by 78 percent in 2016 from 66 percent in 2015, due to attractive deals and aggressive marketing of an ever-expanding range of merchandise from clothes to jewelry, from electronics to books,” said a study by Assocham and international accounting firm Price water house Coopers (PwC).
3.2 ONLINE SHOPPING SITES
I. SNAPDEAL.COM
Snapdeal is an e-commerce company based in India. It is a daily deals website that features discount offers across lifestyle segments such as dining, health & beauty, entertainment, and travel. It also offers discounts on products like electronics, perfumes, watches, bags, sunglasses, apparel, and mobile phones.
Headquartered in Delhi, Snapdeal.com was launched in February 2010. The company was founded by Kunal Bahl a Wharton graduate and Rohit Bansal, an alumnus of IIT Delhi who are friends since school. They had agreed that after finishing their studies and gaining the required work experience, they would start a project of their own.
Snapdeal.com serves as an advertising platform for merchants and a discount platform for customers. For the merchants who partner wily Snapdeal, it is a cost-effective channel for acquiring new customers. It also works as a risk-free alternate marketing channel. From the merchant’s standpoint, they are passing on the customer acquisition cost in the form of a discount offer.
PRODUCT CATEGORIES PROVIDED BY SNAPDEAL.COM
- Mobiles & Accessories o Men’s & Women’s Apparel o Watches, Bags & Accessories o Electronics & Cameras o Computers & Peripherals oPerfumes, Beauty & Health o Jewellery o Books & Movies o Footwear oHome, Kitchen & Appliances o Infants, Kids & Toys o Sports & Hobbies oTravel Packages
- Adventure & Entertainment
Terms of Sale, Website Terms of Use, Privacy Policy
This User Agreement which is intended to be a legally binding contract between you and us contains the following;
- Terms of Sale: this governs your purchase and use of the coupons/vouchers
- Website Terms of Use: this governs the access and use of the website
- Privacy Policy: this governs the use of your personal information we collect
You agree that you are of legal age to enter into binding contracts, have read, understood, and are bound by the User Agreement. If you do not want to be bound by this User Agreement, you should not use this website or conduct any sale/purchase transaction.
References to ‘you, ‘User’ shall mean the end user accessing the website, its contents and using the functionalities offered through the website, ‘Service Providers’ mean independent third-party service providers or merchants, and ‘we’, ‘us’, ‘Jasper Info Tech’ and ‘our’ shall mean Jasper InfoTech Pvt. Ltd.
Please refer to the Terms and Conditions at www.snapdeal.com
II. AMAZON.COM
Amazon.com is an American multinational electronic commerce company with headquarters in Seattle, Washington, United States. It is the world’s largest online retailer. The company also produces consumer electronics – notably the Amazon Kindle e-book reader – and is a major provider of cloud computing services.
Amazon has separate retail websites for the following countries: United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Japan, and China, with international shipping to certain other countries for some of its products. It is also expected to launch its website in Poland, Netherlands, and Sweden.
Jeff Bezos incorporated the company (as Cadabra) in July 1994, and the site went online as amazon.com in 1995. Amazon.com started as an online bookstore, but soon diversified, selling DVDs, CDs, MP3 downloads, software, video games, electronics, apparel, furniture, food, toys, and jewelry.
The company was founded in 1994, spurred by what Bezos called his ‘regret minimization framework’, which he described as his effort to fend off regret for not staking a claim in the Internet gold rush.
The company began as an online bookstore. While the largest brick-and-mortar bookstores and mail-order catalogs might offer 200, .000 titles, an online bookstore could sell far more. Bezos wanted a name for his company that began with ‘A’ so that it would appear early in alphabetic order. He began looking through the dictionary and settled on ‘Amazon’ because it was a place that was ‘exotic and different and it was the river he considered the biggest in the world, as he hoped his company would be. Since 2000, Amazon’s logotype is an arrow leading from A to Z, representing customer satisfaction. A goal was to have every product in the alphabet.
PRODUCT CATEGORIES PROVIDED BY AMAZON.COM
- Books
- Movies, Music & Games
- Electronic & Computers
- Home, Garden & Tools
- Pet Products
- Grocery, Health & Beauty
- Kitchen & Dining
- Furniture & Decor
- Toy, Kids & Baby
- Clothing, Shoes & Jewellery
- Sports & Outdoors, Automotive & Industrial
Please refer to the Terms and conditions at www.amazon.com
III. EBAY.COM
eBay is an American multinational internet consumer-to-consumer corporation that manages eBay.com, an online auction and shopping website in which people and businesses buy and sell a broad variety of goods and services worldwide. Founded in 1995, eBay is one of the notable success stories of the dot-com bubble; it is now a multi-billion-dollar business with operations localized in over 30 countries. eBay expanded from its original “set-time” auction format to include “Buy It Now” standard shopping; by UPC, ISBN, or another kind of SKU; online classified advertisements; online event ticket trading; online money transfers, and other services.
