Casting is a manufacturing process used in foundries to produce metal components from Ferrous and Non-ferrous metals. Casting is one of the most important manufacturing processes among all processes. Casting is pouring molten metal into the moulds. The mould can be prepared with sand but it can be used only one time. But with Die Casting The mould is made of a metal that can be used as many times as we want. Let us discuss the Die Casting process in detail.

Die Casting
As we have already mentioned that the sand mould is used for the production of only one casting. It cannot be used twice. Die is essentially a metal mould and can be used again and again. A die is usually made in two portions. One portion is fixed and the other is movable. Together, they contain the mould cavity in all its details. After clamping or locking the two halves of the dies together molten metal is introduced into the dies. This can be done in two ways.
- If the molten metal is fed by gravity into the dies, the process is known as the gravity die casting process.
- If the metal is forced into the dies under pressure, the process is called “pressure die casting”. For example, a piston in a cylinder pushes the material through the cylinder nozzle.
The material of which the dies are made should have a melting point much higher than the melting point of casting material. A great number of die castings are made of alloys of zinc, tin and lead, and of alloys of aluminium, magnesium and copper. Hence dies are made out of medium carbon low alloy steels. The dies are usually water or air blast cooled.
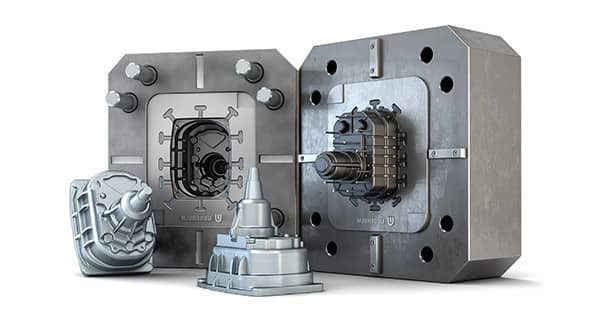
Since most materials contract on cooling, extraction of castings from dies becomes important otherwise they will get entangled in the die as they cool. Therefore, in the design of dies, some arrangement for extraction of casting is incorporated.
Die Casting Procedure
- Close and lock the two halves of a die after coating the mould cavity surfaces with a mould wash, if specified:
- Inject the molten metal under pressure into the die.
- Maintain the pressure until the metal solidifies.
- Open die halves.
- Eject the casting along with runner, riser etc.
- The above cycle is repeated.
There are Two pressure die casting methods are used:
Hot chamber process: This uses pressures up to 35 MPa and is used for zinc, tin, lead, and their alloys. In this process, the chamber, in which molten metal is stored before being pressure injected
into the die, is kept heated.
Cold chamber process: In this process, pressures as high as 150 MPa are used. The storing chamber is not heated. This process is used mainly for metals and alloys having a relatively higher melting
points e.g., aluminium, magnesium and their alloys.
Advantages of Die casting
- It is used for the mass production of castings of small and medium sizes. For Example pistons of motorcycle and scooter engines, valve bodies, carburettor housings etc.
- This process produces high quality, defect-free castings.
- The castings produced by this process are of good surface finish and have good dimensional control and may not require much machining. All castings produced are identical.
- In the case of mass production, castings can be produced cheaply.
- The process does not require the use of sand and requires much less space as compared to a conventional foundry using sand moulds.
Disadvantages of Die casting
- The initial cost of manufacturing a die is very high.
- Large size castings cannot be produced by this process.
- Castings with very complex shapes or with many cores are difficult to produce by die casting.
Conclusion
We have discussed what is Die_Casting and the Die Casting procedure. We also listed the advantages and the disadvantages of Die_Casting. Let us know in the comment section below what products you think you can produce from Die_casting.

Leave a Reply