The online auction website was founded as Auction Web in San Jos, California, on September 5, 1995, by French-born Iranian-American computer programmer Pierre Omidyar as part of a larger personal site that included, among other things, Omidyar’s own tongue–in–cheek tribute to the Ebola virus. One of the first items sold on eBay was a broken laser pointer for $14.83. Astonished, Omidyar contacted the winning bidder to ask if he understood that the laser pointer was broken. In his responding email, the buyer explained: “I’m a collector of broken laser pointers”. The frequently repeated story that eBay was founded to help Omidyar’s fiancée trade Pez candy dispensers was fabricated by a public relations manager in 1997 to interest the media, which were not interested in the company’s previous explanation about wanting to create a “perfect market”. This was revealed in Adam Cohen’s 2002 book, The Perfect Store, and confirmed by eBay.
PRODUCT CATEGORIES PROVIDED EBAY.COM
- Fashion
- Motors
- Electronics
- Collectibles & Art
- Home, Outdoors & Décor
- Entertainment
- Deals & Gifts
- Sporting Goods
Please refer to the Terms and conditions at www.ebay.com
IV. FLIPKART.COM
Flipkart is an Indian e-commerce company headquartered in Bangalore, Karnataka. It was started by two IIT graduates, Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal, in the year 2007. They were working on Amazon.com previously. Earlier, Flipkart mainly dealt with books buy now, it has expanded to electronic goods and a variety of other products.
Initially, they used word-of-mouth marketing to popularize their company. A few months later, the company sold its first book on flipkart.com- John Wood’s Leaving Microsoft to Change the World. Today, as per Alexa traffic rankings, Flipkart is among the top 30 Indian websites and has been credited with being India’s largest online bookseller with over 11 million titles on offer. Flipkart broke even in March 2010 and claims to have had at least 100% growth every quarter since its founding. The store started with selling books and in 2010 branched out to selling CDs, DVDs, mobile phones and accessories, cameras, computers, computer accessories, and peripherals, and in 2011 pens and stationery, other electronic items such as home appliances, kitchen appliances, personal care gadgets, health care products, etc. Further in 2012, Flipkart added A.C, Air coolers, School supplies, Office supplies, Art supplies & lifestyle products to its product portfolio. Today, Flipkart employs over 4500 people.
PRODUCT CATEGORIES PROVIDED BY FLIPKART.COM
- Books
- Mobiles & Accessories
- Computers
- Gaming
- Movies & TV Shows
- Music, CDs, DVDs & Vinyl
- TV, Video & MP3 Players
- Personal & Health Care
- Home & Kitchen
- Pens & Stationary
- Fragrances
Please refer to the Terms and conditions at www.flipkart.com
4. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
The study on Consumer Behaviour Towards Online Shopping has been conducted by collecting primary data from 100 sample respondents. The primary data collected has been analyzed and interpreted with help of percentage analysis. The collected data has been presented in the form of tables and charts. The analysis and interpretation of data is as follows;
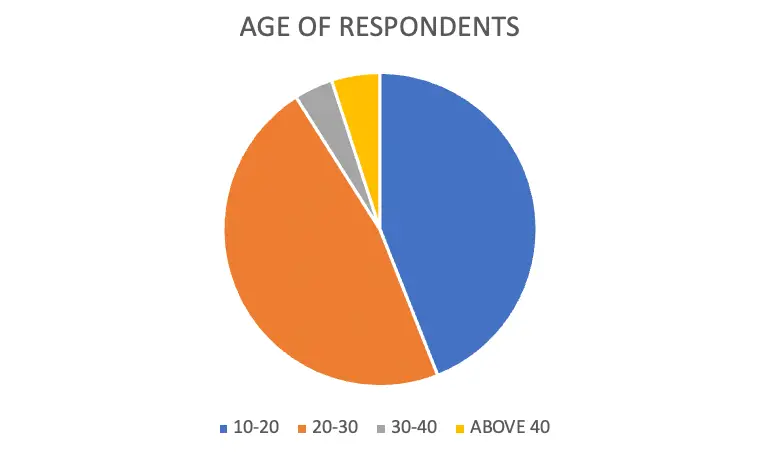
AGE-WISE CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS
Table 4.1
| AGE | NO OF RESPONDENTS | PERCENTAGE |
| 10-20 | 44 | 44 |
| 20-30 | 47 | 47 |
| 30-40 | 4 | 4 |
| ABOVE 40 | 5 | 5 |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 |
Figure 4.1
Interpretation
From the above data, it is clear that 47 % of respondents belong to the age class20-30,44 %of the respondents belongs to the age class 10-20, 5 % of the respondents belong to the age class Above 40 and 4% of the respondents belong to the age class 30-40.
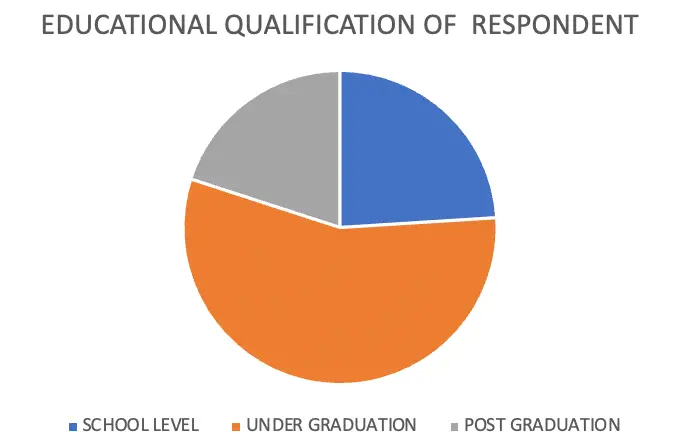
EDUCATIONAL QUALIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS
Table 4.2
| QUALIFICATION | NO OF RESPONDENT | PERCENTAGE |
| SCHOOL-LEVEL | 24 | 24 |
| UNDER GRADUATION | 56 | 56 |
| POST-GRADUATION | 20 | 20 |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 |
Figure 4.2
Interpretation
From the collected data the researcher identifies that 56 % of the respondents are undergraduates,24 %of the respondents are school level and 20 % of the respondents are postgraduates.
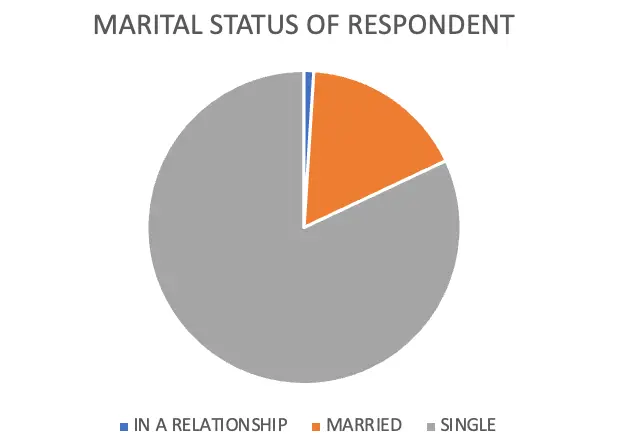
MARITAL STATUS OF RESPONDENT
Table 4.3
| MARITAL STATUS | NO OF RESPONDENT | PERCENTAGE |
| IN A RELATIONSHIP | 1 | 1 |
| MARRIED | 17 | 17 |
| SINGLE | 82 | 82 |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 |
Figure 4.3
Interpretation
From the above table and figure it is clear that 82 % of respondents are single,17 % of the respondents are married and 1 % of the respondents are in a relationship.
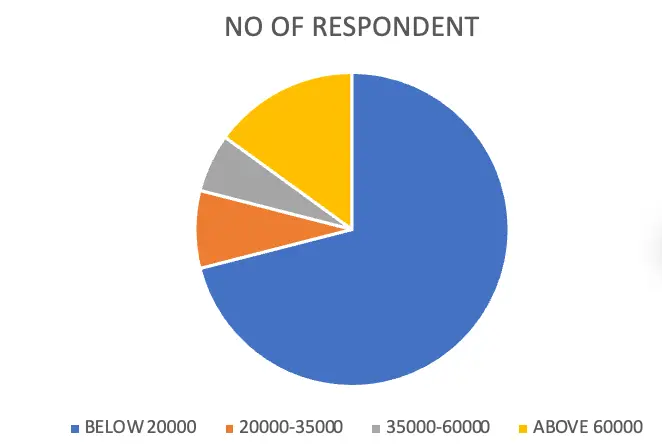
INCOME WISE CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENT
Table 4.4
| INCOME OF RESPONDENT | NO OF RESPONDENT | PERCENTAGE |
| BELOW 20000 | 71 | 71 |
| 20000-35000 | 8 | 8 |
| 35000-60000 | 6 | 6 |
| ABOVE 60000 | 15 | 15 |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 |
Figure 4.4
Interpretation
From the above data, the researcher can say that 71 % of respondents have an income Below 20000, 15 % of respondents have an income Above 60000,8 % of the respondents have an income of 20000-35000 and 6 % of respondents have an income of 35000-60000.
PROFICIENCY OF RESPONDENTS ON THE INTERNET
Table 4.5
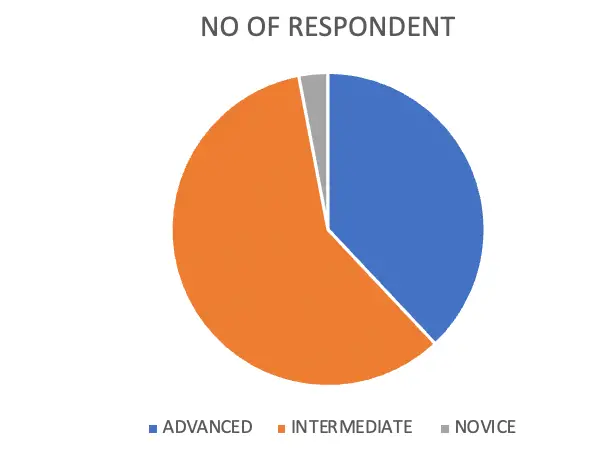
| PROFICIENCY ON INTERNET | NO OF RESPONDENT | PERCENTAGE |
| ADVANCED | 38 | 38 |
| INTERMEDIATE (Average) | 59 | 59 |
| NOVEL | 3 | 3 |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 |
Figure 4.5
Interpretation
From the classified data, the researcher can say that 59 % of respondents have intermediate(Average) proficiency on the internet,38 % of respondents have advanced proficiency on the internet and 3 % have a novel in internet usage.
INFORMATION ABOUT RESPONDENTS BEFORE EXPERIENCE IN ONLINE PURCHASE
Table 4.6
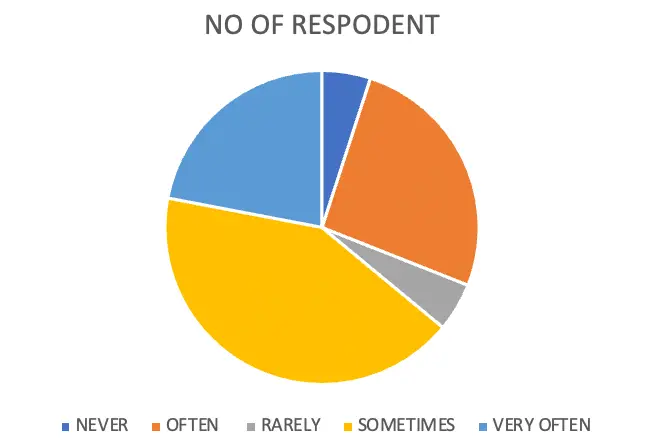
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENT | PERCENTAGE |
| NEVER | 5 | 5 |
| OFTEN | 26 | 26 |
| RARELY | 5 | 5 |
| SOMETIMES | 42 | 42 |
| VERY OFTEN | 22 | 22 |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 |
Figure 4.6
Interpretation
From the above table and figure it is clear that 42 % of respondents sometimes conduct online purchases,26 % of respondents often conduct online purchasing, 22 % of respondents very often conduct online purchasing, 5 % of respondents never conduct online purchasing and 5 % of respondents rarely conduct online purchasing.
BIGGEST CONCERN OF RESPONDENTS TOWARDS ONLINE SHOPPING
Table 4.7
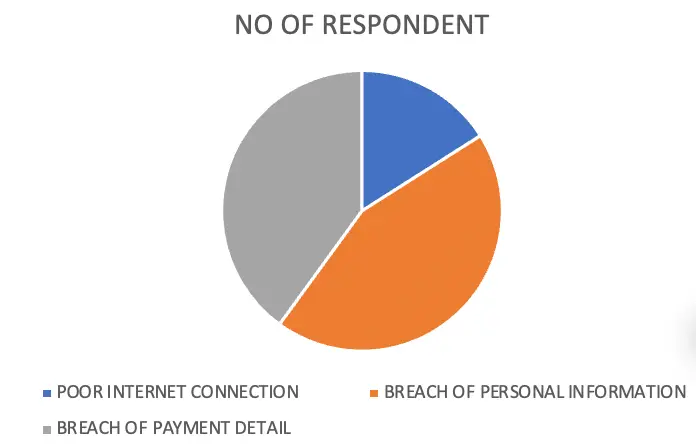
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENT | PERCENTAGE |
| POOR INTERNET CONNECTION | 16 | 16 |
| BREACH OF PERSONAL INFORMATION | 44 | 44 |
| BREACH OF PAYMENT DETAIL | 40 | 40 |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 |
Figure 4.7
Interpretation
From the classified data, it is clear that 44 % of the respondent’s biggest concern is a breach of personal information,40 % of the respondent’s biggest concern is a breach of payment detail and 16 % of the respondent’s biggest concern is a poor internet connection.
CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS ON THE BASIS OF THEIR FREQUENT ONLINE PURCHASE
Table 4.8
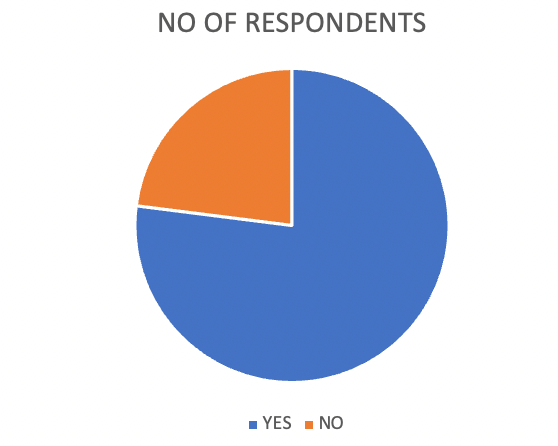
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENTS | PERCENTAGE |
| NO | 23 | 23 |
| YES | 77 | 77 |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 |
Figure 4.8
Interpretation
From the above data, it is clear that 77% of respondents are frequent online buyers and 23% of the respondents are not.
REASON FOR THE HESITATION OF ONLINE PURCHASE
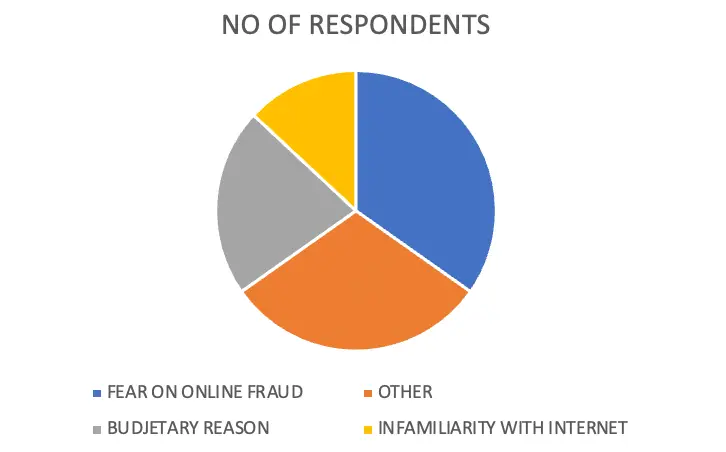
Table 4.8.1.1
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENTS | PERCENTAGE |
| FEAR OF ONLINE FRAUD | 8 | 34 |
| BUDGETARY REASON | 5 | 22 |
| UNFAMILIARITY WITH INTERNET | 3 | 13 |
| OTHER | 7 | 31 |
| TOTAL | 23 | 100 |
Figure 4.8.1.1
Interpretation
From the collected data the researcher identifies that the reason for the hesitation of online purchase by 34% of respondents was fear of online fraud, 22% of respondents avoid it just because of budgetary reasons, 13% of respondents reason is they are unfamiliar with the internet usage and 31% of respondents have other reason.
OPINION OF RESPONDENTS ABOUT THE PRESENCE OF COMFORTABLE RETAIL OUTLET
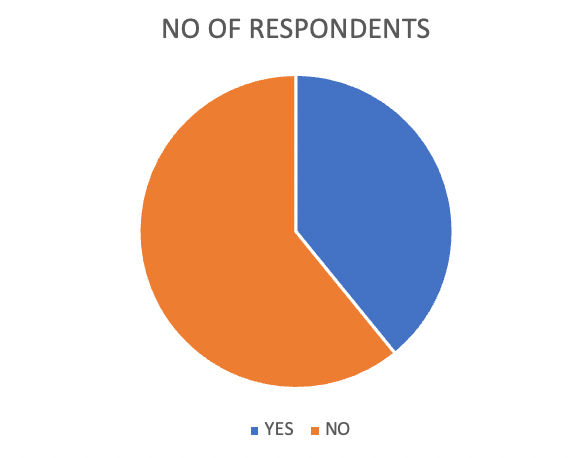
Table 4.8.1.2
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENTS | PERCENTAGE |
| YES | 9 | 39 |
| NO | 14 | 61 |
| TOTAL | 23 | 100 |
Figure 4.8.1.2
Interpretation
From the above table and figure, the researcher can say that 61% do not prefer any specific retail outlet for purchase and 39% of respondents prefer some retail outlet for purchase.
COMPARISON ABOUT ONLINE SHOPPING V/S OFFLINE SHOPPING
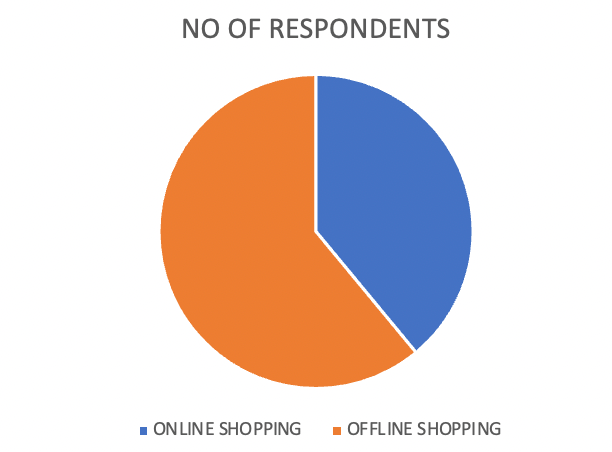
Table 4.8.2.1
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENTS | PERCENTAGE |
| ONLINE SHOPPING | 30 | 39 |
| OFFLINE SHOPPING | 47 | 61 |
| TOTAL | 77 | 100 |
Figure 4.8.2.1
Interpretation
From the above data, it is clear that 61% of respondents’ opinions were offline shopping was better and the remaining 39%of respondents say online shopping is better.
INFORMATION ABOUT THE MOST PREFERRED ONLINE SHOPPING SITE
Table 4.8.2.2
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENTS | PERCENTAGE |
| FLIPKART | 45 | 58 |
| AMAZON | 32 | 42 |
| EBAY | 0 | 0 |
| SNAPDEAL | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 77 | 100 |
Figure 4.8.2.2

Interpretation
From the classified data, the researcher can say that 58% of respondents respond prefer Flipkart as the most visited online shopping site and 42% of respondents respond says the most visited online shopping site is amazon.
MOST PREFERRED PRODUCT CATEGORY FOR ONLINE SHOPPING
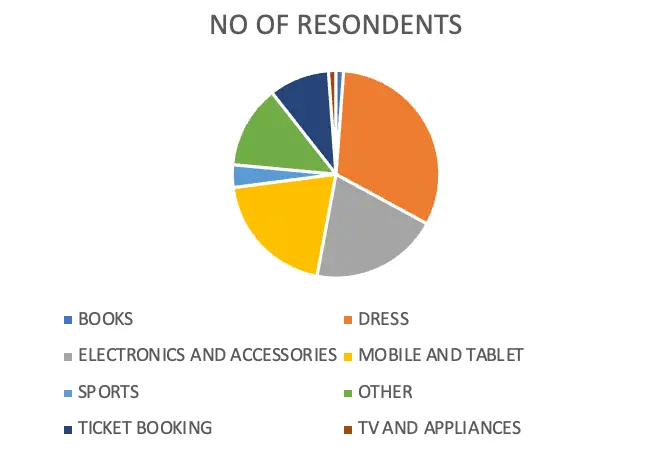
Table 4.8.2.3
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENTS | PERCENTAGE |
| BOOKS | 1 | 1 |
| DRESS | 22 | 27 |
| ELECTRONICS AND ACCESSORIES | 14 | 17 |
| MOBILE AND TABLET | 14 | 17 |
| SPORTS | 10 | 13 |
| OTHER | 9 | 11 |
| TICKET BOOKING | 6 | 8 |
| TV AND APPLIANCES | 1 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 77 | 100 |
Figure 4.8.2.3
Interpretation
From the above table and figure it is clear that 27% of respondents buy dresses from online sites,17% of respondents buy electronics and accessories from online sites, 17% of respondents buy mobiles and tablets from online sites, 3% of the respondents buy sports items from online sites, 11% of the respondents buy others items from online sites, 8% of the respondents use ticket booking option on online sites, 1% of the respondents buy tv and appliances from online sites and1% of respondents buy books from online shopping
.
REASON FOR ONLINE PURCHASE
Table 4.8.2.4
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENTS | PERCENTAGE |
| 24*7 AVAILABILITY | 20 | 26 |
| COMFORT | 13 | 17 |
| OFFER | 36 | 46 |
| VARIETY | 8 | 11 |
| TOTAL | 77 | 100 |
Figure 4.8.2.4
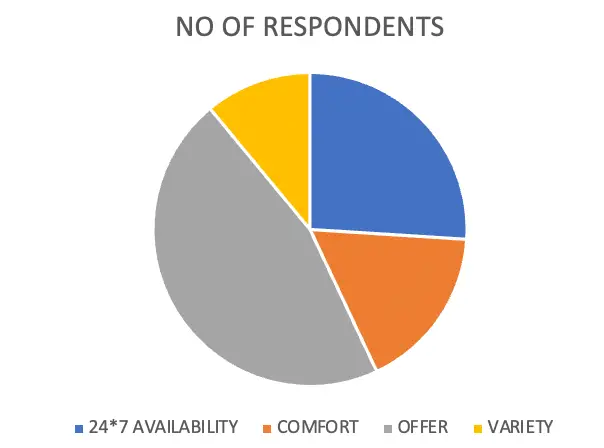
Interpretation
From the above-classified data, it is clear that 46% of respondents prefer online purchase because of offers,26% of respondents prefer online purchase because of 24*7 availability, 17% of respondents reason for online purchase was comfort and 11% of respondents reason for online purchase was variety.
MOST PREFERRED PAYMENT MODE
Table 4.8.2.5
| OPTIONS | NO OF RESPONDENTS | PERCENTAGE |
| CARD | 25 | 32 |
| COD | 34 | 44 |
| INTERNET BANKING | 18 | 24 |
| TOTAL | 77 | 100 |
Figure 4.8.2.5
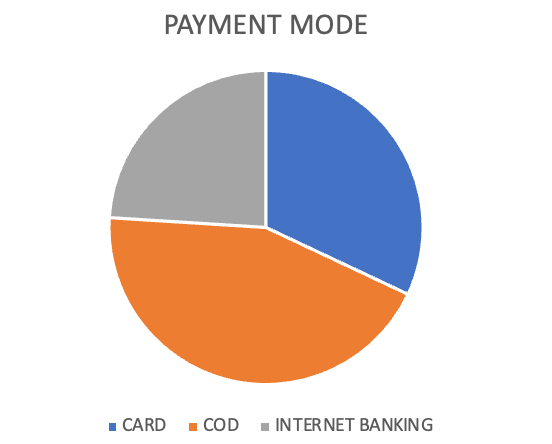
Interpretation
From the above data, researchers can say that 44% of respondents preferred payment mode is cash on delivery, 32% of respondents prefer card for payment and 24% of respondents prefer internet banking facilities.
5. Findings, Suggestion And Conclusion of the Study on Consumer Behaviour Towards Online Shopping
The study entitled “A study on the topic consumer behavior towards online shopping“ has been conducted to analyze and evaluate consumer behavior towards online shopping. The study has been conducted by collecting primary data with the help of a structured questionnaire from 100 respondents. The collected primary data have been analyzed and interpreted with help of ratios and percentages and the analysis is presented in the form of tables and charts.
Findings Of The Study On Consumer Behaviour Towards Online Shopping
The major findings of the study on Consumer Behaviour Towards Online Shopping are:
- 91% of respondents are belonging to the age group of 10- 30.
- Majority of respondents(56%) are under graduates.
- 82% of respondents are single.
- Majority of respondents (71%) belong to income below 20000.
- 97% of respondents are somewhat aware about internet usage, in it 38% are experts.
- 95% of respondents are conducting online purchasing.
- Fear about the breach of personal information and payment details(bank details) are the biggest concern (44:40) of the respondents on online shopping.
- Only 77% of respondents are frequently conduct online buying.
- Fear on online fraud and budgetary reason are the major hesitating factor for the online purchase.
- Only a lower number of respondents have some specific shops for conducting offline shopping.
- Out of the 77 respondents 61% says offline shopping is good.
- Most preferred (58%) online shopping site is flipkart.
- Main products that are preferred by the online buyers are :Dress ,Electronics And Accessories and Sports .
- Major reasons for online shopping are Offers and 24*7 Availability.
- Most preferred payment mode is cash on delivery.
SUGGESTIONS
- Providing more competitive price can attract customers.
- Online shopping sites should increase the security for online payment.
- More attractive offers on products can attract more customers.
- Measures to be taken in order to avoid delivery of duplicate products.
- Measures to be taken in order to reduce delivery of damaged products.
CONCLUSION
After completing the project, it is revealed that customers are partially satisfied with online shopping. Some corrections in the facility can fully satisfy the customers. Online shopping sites provide a big platform for customers for shopping and they can save time by shopping online. By removing the online frauds, sites can create a high place in the mind of customers. Customers need fast delivery of good quality products, a wide range of products and competitive prices are of the main factor that attracts people towards online shopping, more improvements in this two field attract people more. Online shopping provides an important role in the mind of customers.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
BOOKS
- Armstrong, Gary. Y Kotler, Philip (2003), “Fundamentos de marketing”, EditorialPrentice Hall, 6a Edition, pp.14-15.
- Bansal and Sunita Pant (2005), ‘Encyclopedia of India’, Delhi: Smriti Books.
- Botha, J, Bothma, C, Geldenhuys, P (2008), ‘Managing E-Commerce in Business’, Cape Town: Juta and Company Ltd, pp.3.
- Del. I Hawkins, David. L Mothersbaugh, Roger. J Best (2007), ‘Consumer Behavior: Building Marketing Strategy’, McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
- Donald, R Cooper & Pamela S Schindler (2007), Business Research Methods, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi.
- Engel. J.F, Kollat. D.T and Blackwell. R.D (1968), ‘Consumer Behaviour’, Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
- Enis. B.M (1974), ‘Marketing Principles: The Management Process’, pp.228.
- Hollensen, S (2004), ‘Global Marketing a decision-oriented approach’, Essex: Pearson Education, 3rd Edition.
- Kotler. P and Keller. K (2011), ‘Marketing Management’, 14th Edition, London: Pearson Education.
JOURNALS
- Abadi, D.R.H. Hafshejani, A.N.S and Zadeh, K.F (2011), ‘Considering Factors that Affect User’s Online Purchase Intentions with Using Structural Equation Modeling’, Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, Vol.3, No.8, Pp.465-468.
- Aimol Agift, VermaRekha and Chacko Nisha (2014), ‘Consumers Attitude towards
- Online Shopping’, Research Journal of Community and Consumer Sciences, International Science Congress Association, Vol.2, No.8, pp.4-7.
- Ajay Kumar (2016), ‘Beyond Buying to Shoppers: Motivation towards Online Shopping’, BVIMSR’s Journal of Management Research, Vol. 8, Issue-1.
- Alba, J. Lynch, J. Weitz, B. Janiszewski, C. Lutz, R. Sawyer, A. and Wood, S (1997), ‘Interactive Home Shopping: Consumer, Retailer and Manufacturer Incentives to participate in Electronic marketplaces’, Journal of Marketing, vol.61, No.3, pp.38-53.
- Al-Azzam, Abdel Fattah Mohmoud (2014), ‘Evaluating the Antecedents of Online Consumer Purchasing Behaviour: An Empirical Study based on Theory of Planned Behaviour’, International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management, Vol. II, Issue-4, pp. 1-18.
- Aldrich.M (2011), ‘Online Shopping in the 1980s’ IEEE Annals of the History of Computing, Vol.33, No.4, pp.57-61.
Credit: This Study on Consumer Behaviour Towards Online Shopping was conducted in Kottayam Municipality by Bijil Jacob Biju, Aju K Jacob, and Amal Ji Thomas under the guidance of Asst. Prof. Robin Jacob Kuruvilla MBA, M.Phil, Department of Commerce at the Bishop Speechly College For Advanced Studies Pallom, Kottayam.

You gave well-organized data, which is beneficial to everyone interested in eCommerce and building an online store. Thanks for presenting this data, which indicates that internet purchasing is the way of the future.